HOBO MicroRX Station Manual
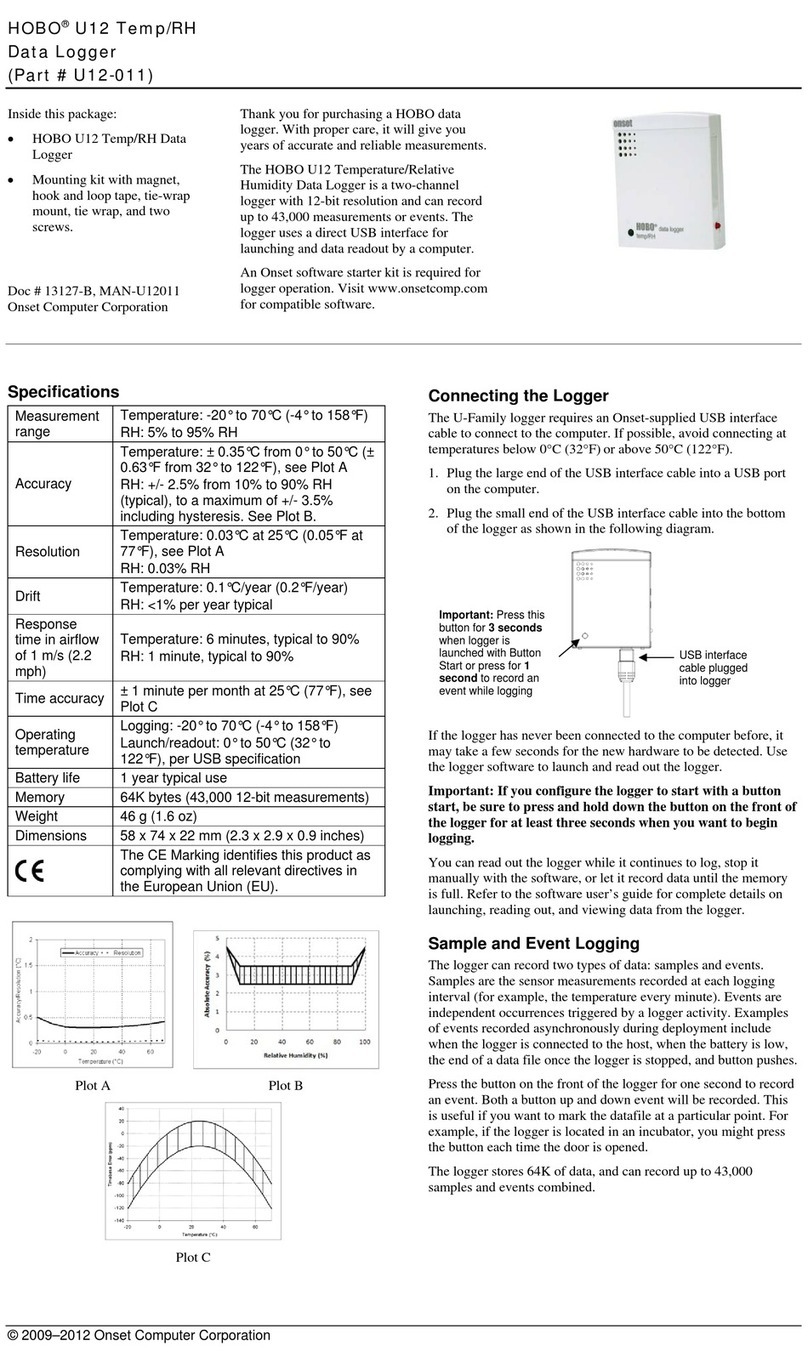
18
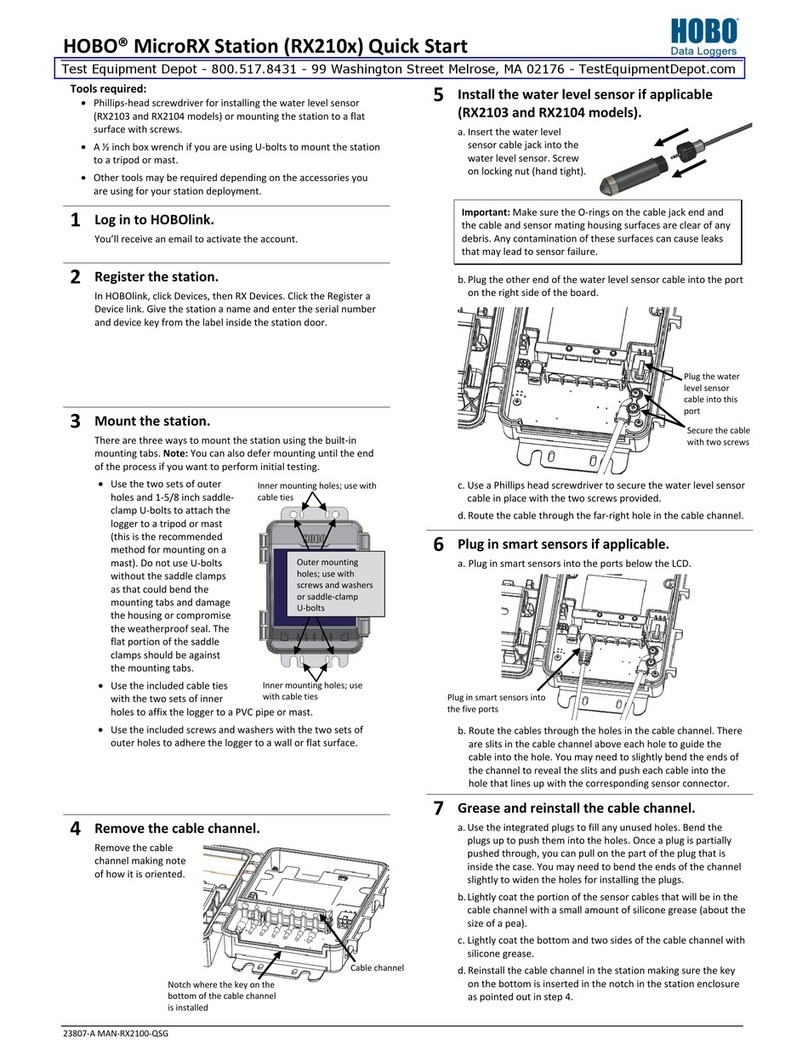
3. Open the station door.
4. Unplug any smart sensors you wish to remove. Plug in any
new smart sensors. Lightly coat the portion of the cable(s)
that will be placed in the cable channel with a small amount
of silicone grease. Push each new sensor cable into the hole
that lines up with the corresponding sensor connector. Use
the integrated plugs in the cable channel to fill any empty
holes.
5. Press the Select button to view the smart sensors on the
LCD screen.
6. Press the Search button for the station to detect all the
smart sensors currently connected (the magnifying glass
icon should be visible as in the previous example).
7. Press the Start button to begin logging again. The station
will automatically connect to HOBOlink.
8. Make sure the cable channel is securely in place and close
the station door.
9. Make any configuration changes in HOBOlink as desired,
such as adding sensor labels or scaling (see Setting up the
Station).
Note that any existing alarms associated with removed sensors
will still be listed in HOBOlink. See the HOBOlink Help for details
on deleting alarms.
Managing Connections to HOBOlink
The station will connect to HOBOlink on the connection interval
you selected in Readout Configuration.
To change the connection schedule:
1. Click Devices and then RX Devices, and find the station you
want to configure. Click the arrow next to on the
Devices page and select Readout Configuration.
2. Set the connection interval. The minimum connection
interval depends on your communication plan.
3. If you wish to set up a second connection interval, select
the “Night Mode” checkbox. Select when night mode
