ENPC EP-KB11 User manual

User’s Manual Rev. A 22/07/09
CONTENTS
I. INTRODUCTION...................................................................… 2
How this manual is organized ...........................................… 2
Item Checklist..............................................................………. 2
II. FEATURES…………………………………………………….…… 3
III. INSTA ATION.....................................................................… 6
Motherboard Layout .......…………….....................…..………. 6
1. umpers Setting........................................................…. 7
2. Install System Memory Module.................................... 8
3. Install the CPU………………………………...............…. 9
4. Install the Expansion Cards…………… ...................... 12
Assigning IRQs for Expansion Cards......................... 13
Assigning DMA Channels for ISA Cards..................… 14
5. External Connection...................................................... 15
6. Power on Procedures .......................................………. 22
IV. BIOS SETUP Tips .................................................................... 23
VI. Year 2000 (Y2K) Compliant ……………………………………… 32
1

I. INTRODUCTION
How this manual is organized
This manual is divided into the following sections:
I Introduction : Manual information and checklist
II. Features : Information and specifications concerning this product
III. Installation : Instructions on setting up the motherboard
IV. BIOS Setup : Instructions on setting up special feature in the BIOS
Item Checklist
Please check that your package is complete. If you discover damaged or
missing items, please contact your retailer.
Motherboard x 1
40-pin IDE Connector Flat Cable x 1
34-pin Floppy Disk Drive Flat Cable x 1
User’s Manual x 1
CD x 1
RS232 9 Pins & 25 Pins connector & PRT 25 Pins connector
Retention Holder for Pentium II CPU
LDCM Diskette x 1 (Option)
USB Connector Cable with bracket x 1 (Option)
IrDA Module x 1 (Option)
Option : Components will be include upon customer ordering instructions
per Proforma Invoice & additional external procurement cost will
be included.

II FEATURES
The motherboard is designed with the Intel 82443BX PCI chipset which is
developed by Intel Corporation to fully support the Pentium II Processor
PCI/ISA system. And implement the CPU speed umper-less function.
The Intel 82443BX PCI chipset provides increased integration and
improved performance designs. The chipset provides an integrated IDE
controller with two high performance IDE interfaces for up to four IDE
devices (hard devices, CD-ROM device, etc). The Super I/O controller
provides the standard PC I/O function: floppy interface, two 16Byte FIFO
serial ports and EPP/ECP capable parallel port. Care must be taken when
inserting memory modules, inserting CPU or even plugging PCI card into
associated slots to avoid damaging any circuits or sockets on board. A
cooling fan is strongly recommended. The motherboard supports minimum
of 8MB of system memory and a maximum of 384MB SDRAM. The
motherboard provides 3 168-pin DIMM. The socket supports 1Mx32
(32MB) single-sided or double-sided memory modules. The board also
supports two onboard PCI IDE connectors, and detects the IDE hard disk
type by the BIOS utility which is automatic. The system also supports
Award Plug & Play BIOS for the ISA and PCI cards.
Intel Chipset:
Features Intel's 440BX AGPset with I/O subsystems.
Multi-Speed:
Supports an Intel Pentium II processor from 233MHz-450MHz. With CPU
umperless function support. User can change the CPU speed in the BIOS
setting.
Multi-Cache:
Supports a Pentium II processor with either 512KB, 256KB, or 0KB
Pipelined Burst Level 2 cache in the Single Edge Contact (SEC) cartridge.
Versatile Memory:
Is equipped with three DIMM sockets to support 8MB-128MB 168-pin
3.3Volt SDRAM/EDO memory modules up to 384MB.
AGP:
Supports an Accelerated Graphics Port card for high performance,
component level interconnect targeted at 3D graphical display applications.

