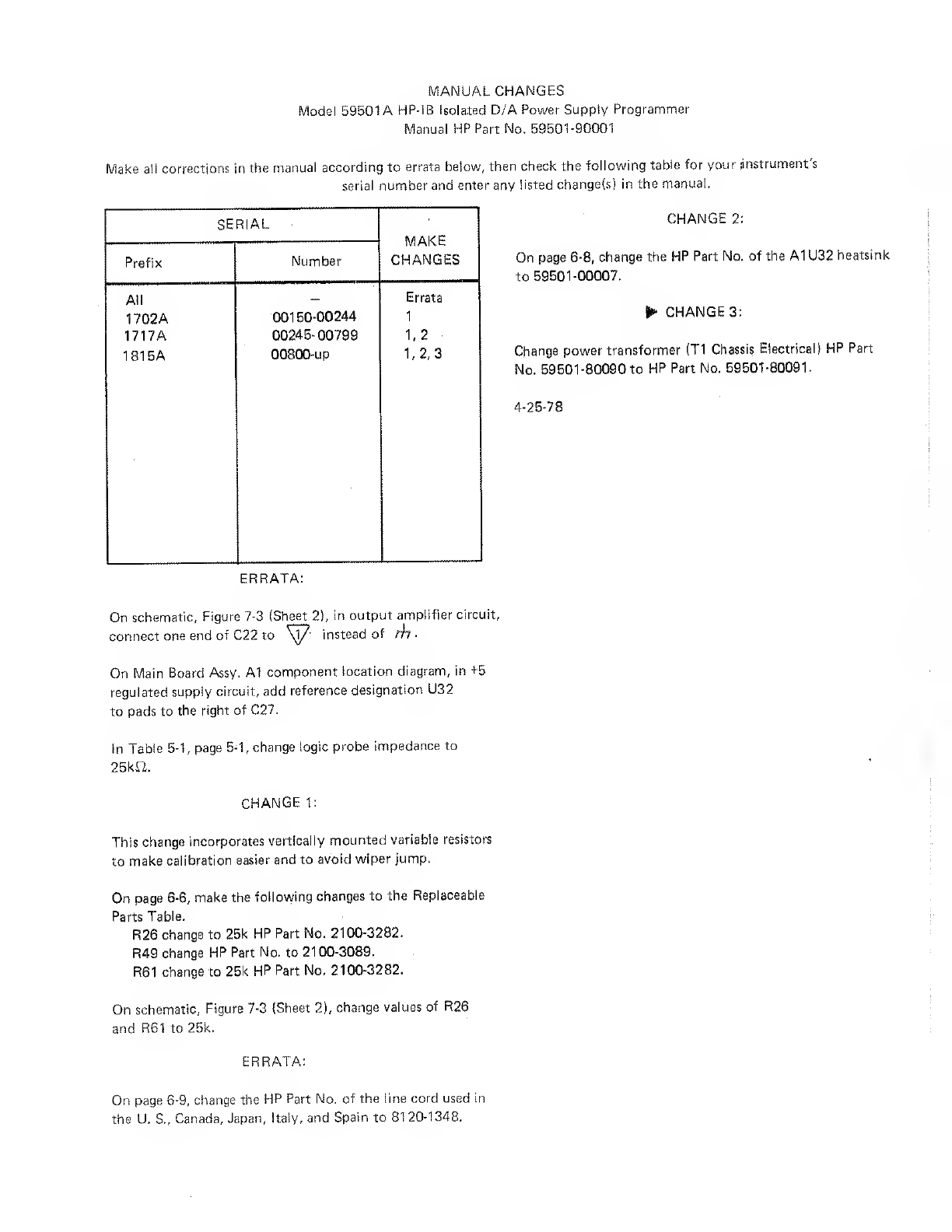
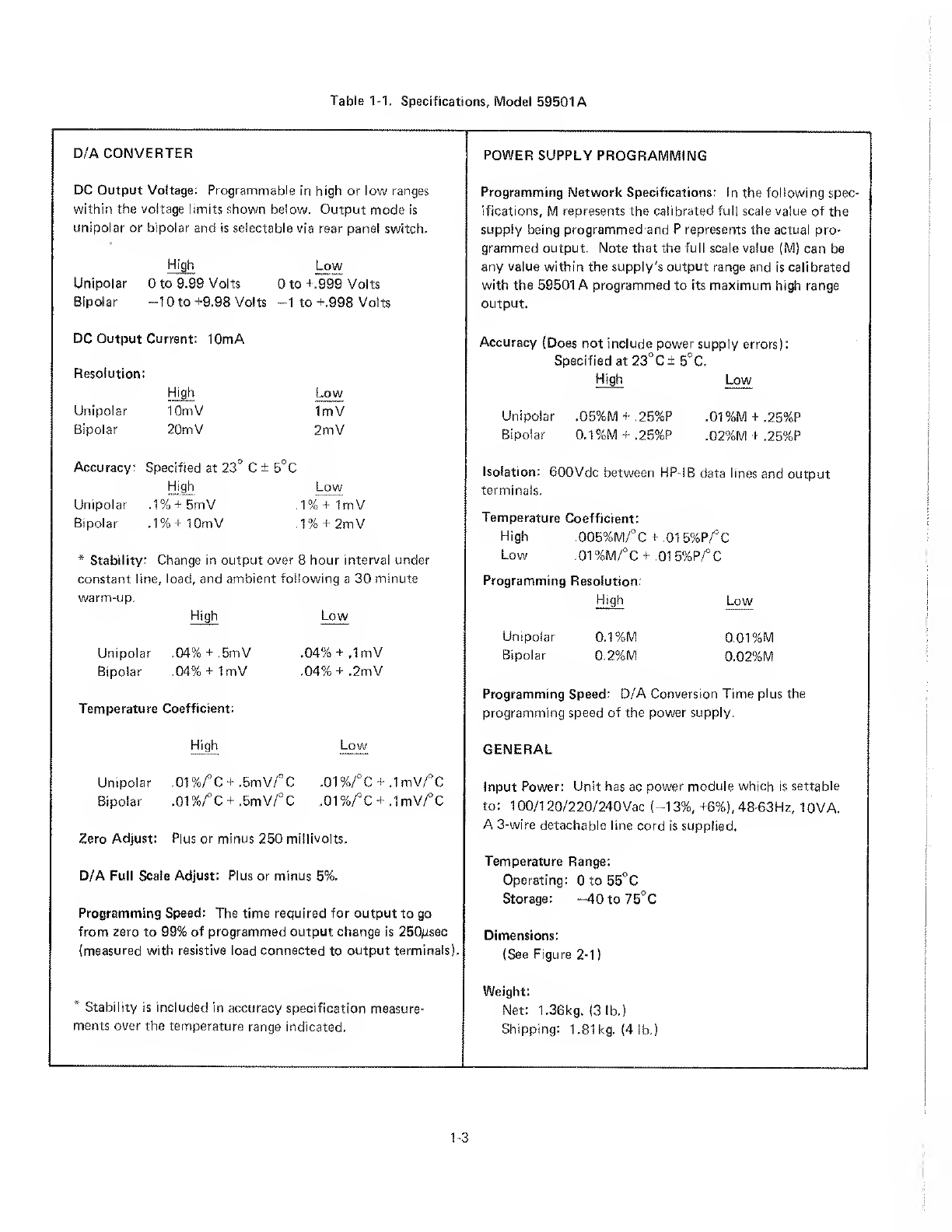