should begin and end and then enter the connection
interval you want to use during that part of the day.
4. Click Save. The changes to the connection interval will take
place the next time the station connects to HOBOlink.
You can also connect to HOBOlink from the station at any time,
regardless of the connection schedule. Press the Connect
button on the station to connect to HOBOlink. Unless the
station is running on a night mode connection interval, the
normal connection schedule will then restart after the
connection is complete. For example, a station is configured to
connect hourly and the last connection on its regular schedule
occurred at 10:05. If you use the Connect button on the station
to connect to HOBOlink at 10:15, the next connection will then
be about 11:15 based on the one-hour connection interval.
Similarly, if a station misses a connection, the connection
schedule will shift depending on the time of the next successful
connection. While the station is using a second, night mode
schedule, all connections will follow that schedule only; any
extra connections while the station is in night mode will not
cause a shift in the connection schedule.
Also note that the station will connect to HOBOlink when the
device is powered up and when you press the Start button.
Note: All connections to HOBOlink count toward your
communications plan. If the station is nearing its limit for
monthly cell use, minimize unscheduled connections. This
includes any connections for alarms or changes you make to
the connection schedule. You can also increase the connection
interval to reduce the number of connections to HOBOlink per
day. Go to the Device Information section on your station page
in HOBOlink to check the status of the monthly
communications plan usage for the station.