Dual Power Supply:
Has both AT and ATX power connectors onboard to support an AT or ATX
power supply with soft-on/off features.
ISA & PCI Expansion:
Provides three 16-bit ISA expansion slots and four 32-bit PCI expansion
slots.
Super Multi-l/O:
Provides two high-speed UART compatible serial ports and one parallel
port with EPP and ECP capabilities. UART2 can also be directed from
COM2 to the Infrared Module for wireless connections.
PCI Bus Master IDE:
Comes with an onboard PCI Bus Master IDE controller with two connectors
that supports four IDE devices in two channels, supports PIO Modes 3 and
4 and Bus Master IDE DMA Mode 2, and supports Enhanced IDE devices
such as Tape Backup and CD-ROM drives. Supports two drives of either
5.25-inch (360KB or 1.2MB) or 3.5-inch (720KB, 1.44MB, or 2.88MB) disk
drives and supports LS-120 floppy disk drives (3.5-inch disk drive: 120 MB,
1.44MB, 720K). BIOS supports IDE, CD-ROM or SCSI device boot-up.
Easy Installation:
Is equipped with BIOS that supports auto detection of hard drives, PS/2
mouse, and Plug and Play devices to make setup of hard drives, expansion
cards, and other devices virtually automatic.
Optional USB, lrDA:
Supports USB or IrDA optional cable and bracket set to mount the
connectors to an unused expansion slot on the system chassis.
ACPI Ready :
ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface) is also implemented
on this motherboards. ACPI provide more Energy Saving Features for the
future operating systems (OS) supporting OS Direct Power Management
(DPM) functionality. With these features implemented in the OS, PCs can
be ready around the clock everyday, yet satisfy all the energy saving
standards. To fully utilize the benefits of ACPI, an ACPI-supported OS such
as in the next release of Windows 95/98 must be used.

PC '97 Compliant –
Both the BIOS and hardware levels of smart series of motherboards meet
PC '97 compliance. The PC 97 requirements for systems and components
are based on the following high-level goals: Support for Plug and Play
compatibility and power management for configuring and managing all
system components, and 32-bit device drivers and installation procedures
for both Windows 95/98 and Windows NT.
Modem Ring On –
This allows a computer to be turned on remotely through an external
modem. With this benefit on-hand, any user can access vital information
from their computer from anywhere in the world.
Wake ON AN –
This main board implements a LAN-Wake UP connector, to use LAN Wake-
up function, user need a network card that supports this feature. In addition,
user also needs to install network management software, such as LDCM.
The connector will receive a wakeup packet or signal from LAN Card to
power up the system.
Temperature Monitoring and Alert – ( Option )
To prevent system overheat and system damage, there are heat sensors to
monitor the CPU and system temperatures to warn of damaging
temperatures.
Voltage Monitoring and Alert – ( Option )
System voltage levels are monitored to ensure stable current to critical
motherboard components. Voltage specifications are more critical for future
processors, so monitoring is necessary to ensure proper system
configuration and management.
Sometimes, the external MODEM just power ON/OFF, the pulse
will be taken as the Ring in signal, which will make the machine
power up. User needs to pay more attention about this symptom.
III. INSTALLATION
FAN 2
AGP
Slot
WO
FAN 1
Front Panel
Connector
IR 2
Battery
IR 1
BIOS
I/O Chip
ISA
Slots
PCI
Slots
Hardware Monitor (Option)
Slot1
CPU
Printer
Port
COM 2
COM 1
Keyboard
AT SPS
ATX
SPS
DIMM
Socket
Thermal
Sensor
(Option)
FDD
IDE 2
IDE 1
PS/2 Mouse
Connector
USB
Intel 440BX AGP Set
CMOS Clear

III. INSTA ATION
III-1 umpers Setting
1 2 3
CMOS Clear:
1 – 2 Normal
2 – 3 Clear
CMOS Clearing
CMOS Clear, which is a safety hook if you forget the password. Follow the
steps:
After you have turned off your computer, clear the CMOS memory by
momentarily shorting pins 2-3, for a few seconds. Then restore it to the
initial 1-2 jumper setting in order to recover and retain the default settings.
Reset your computer now.
Front Panel
Connector