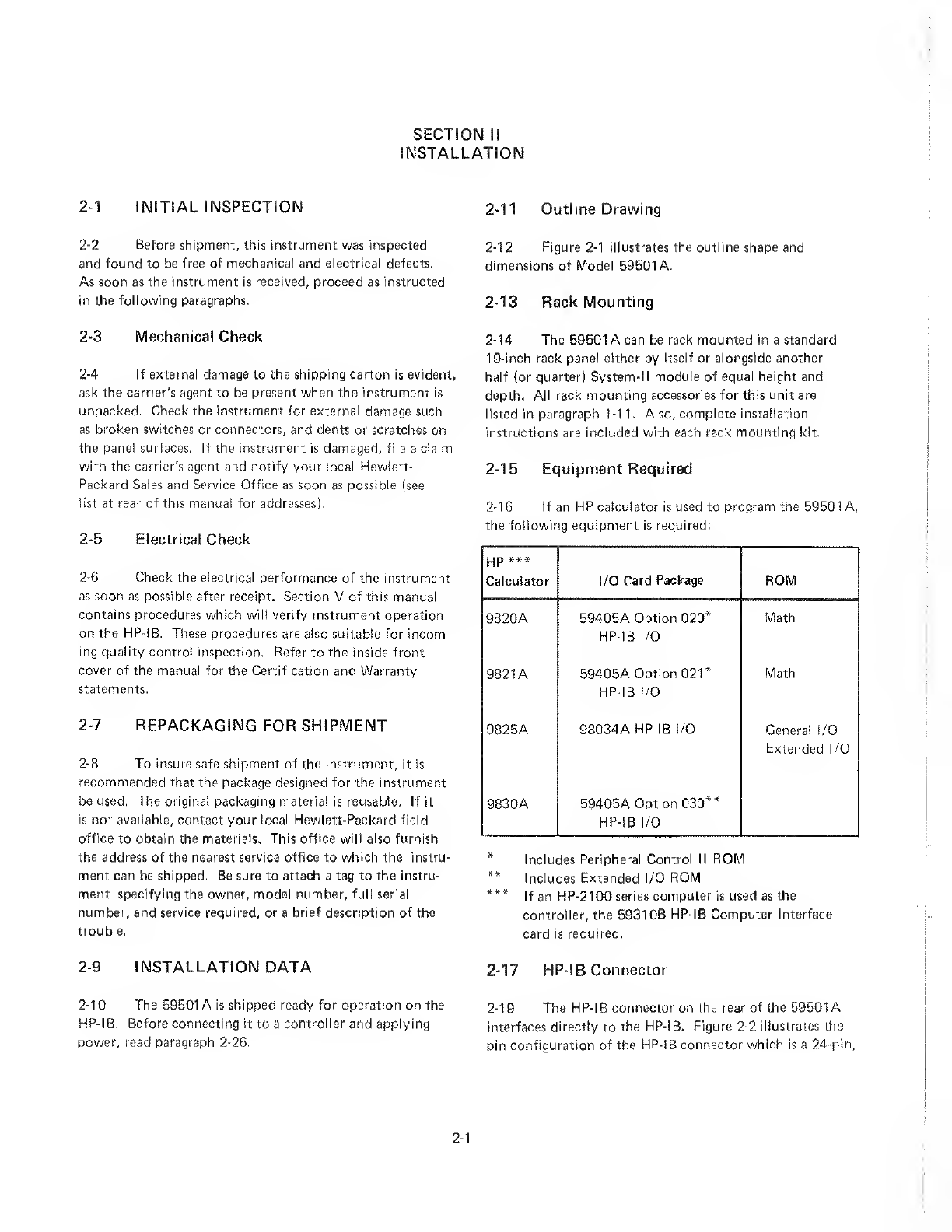
HP 59501A Service manual
Other HP Power Supply manuals