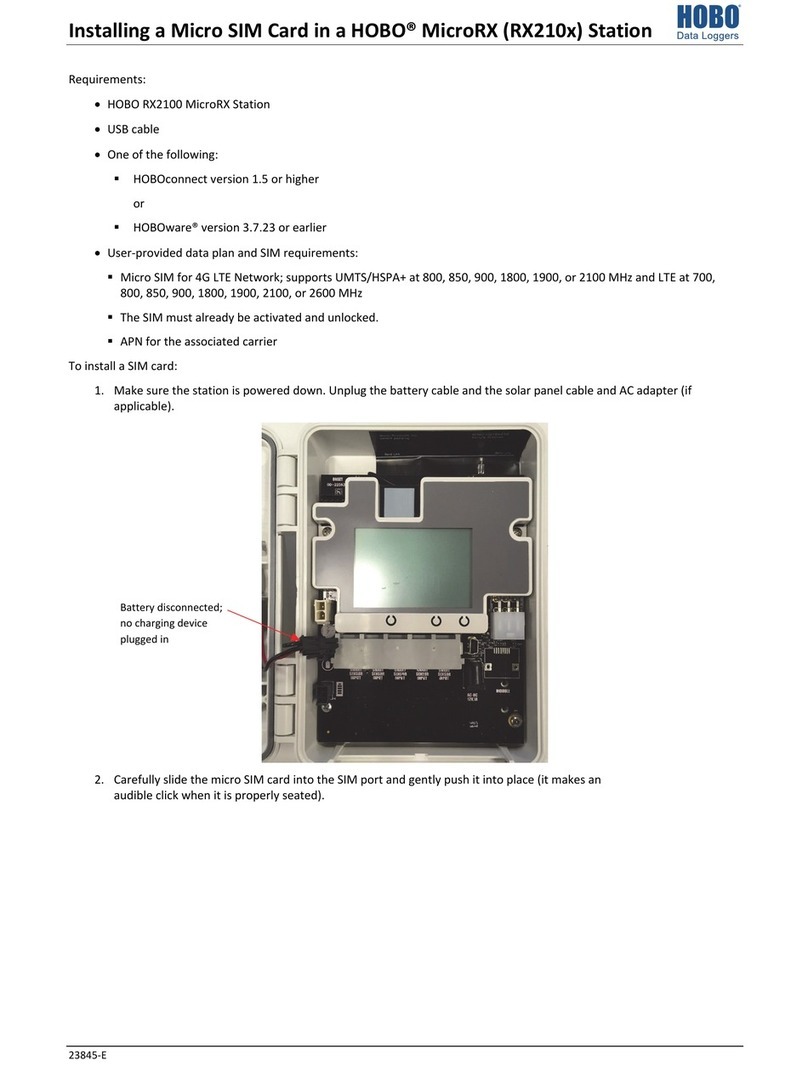
Deployment Guidelines
Follow the guidelines and steps in this section for deploying and
mounting the station.
Guidelines for All Models
• Check the signal strength on the LCD in the location you
wish to deploy the station to make sure it will be able to
reliably connect to HOBOlink. The station may have
difficulty connecting if there is only one bar illuminated in
the signal strength icon on the LCD. (The signal strength
shown on the LCD is from the last connection.)
• The station must be mounted at least one foot from all
sensors to avoid interference from the built-in radio
module and antenna with the measurements made by the
sensors.
• Make sure the station remains in a vertical position once it
is placed in its deployment location to prevent pooling of
water on the cable entries. In addition, if it is mounted
horizontally, the battery could be damaged over time in
RX2102 and RX2104 models as it is charged and the
antenna in all models will not have optimal range.
• If possible, avoid sites immediately adjacent to
radio/television/microwave towers and equipment. In rare
situations, strong electromagnetic interference may result
in sensor network errors.
• If you are using a wind speed/direction sensor or if the
station will be installed on a roof or in a location with
exposure to lightning, use a grounding wire (CABLE-
MICRO-G). A grounding wire may also reduce potential
sensor errors that can result from installing near other
radio or electrical equipment or antennas. See Installing
the Grounding Wire. Also, ground the tripod or mast using
appropriate grounding, such as the Grounding Kit (M-
GKA).
• Take note of the mounting considerations in the sensor
Press the Select button to view
the smart sensor screen
Press the Search button for the station
to find all connected smart sensors
www. .com information@itm.com1.800.561.8187