III-2 Install System Memory Modules
This motherboard support 3 slots for 168-pin 3.3V Non-buffered DIMM
modules, providing support for up to 1GB of main memory using DIMM
modules from 8MB to 128MB. For 66MHz host bus CPUs, please use 12ns
or faster DIMM modules. For 100MHz host bus CPUs, please use 8ns or
faster DIMM modules that support the PC-100 specification. The following
is the example to install the system SDRAM memory module combination:
if you have two DIMM Modules, you has better install them into DIMM Slot
1 & Slot 2 with the Max possible memory size up to 256MB ( 128 + 128 ) if
the 128MB DIMM module is available.
Number Of
Memory
Module
DIMM1 DIMM2 DIMM3
Memory
Module Max. Size
1 1 st 8~128MB 128 MB
2 1 st 2 nd 8~128 MB 256 MB
3 1 st 2 nd 3 rd 8~128 MB 384 MB
DIMM 1
DIMM 2
DIMM 3
The DIMM types supported SDRAM
(Synchronous DRAM). The following is the
summary:
Single side:
1Mx64 (8MB), 2Mx64 (16MB), 4Mx64
(32MB), 8Mx64 (64MB), 16Mx64 (128MB)
Double side:
1Mx64x2 (16MB), 2Mx64x2 (32MB),
4Mx64x2 (64MB), 8Mx64x2 (128MB).
Total Memory Size:
There is no jumper setting required for the
memory size or type. It is automatically
detected by the system BIOS, and the
total memory size is to add them together.

III-3 Install the Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Selecting the CPU Frequency
CPU voltage auto-detection and allow user to set CPU frequency through
CMOS setup, no jumper or switch is needed. The correct CPU information
is saved into EEPROM, with these technologies, the disadvantages of
Pentium base jumper-less design are eliminated. There will be no worry of
wrong CPU voltage detection and no need to re-open the housing if CMOS
battery loss. The CPU frequency selection is set with the followings by the
BIOS Setup Utility.
BOIS Setup CPU Speed Setting
(The possible setting is 66, 75, 83 , 100, 103, 112, 133 MHZ)
The BIOS will auto detect the CPU type, if the CPU type is 66MHZ front
side bus, the setting only could be 66, 75, 83 MHZ. If the CPU type is
100MHZ FSB, the setting only could be 100, 103,112, 133 MHZ
BOIS Setup CPU Speed Setting
(The possible setting is 3x, 3.5x, 4x, 4.5x, 5x, 5.5x, 6x)
The following table is the recommendation for the CPU setting
with the Frequency and the Ratio.
CPU Host Cock
(MHz)
X Multiplier = CPU Frequency (MHz)
66 X 3.5 = 233
66 X 4.0 = 266
66 X 4.5 = 300
66 X 5 = 333
100 X 3 = 300
100 X 3.5 = 350
100 X 4 = 400
100 X 4.5 = 450
Notes:
1. If you want to Over-Clock the CPU, please make sure the other
peripherals can work fine with one another. That mean you need
to well test the whole system with your own configuration,
otherwise, please set the default and safe setting with 66MHZ or
100MHZ front side bus.
2. Once the machine can’t power up, sometimes, that is because
the CPU auto-detect function cannot well detect your CPU due to
the change of the CPU type. Please do the following method to
correct it. [Clear the CMOS data] or [press Insert key then
power on the machine] or [Power on the machine with 3 ~4
times].

