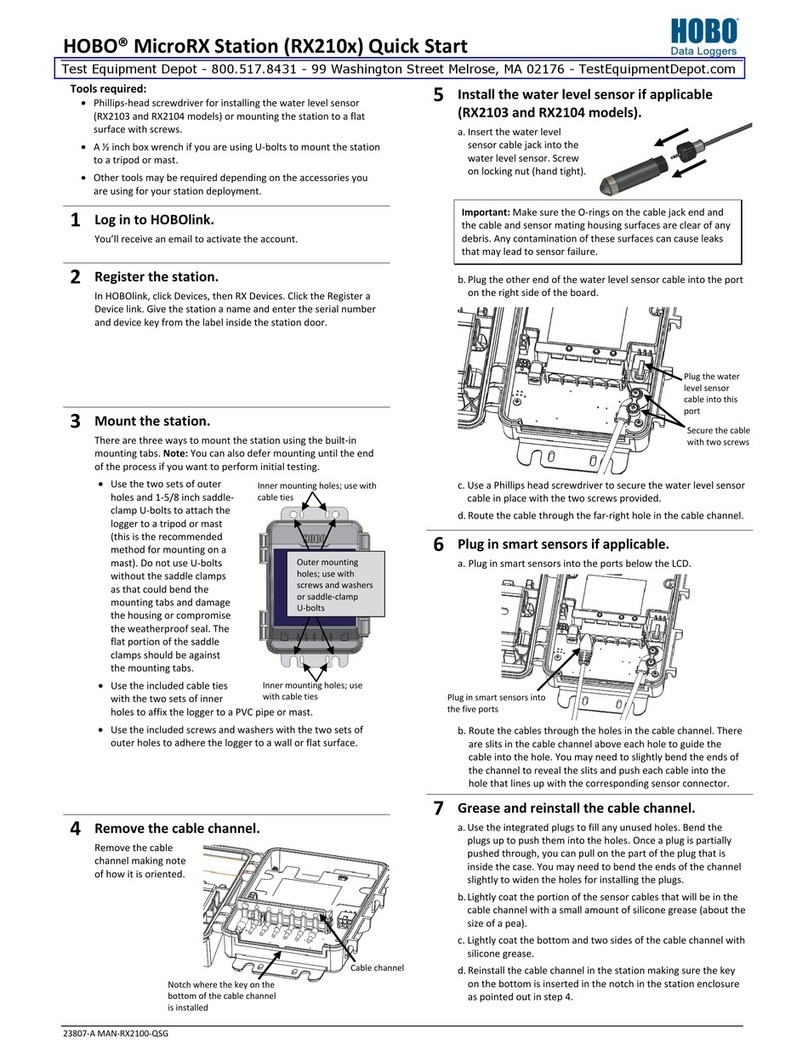
HOBO MX2300 Series Data Logger Manual
7www.hobodataloggers.com.au
burst logging began at 9:06. Burst logging then continued
until 9:12 when the sensor reading fell back below the
high limit. Now back in normal mode, the next logging
interval will be 10 minutes from the last burst logging
point, or 9:22 in this case. If burst logging had not
occurred, the next data point would have been at 9:15.
•A New Interval event is created each time the logger
enters or exits burst logging mode. See Logger Events for
details on plotting and viewing the event. In addition, if
the logger is stopped with a button push while in burst
logging mode, then a New Interval event is automatically
logged and the burst condition is cleared, even if the
actual high or low condition has not cleared.
Statistics Logging
During fixed interval logging, the logger records data for
enabled sensors and/or selected statistics at the logging
interval selected. Statistics are calculated at a sampling rate you
specify with the results for the sampling period recorded at
each logging interval. The following statistics can be logged for
each sensor:
•The maximum, or highest, sampled value,
•The minimum, or lowest, sampled value,
•An average of all sampled values, and
•The standard deviation from the average for all sampled
values.
For example, a logger is configured with both the temperature
and RH sensors enabled, and the logging interval set to 5
minutes. The logging mode is set to fixed interval logging with
Normal and all four statistics enabled and with a statistics
sampling interval of 30 seconds. Once logging begins, the logger
will measure and record the actual temperature and RH sensor
values every 5 minutes. In addition, the logger will take a
temperature and RH sample every 30 seconds and temporarily
store them in memory. The logger will then calculate the
maximum, minimum, average, and standard deviation using the
samples gathered over the previous 5-minute period and log
the resulting values. When reading out the logger, this would
result in 10 data series (not including any derived series, such
as dew point): two sensor series (with temperature and RH
data logged every 5 minutes) plus eight maximum, minimum,
average, and standard deviation series (four for temperature
and four for RH with values calculated and logged every 5
minutes based on the 30-second sampling).
To log statistics:
1. Tap the Devices icon and then tap Loggers at the top of the
screen. Tap the logger to connect to it. If the logger was
configured with Bluetooth Always On disabled, press the
button on the logger to wake it up. When working with
multiple loggers, you can also press the button on the
logger to bring it to the top of the list.
2. Once connected, tap Configure.
3. Tap Logging Mode and then select Fixed Interval Logging.
4. Select Normal to record the current reading for each
enabled sensor at the logging interval shown at the top of
the screen. Do not select this if you only want to log
statistics.
5. Select the statistics you want the logger to record at each
logging interval: Maximum, Minimum, Average, and
Standard Deviation (average is automatically enabled when
selecting Standard Deviation). Statistics will be logged for all
enabled sensors. In addition, the more statistics you record,
the shorter the logger duration and the more memory is
required.
6. Tap Statistics Sampling Interval and select the rate to use
for calculating statistics. The rate must be less than, and a
factor of, the logging interval. For example, if the logging
interval is 1 minute and you select 5 seconds for the
sampling rate, then the logger will take 12 sample readings
between each logging interval (one sample every 5 seconds
for a minute) and use the 12 samples to record the resulting
statistics at each 1-minute logging interval. Note that the
faster the sampling rate, the greater the impact on battery
life. Because measurements are being taken at the statistics
sampling interval throughout the deployment, the battery
usage is similar to what it would be if you had selected this
rate for the normal logging interval.
7. Tap Done.
8. Tap Done again to exit the Logging Mode screen.
9. Tap Start in the Configure screen to load the statistics
settings onto the logger if you are ready to start.
Setting a Password
You can create an encrypted password for the logger that will
be required if another phone or tablet attempts to connect to
it. This is recommended to ensure that a deployed logger is not
mistakenly stopped or purposely altered by others. This
password uses a proprietary encryption algorithm that changes
with every connection.
To set a password:
1. Tap the Devices icon and then tap Loggers at the top of the
screen and connect to the logger.
2. Tap Logger Password.
3. Type a password up to 10 characters.
4. Tap Save.
Only the phone or tablet used to set the password can then
connect to the logger without entering a password; all other
mobile devices will be required to enter the password. For
example, if you set the password for the logger with your tablet
and then try to connect to the device later with your phone,
you will be required to enter the password on the phone but
not with your tablet. Similarly, if others attempt to connect to
the logger with different devices, then they would also be
required to enter the password. To reset a password, connect
to the logger, tap Set Logger Passkey, and select Reset to
Factory Default or press the button on the logger for 10
seconds.
1300 186 107