HP
HP 6034A User manual

HP
HP FlexFabric 11900 2500W AC User manual

HP
HP SCR-1P Series Service manual

HP
HP 6434B Service manual

HP
HP 6033A series User manual

HP
HP D7171A - NetServer - LPr User manual

HP
HP R6000 series User manual

HP
HP Lab Series Instruction and safety manual

HP
HP 6259B User manual

HP
HP 6205C Service manual

HP
HP E3630A User manual

HP
HP D7171A - NetServer - LPr Installation and operation manual
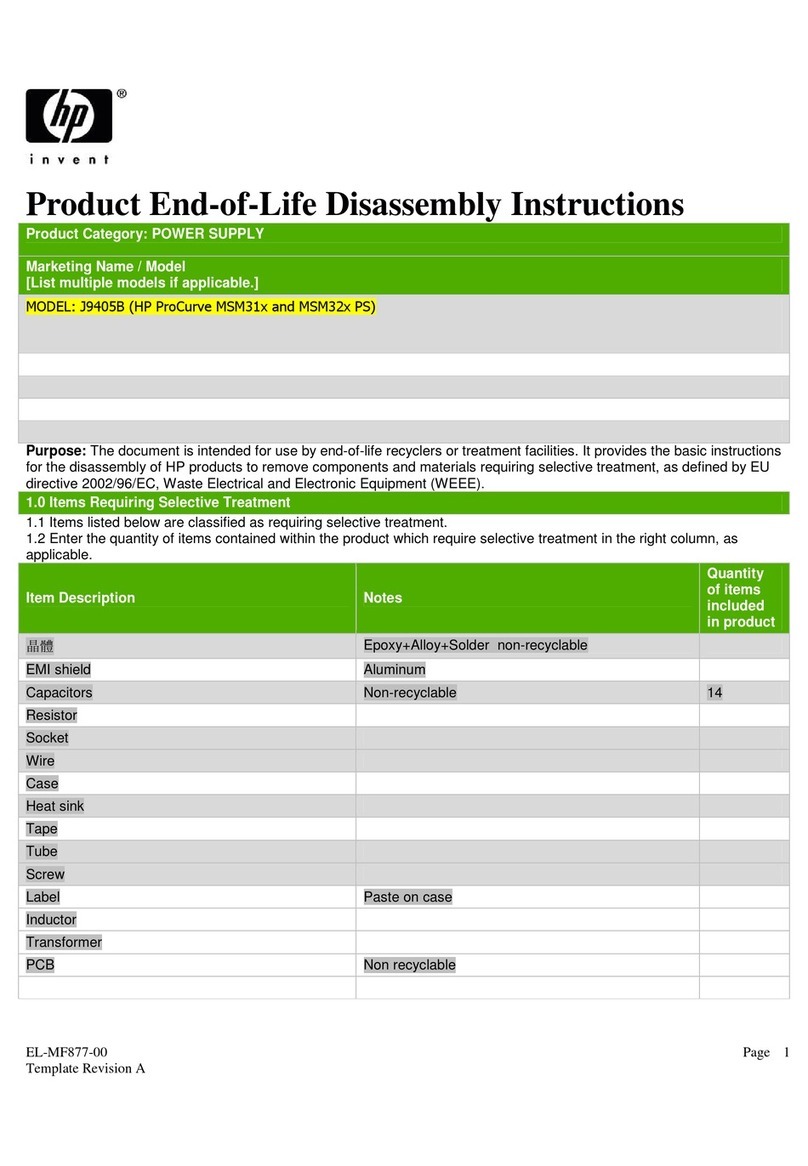
HP
HP J9405B Assembly instructions
HP
HP A3550A - High Availability Disk Arrays Model 20 Storage... User manual

HP
HP 59501A User manual

HP
HP 6034A User manual

HP
HP 6236A Service manual

HP
HP J2962A Installation and operating manual

HP
HP PSR1800-56A User manual

HP
HP Harrison 6516A Service manual