Install the CPU on the Motherboard
1. Insert the attach mount bridges (For the remaining instructions) into the
bottom of the mainboard with the curved edges facing outwards, toward
the edge of the mainboard.
2. Use a screw driver to lightly tighten the attach mount bridges and the
Pentium II Retention Mechanism
3. Insert the Pentium II processor into the Pentium II retention Mechanism
with the processor Heatsink. Press evenly and gently until the snaps on
the upper side of the processor have been inserted into the holes at the
top of the retention base. Note that when removing the processor, these
snaps can be clicked into a completely vertical position, leaving your
hands free to stabilize the board and pull the processor evenly and
gently out of the board. Also note that like PCI and ISA slots, Slot 1 has a
divider that prevents backwards insertion.
4. Attach the Thermal Sensor (optional): If you purchased the specially
designed thermal sensor, you can contact the thermal sensor to the CPU
Heatsink as nearest as possible.
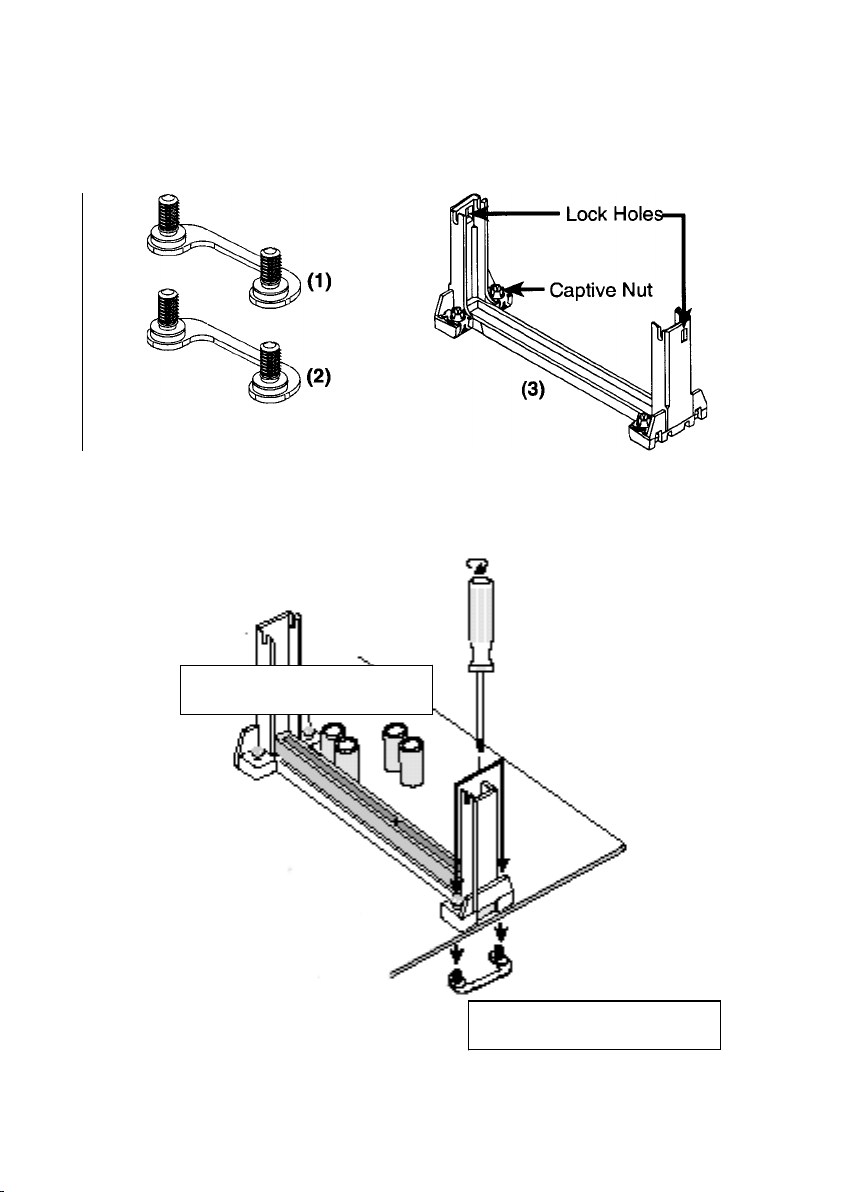
Install the CPU on the Motherboard
NOTE: The pictures in the following pages will have the same item numbers next to
them for your reference. The design and color of your items may be slightly
different.
Attach Mount Bridges
(Items 1,2) Pentium II Retention Mechanism
(Item 3)
Retention Mechanism
Attach mount bridges
III-4 Install Expansion Cards
Expansion Card Installation Procedure
Read the documentation for your expansion card and make any
necessary hardware or software settings for your expansion card,
such as jumpers.
Remove your computer system's cover and the bracket plate on the
slot you intend to use. Keep the bracket for possible future use.
Carefully align the card's connectors and press firmly.
Secure the card on the slot with the screw you removed above.
Replace the computer system's cover.
Set up the BIOS if necessary (such as IRQ xx Used By ISA: Yes in
PNP AND PCI SETUP)
Install the necessary software drivers for your expansion card.
This motherboard also provides an AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
slot to support a new generation of graphics cards with ultra-high
memory bandwidth.
WARNING!
Unplug your power supply when adding or removing expansion cards or
other system components. Failure to do so may cause severe damage to
both your motherboard and expansion cards.
AGP Slot
4 PCI Slots
3 ISA Slots

