GE AV-Line Instruction Manual
Other GE Switch manuals

GE
GE Entellisys DEH-230 User guide

GE
GE BM-C303US5-04 User manual

GE
GE GE-DSH-82 Assembly instructions

GE
GE GuardSwitch 300 Series User manual
GE
GE Manual Service Bypass User manual

GE
GE 45853GE User manual
GE
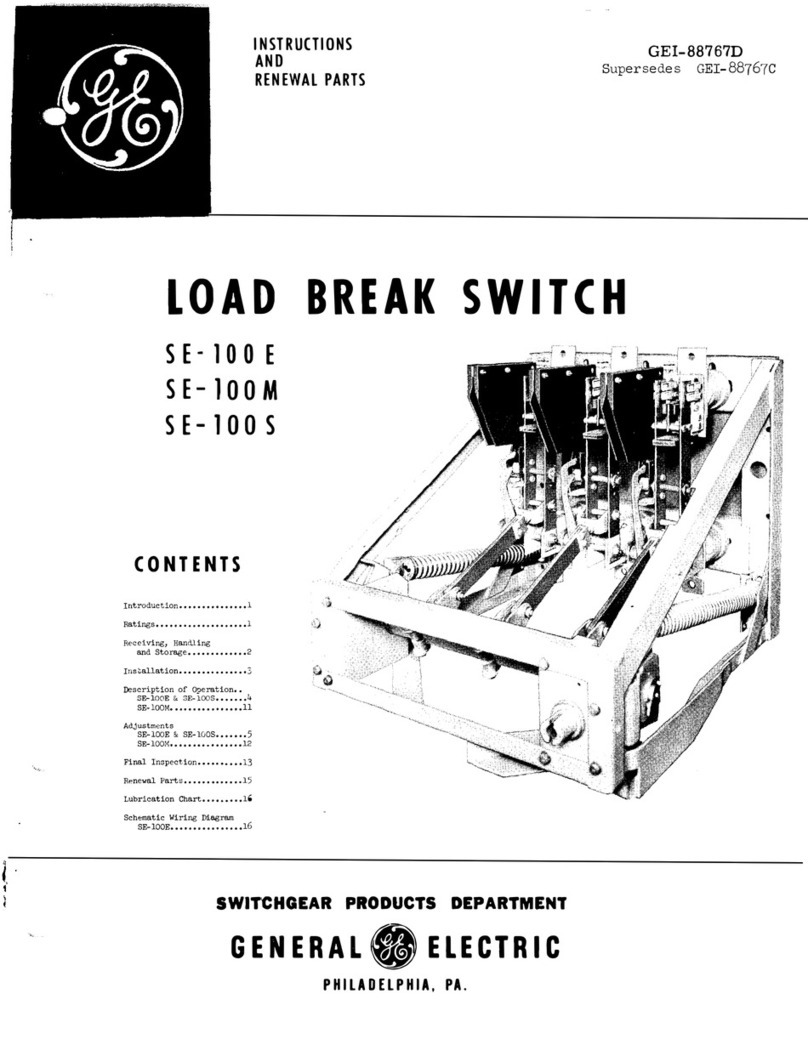
GE SE-100E User manual

GE
GE C-Start User manual

GE
GE Digital Energy STS-230-25-2-RM User manual

GE
GE 40792 User manual