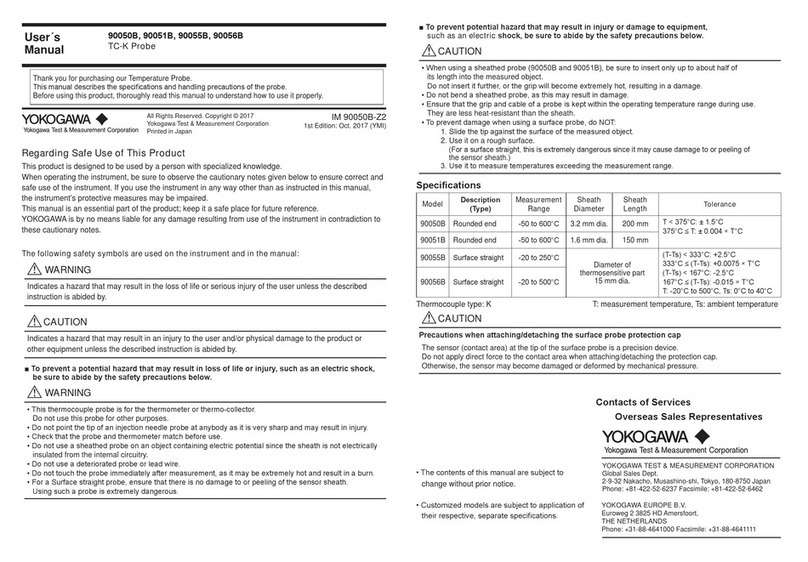
In This Book
Quick Start Chapter 1 prepares the multimeter for use and helps you
get familiar with a few of its front-panel features.
Front-Panel Menu Operation Chapter 2 introduces you to the
front-panel menu and describes some of the multimeter’s menu features.
Features and Functions Chapter 3 gives a detailed description of the
multimeter’s capabilities and operation. You will find this chapter
useful whether you are operating the multimeter from the front panel or
over the remote interface.
Remote Interface Reference Chapter 4 contains reference
information to help you program the multimeter over the remote interface.
Error Messages Chapter 5 lists the error messages that may appear
as you are working with the multimeter. Each listing contains enough
information to help you diagnose and solve the problem.
Application Programs Chapter 6 contains several remote interface
application programs to help you develop programs for your
measurement application.
Measurement Tutorial Chapter 7 discusses measurement
considerations and techniques to help you obtain the best accuracies
and reduce sources of measurement error.
Specifications Chapter 8 lists the multimeter’s specifications and
describes how to interpret these specifications.
If you have questions relating to the operation of the HP 34401A,
call 1-800-452-4844 in the United States, or contact your nearest
Hewlett-Packard Sales Office.
If your HP 34401A fails within three years of purchase, HP will repair
or replace it free of charge. Call 1-800-258-5165 (“Express Exchange”)
in the United States, or contact your nearest Hewlett-Packard Sales Office.
6