Install Expansion Cards Tips:
Assigning IRQs for Expansion Cards:
Some expansion cards need to use an IRQ to operate. Generally an IRQ
must be exclusively assigned to one use. In a standard design there are 16
IRQs available but most of them are already in use, leaving 6 IRQs free for
expansion cards.
Both ISA and PCI expansion cards may require to use IRQs. System IRQs
are available to cards installed in the ISA expansion bus first, then any
remaining IRQs are available to PCI cards. Currently, there are two types of
ISA cards. The original ISA expansion card design, now referred to as
legacy ISA cards, requires that you configure the card's jumpers manually
and then install it in any available slot on the ISA bus. You may use
Microsoft Diagnostics (MSD.EXE) utility located in the Windows directory to
see a map of your used and free IRQs. If you use Windows 95/98, the
Resources tab under Device Manager displays the resource settings being
used by a particular device (to gain access, double-click the System icon
under the Control Panel program). Ensure that no two devices share the
ame IRQs or your computer will experience problems when those two
devices are in use at the same time. The original ISA expansion card
design, now referred to as "Legacy" ISA cards, requires that you configure
the card's jumpers manually and then install it in any available slot on the
ISA bus. You may use Microsoft's Diagnostic (MSD.EXE) utility included in
the Windows directory to see a map of your used and free IRQs. For
Windows 95/98 users, the "Control Panel" icon in "My Computer," contains
a "System" icon which gives you a "Device Manager" tab. Double clicking
on a specific device give you "Resources" tab which shows the Interrupt
number and address. Make sure that no two devices use the same IRQs or
your computer will experience problems when those two devices are in use
at the same time. To simplify this process this motherboard has complied
with the Plug and Play (PnP) specification which was developed to allow
automatic system configuration whenever a PnP-compliant card is added to
the system. For PnP cards, IRQs are assigned automatically from those
available. If the system has both Legacy and PnP ISA cards installed, IRQs
are assigned to PnP cards from those not used by Legacy cards. The PCI
and PnP configuration of the BIOS setup utility can be used to indicate
which IRQs are being used by Legacy cards. For older Legacy cards that
do not work with the BIOS, you can contact your vendor for an ISA
Configuration Utility. An IRQ number is automatically assigned to PCI
expansion cards after those used by Legacy and PnP ISA cards. In the PCI
bus design, the BIOS automatically assigns an IRQ to a PCI slot that has a
card in it that requires an IRQ. To install a PCI card, you need to set
something called the INT (interrupt) assignment. Since all the PCI slots on

this motherboard use an INTA #, be sure that the jumpers on your PCI
cards are set to INT A.
Assigning DMA Channels for ISA Cards
Some ISA cards, both legacy and PnP, may also need to use a DMA
(Direct Memory Access) channel. DMA assignments for this motherboard
are handled the same way as the IRQ assignment process described
earlier. You can select a DMA channel in the PCI and PnP configuration
section of the BIOS Setup utility.
IMPORTANT:
To avoid conflicts, reserve the necessary IRQs and DMAs for legacy ISA
cards (under PnP AND PCI SETUP of the BIOS SOFTWARE, choose Yes
in IRQ xx Used By ISA and DMA x Used By ISA for those IRQs and DMAs
you want to reserve).
Notes:
If you have the problem to install the Windows 95 /98, maybe
system hung up or something wrong, the installation can’t
complete. Please try the following step:
1. Remove all the Add-ons, only remain the Display Card.
2. Set the BIOS default value.
3. Re- Install the OS ( Windows 95 or Windows 98. )
4. After completely install the OS, add the other expansion cards
one by one.
If your system can’t power on or no display, you may do the
following step to verify the problem:
1. Check the jumper on the Mother Board.
2. Set the BIOS to default value.
3. Remove all the add-ons only remain the VGA Card.
4. Change the VGA Card with different Slot.
5. Change the DIMM module.
6. Remove all the HDD, FDD Cable.

