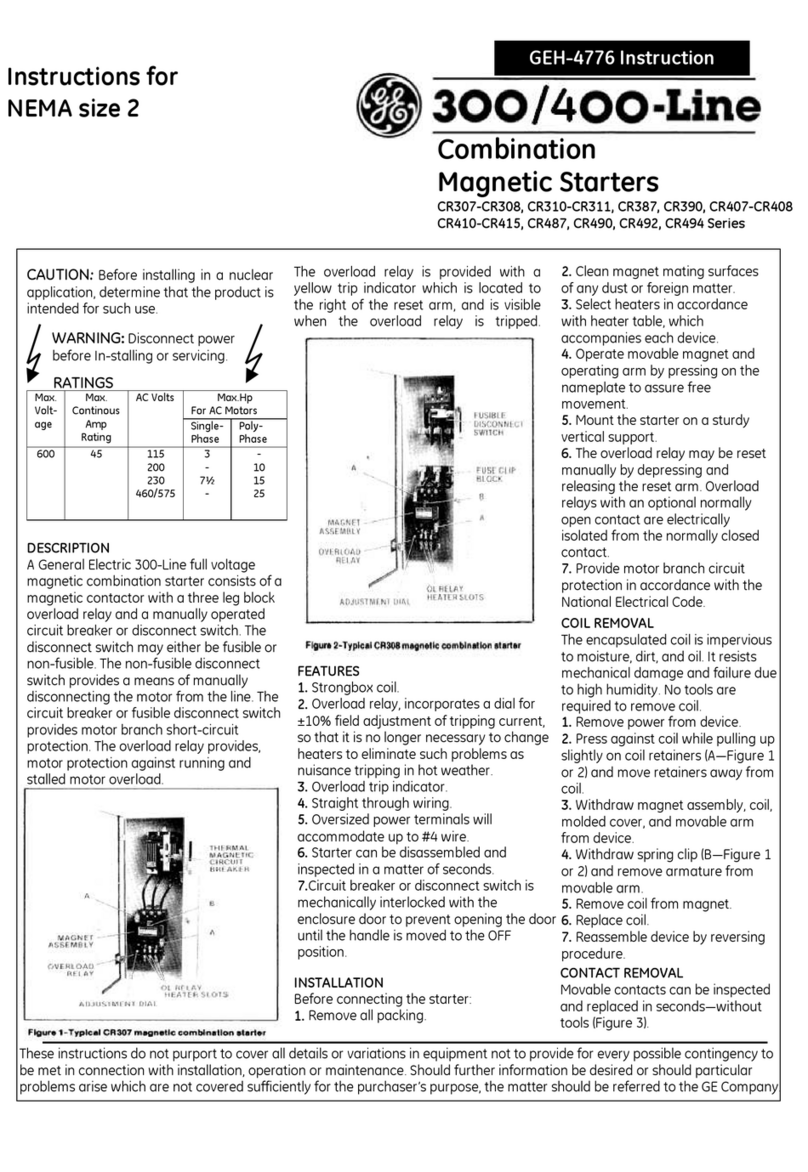
Safety
WARNING
HIGH VOLTAGE!
Frequency converters contain high voltage when
connected to AC mains input power. Installation, start up,
and maintenance should be performed by qualified
personnel only. Failure to perform installation, start up, and
maintenance by qualified personnel could result in death
or serious injury.
High Voltage
Frequency converts are connected to hazardous mains
voltages. Extreme care should be taken to protect against
shock. Only trained personnel familiar with electronic
equipment should install, start, or maintain this equipment.
WARNING
UNINTENDED START!
When the frequency converter is connected to AC mains,
the motor may start at any time. The frequency converter,
motor, and any driven equipment must be in operational
readiness. Failure to be in operational readiness when the
frequency converter is connected to AC mains could result
in death, serious injury, equipment, or property damage.
Unintended Start
When the frequency converter is connected to the AC
mains, the motor may be started by means of an external
switch, a serial bus command, an input reference signal, or
a cleared fault condition. Use appropriate cautions to
guard against an unintended start.
WARNING
DISCHARGE TIME!
Frequency converters contain DC link capacitors that can
remain charged even when AC mains is disconnected. To
avoid electrical hazards, remove AC mains from the
frequency converter before doing any service or repair and
wait the amount of time specified in Table 1.1. Failure to
wait the specified time after power has been removed
prior to doing service or repair on the unit could result in
death or serious injury.
Voltage (V) Minimum waiting time (minutes)
415
200 - 240 1/3 - 5HP 7.5 - 50HP
380 - 480 1/2 - 10HP 15 - 100HP
525 - 600 1/2 - 10HP 15 - 100HP
525 - 690 15 - 100HP
High voltage may be present even when the warning LEDs are
off!
Discharge Time
Symbols
The following symbols are used in this manual.
WARNING
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, may result in minor or moderate injury. It may
also be used to alert against unsafe practices.
CAUTION
Indicates a situation that may result in equipment or
property-damage-only accidents.
NOTE
Indicates highlighted information that should be regarded
with attention to avoid mistakes or operate equipment at
less than optimal performance.
Approvals
Safety AF-650 GP Operating Instructions