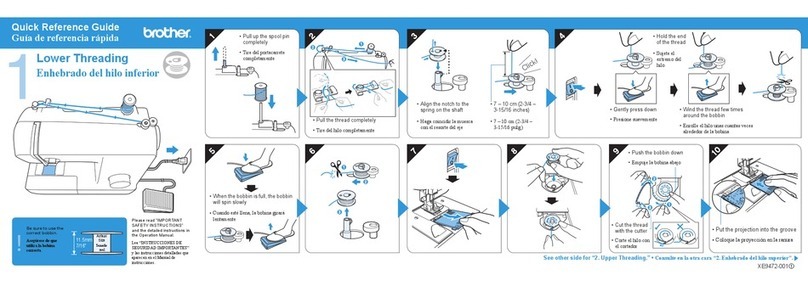
* For the control box and the operation panel, read the Instruction Manual for the SC-900.
CONTENTS
1. OUTLINE .................................................................................................................................1
1-1 Features.........................................................................................................................................................1
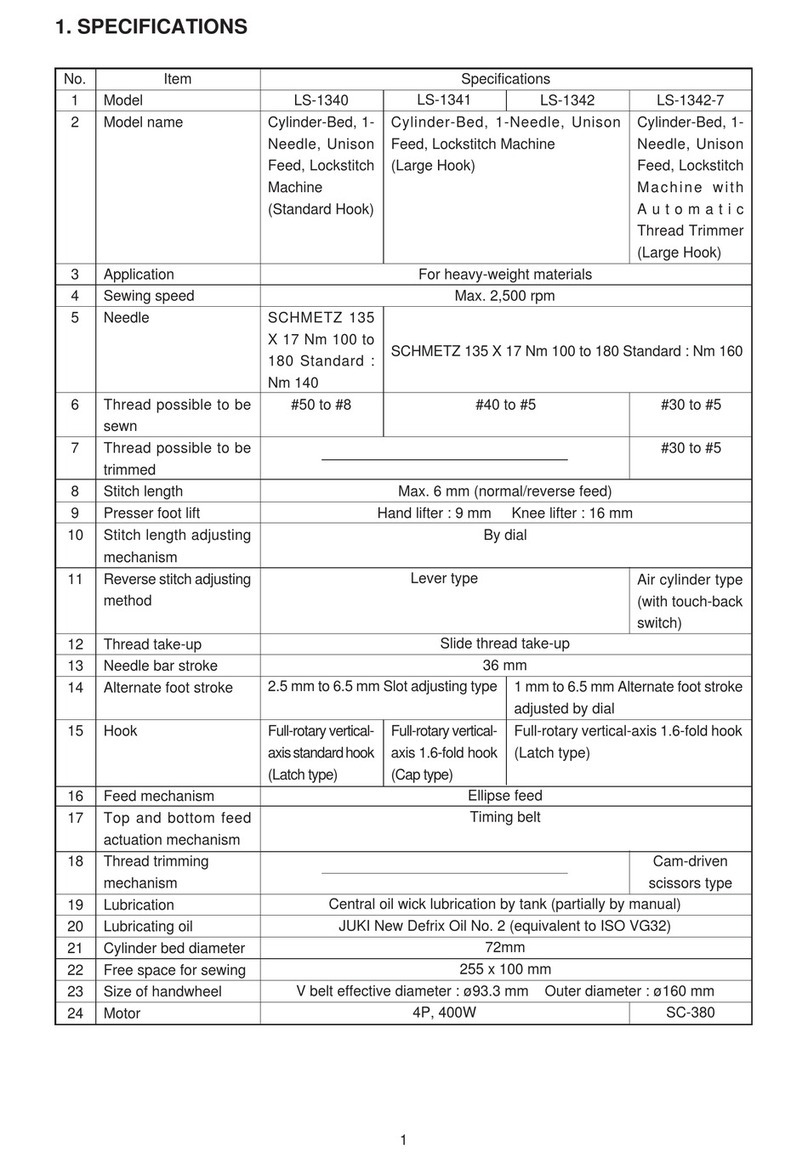
1-2 Specifications (Table of DDL-9000 series specifications) ........................................................................2
1-3 Application ....................................................................................................................................................4
1-4 Cautions when operating.............................................................................................................................4
2. OPERATION............................................................................................................................5
2-1 Configuration ................................................................................................................................................5
2-2 Check points before trial operation and operation ...................................................................................5
3. CONFIGURATION...................................................................................................................9
3-1 Adjusting the needle stop position.............................................................................................................9
3-2 Adjusting the wiper (WB type).....................................................................................................................9
3-3 Principle of thread trimming......................................................................................................................10
3-4 Sequence of thread trimming ....................................................................................................................10
3-5 Observing and adjusting the thread trimmer cam timing.......................................................................12
3-6 Adjusting the position of moving knife movement .................................................................................13
3-7 Properly installing the counter knife ........................................................................................................15
3-8 Rising amount of the thread tension disk No. 2 ......................................................................................16
3-9 Sharpening the knife blade........................................................................................................................16
3-10 Replacing the moving knife .....................................................................................................................17
3-11 Replacing the thread guide for knife ......................................................................................................18
3-12 Adjusting the thread take-up picker .......................................................................................................18
3-13 Adjusting the clutch plate and the thread trimmer solenoid................................................................19
3-14 Driving arm stopper..................................................................................................................................19
3-15 Installing/removing the knife installing base .........................................................................................20
3-16 Adjusting the position of the touch-back switch...................................................................................21
3-17 Adjusting the position of the handwheel ...............................................................................................21
3-18 Adjusting the automatic presser lifter (AK118) .....................................................................................21
3-19 Optionals (Presser foot micro-lifter) .......................................................................................................25
3-20 AE-8 (Bobbin thread remaining amount detector) ................................................................................25
3-21 ED-4 (Compact material end sensor)......................................................................................................25
3-22 PK-70 and -71 (3-step pedal)....................................................................................................................25
3-23 Adjusting the tension release change-over ...........................................................................................26
3-24 Adjusting the presser foot micro-lifter ...................................................................................................26
3-25 Installing the operation panel..................................................................................................................26
3-26 Dimensions of table..................................................................................................................................27
3-27 Points of adjustment and assembly of the feed mechanism ...............................................................28
3-29 Points of adjusting and assembling the thread take-up and the needle bar mechanism .................34
3-29 Replacing the motor .................................................................................................................................35
3-30 Replacing the timing belt .........................................................................................................................35
3-31 Points of adjusting and assembling of the bobbin winder...................................................................36
3-32 Points of adjusting and assembling of the lubrication mechanism (SS, SH) .....................................37
3-33 Applying the exclusive grease ................................................................................................................38
3-34 Removing/attaching the gear box cover ................................................................................................39
3-35 Points of adjuting the sewing..................................................................................................................40
3-36 Adjusting the amount of oil in the hook ................................................................................................. 42
4. TROUBLES AND CORRECTIVE MEASURES (MECHANICAL PARTS)............................44
5. TROUBLES IN SEWING AND CORRECTIVE MEASURES ................................................50
6. BOBBIN CASE WITH IDLE-PREVENTION SPRING ...........................................................60