III-5 External Connection
Important:
1. Ribbon cables should always be connected with the red stripe on the
Pin 1 side of the connector. The Four Corners of the connectors are
labeled on the motherboard. Pin 1 is the side closest to the power
connector on hard drives and floppy drives. IDE ribbon cable must be
less than 18in. (46cm), with the second drive connector no more than
6in. (15cm) from the first connector.
2. The motherboard requires a power supply with at least 250 Watts and a
"power good" signal. Make the ATX power supply can take at least
10mAmp load on the 5V Standby lead (5VSB) to meet the standard
ATX specification.
3. To prevent electrical spikes, make sure that the power supply is not
connected to an outlet when making or removing connections. Power
supplies contain power remains, which can damage electrical
components.
III-5-1 Power Supply Connector
ATX Power Supply Connector (ATXPWR, 20-pins)
Plug the connector from the power directly into the 20-pin male ATX
PW connector on the motherboard as shown in the following figure.
The plug from the power supply will only insert in one orientation
because of the different hole sizes. Find the proper orientation and
push down firmly making sure that the pins are aligned and the power
supply is off before connecting or disconnecting the power cable.
IMPORTANT:
Make sure that your ATX power supply can supply at least 10 mAmp on the
5-volt standby lead (5VSTB). You may experience difficulty in powering on
your system if your power supply cannot support the load. For Wake on
LAN support, your ATX power supply must supply at least 720mAmp.
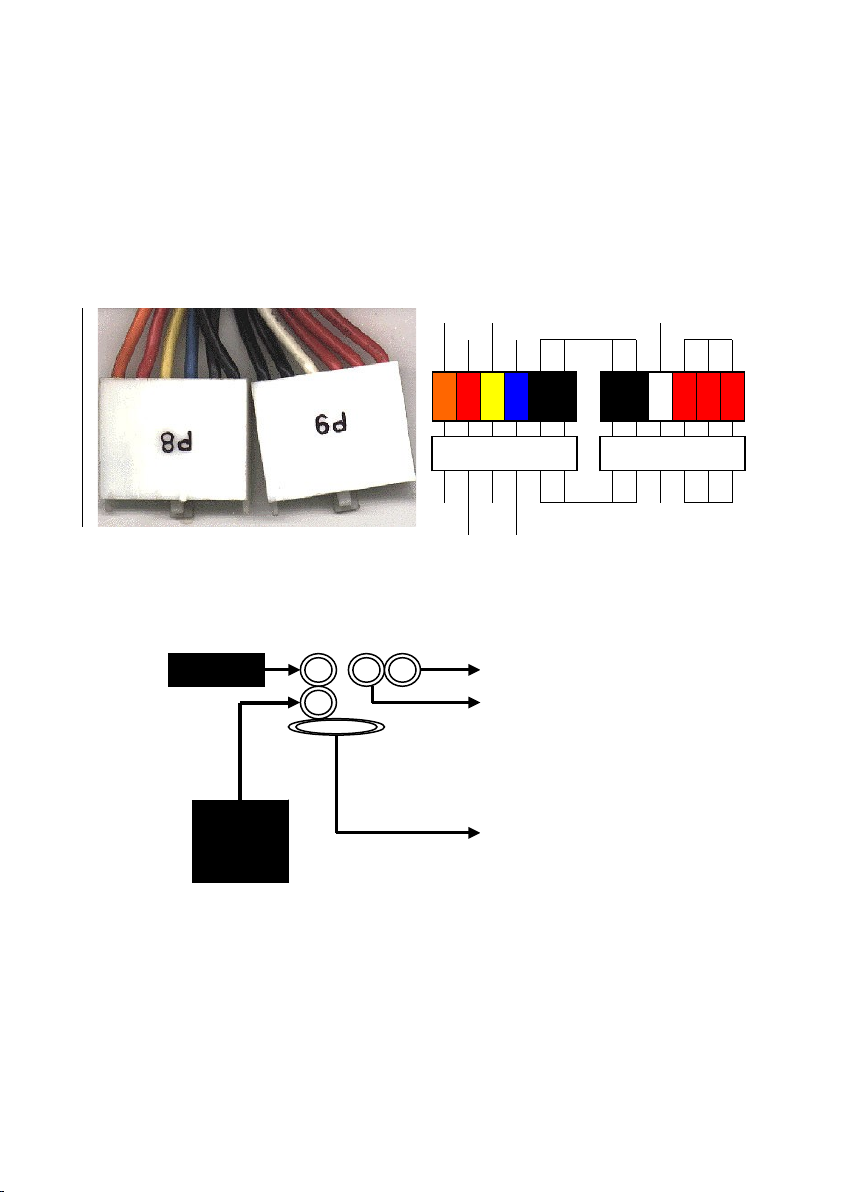
AT Power Supply Connector (ATPOWER, 12-pins)
This connector connects to a standard AT power supply. To connect the
leads from the power supply, ensure first that the power supply is not
plugged. Most power supplies provide two plugs (P8 and P9), each
containing six wires, two of which are black. Orient the connectors so that
the black wires are together. Please refer to the following:
ORG Y W B K WHT RED
RED B U
PG +12V GND -5V +5V
+5V -12V
III-5-2 Keyboard, Mouse, USB, COM Port and Printer port
Keyboard Connector
P8
P9
Printer Port
COM 1
COM 2
USB
PS/2 Mouse connector

Keyboard:
The onboard keyboard connector is a five-pin AT-compatible
connector. The view angle of drawing shown here is from
back panel of the housing. If you want to use the PS/2
Keyboard, you need to add one adapter that converts the
signal from AT to PS/2 specification.
PS/2 Mouse Connector
7 5 3 1
8 2
The onboard PS/2 mouse connector is a 6-pin Mini-Din
connector marked PS2.
123578
+5V NC NC MS Data GND MS C K
USB (Universal Serial Bus Connector)
4 3 2 1
8 7 6 5
Pin Description Pin Description
1 +5 VDC 5 +5VDC
2 D0 - 6 D1-
3 D0+ 7 D1+
4 GND 8 GND
You can attach USB devices to the USB connector. The Mother board
contains two USB connectors. USB is a new serial bus design that is
capable of cascading low-/medium-speed peripherals (less than 12Mbps)
such as keyboard, mouse, joystick, scanner, printer and modem/ISDN.
Serial Devices (COM1/COM2)
The serial port 1 connector is marked as COM1 and the
serial port 2 connector is marked as COM2. These are
standard Serial Port Pin assignment. To support serial
devices, insert the serial device connector into the serial
port on the bracket. Plug in the 10-pin flat cable to the
appropriate onboard connectors.
Printer Port ( PT )
Plug in the 26-pin printer flat cable to the onboard parallel
connector

III-5-3 Front Panel Connector
1). IDE Activity ED ( Pin 9,10)
This connector connects to the IDE (hard disk) activity indicator light on the
system abinet.
2). System Power ED ( Pin 15,16,17)
This 3-pin connector lights the system power LED when the motherboard
has power.
3). Turbo ED (Pin 7,8)
If the cabinet provide the turbo LED cable, connect the cable to this two pin
connector to turn on the LED on the front panel.
4). ATX Power Switch ( Pin 5,6 )
The system power is controlled by a push-switch, connected to this lead.
Pushing the button once will turn on the power and pushing again will turn
off the power. The system power LED shows that status of the system’s
power. If the power to the ATX power supply is interrupted while the
motherboard is on, standby power will remember that the motherboard
should be on and boot the computer when power is reapplied to the ATX
power supply.
5). Reset Switch ( Pin 1,2 )
This 2-pin connector connects to the case-mounted reset switch for
rebooting your computer without having to turn off your power switch. This
is a preferred method of rebooting in order to prolong the life of the
system’s power supply.
6). Keyboard ock Switch ead ( Pin 18,19 )
This 3-pin connector connects to the case-mounted keyboard lock switch
for locking the keyboard.
7). Speaker Connector ( Pin 11,12,13,14 )
This 4-pin connector connects to the case-mounted speaker.

III-5-4 FAN Connector
1).This connectors support a CPU cooling fan of 500 mA (6WATT, +12V) or
less. Orient the fan so that the heat sink fins allow airflow to go across the
onboard heat sink(s). Depending on the fan manufacturer, the wiring and
plug may be different. The red wire should be positive (+12V), while the
black should be ground. Connect the fan’s plug to the board taking into
consideration the polarity of the connector.
WARNING!
The CPU and/or motherboard will overheat if there is no airflow
across the CPU and onboard Heatsink. Damage may occur to the
motherboard and/or the CPU fan if these pins are incorrectly used.
These are not jumpers, do not place jumper caps over these pins.
GND
Sensor
GND
Vcc
Sensor
Vcc
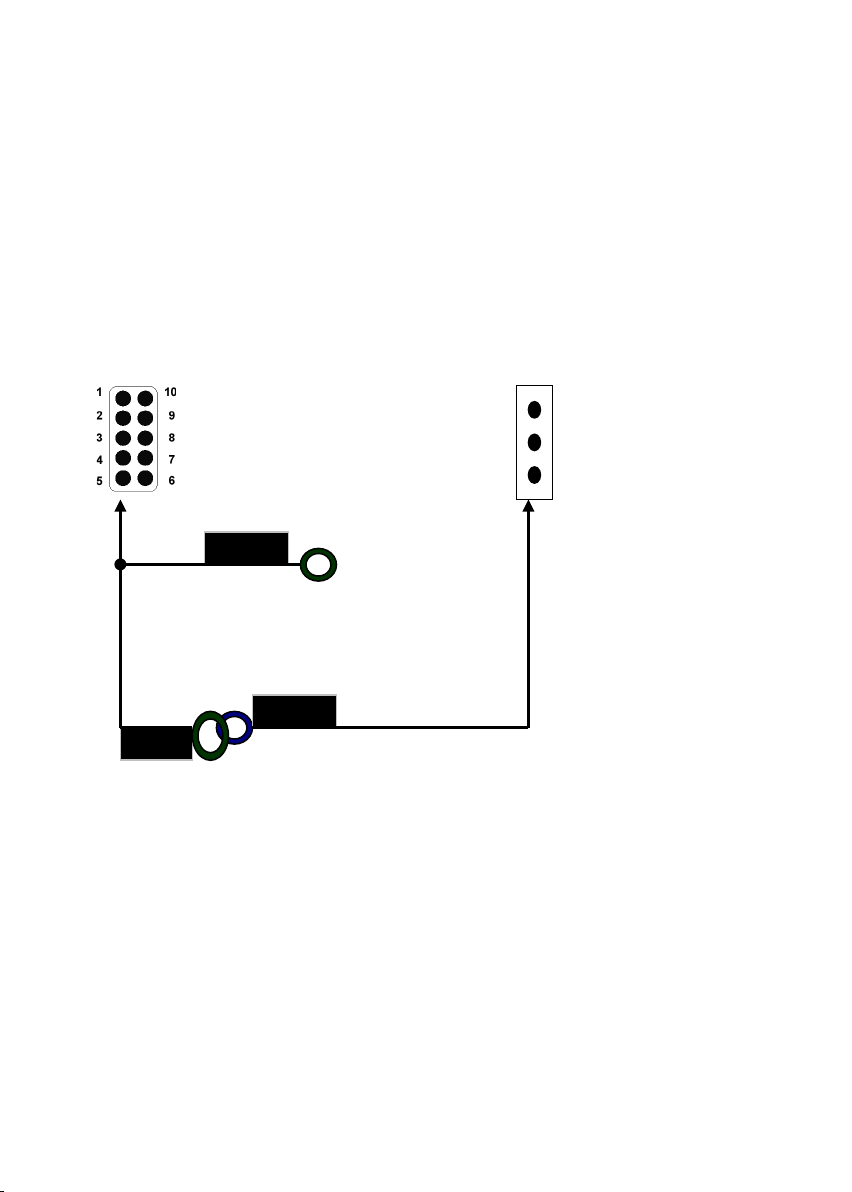
III-5-5 IrDA Compliant Infrared Module Connector
These connectors support the optional wireless transmitting and receiving
infrared module. This module mounts to a small opening on system cases
that support this feature. You must also configure UART 2. Use Infrared in
Chipset Features Setup to select whether UART 2 is directed for use with
COM2 or IrDA. When IrDA is selected in BIOS, COM2 will be disabled. Use
the five pins or six pins as shown and connect a ribbon cable from the
module to the motherboard to the pin definitions. There are two connectors
are available for the IrDA, one is near to Front Panel the other is rear, user
can use one of them to connect to IrDA module depending on the location
you want.
III-5-6 Wake-On- AN (WO )
Attach the 3-pin connector from the LAN card which supports the Wake-
On-LAN (WOL) function to the WOL connector on the motherboard. This
WOL function lets users wake up the connected computer through the LAN
card. Please install according to the above pin assignment:
Pin 1: Vcc Pin 6~10: NC
Pin 2: NC
Pin 3: IR_RX
Pin 4: GND
Pin 5: IR_TX
SENSOR
GND
5VSB
WO
IR1
IR 2
WO
This manual suits for next models
3
Table of contents
Other ENPC Motherboard manuals