DP770 Service Manual
Contents
1.General Introduction...................................................................................................................................3
1.1. Scope.......................................................................................................................................................................3
1.2. Safety Precaution...................................................................................................................................................3
2.External View and Functional Keys..........................................................................................................4
2.1. External View and Functional Keys.....................................................................................................................4
2.2. LED Indicator..........................................................................................................................................................5
3.Circuit Description......................................................................................................................................6
3.1. RF Section...............................................................................................................................................................6
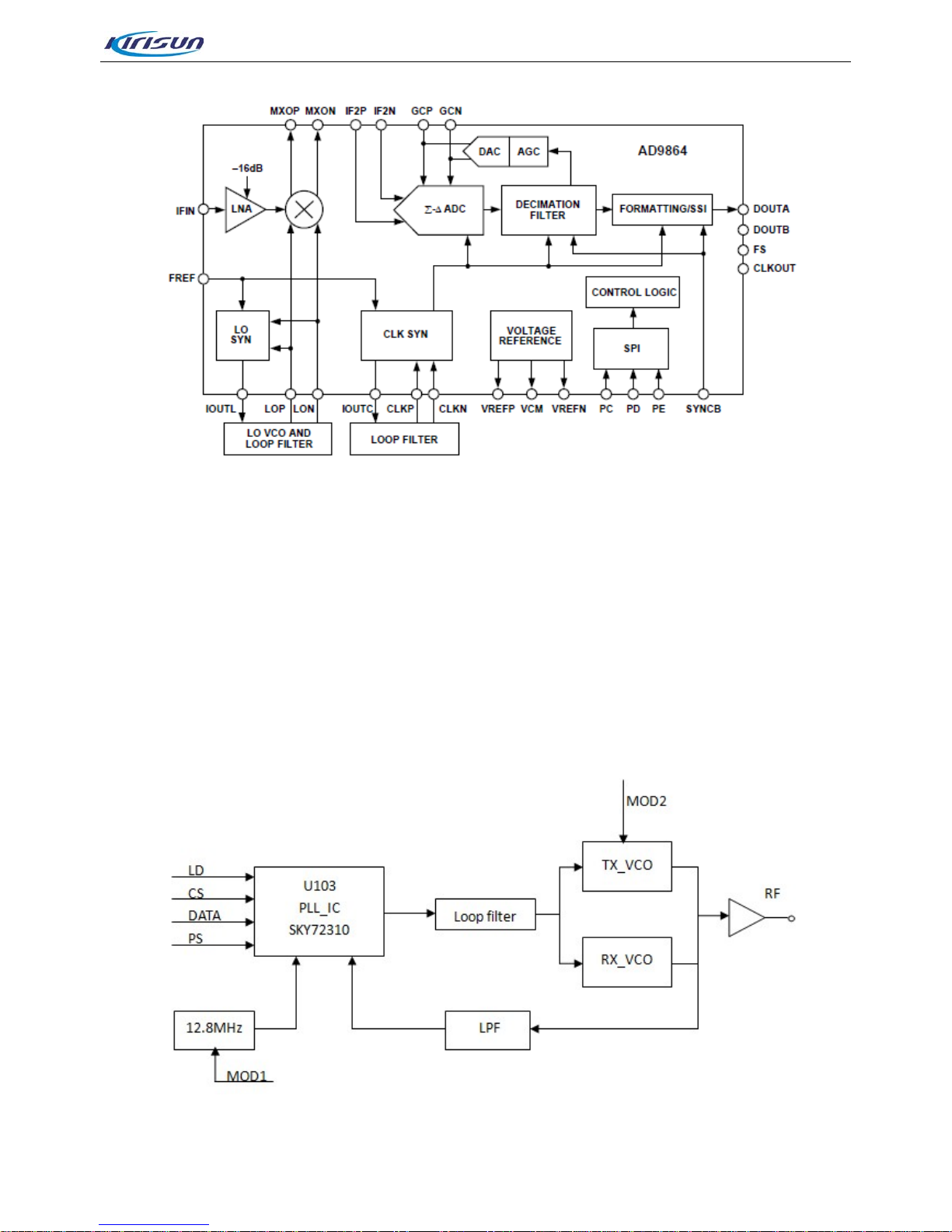
3.1.1. Transmitter Circuit..................................................................................................................................6
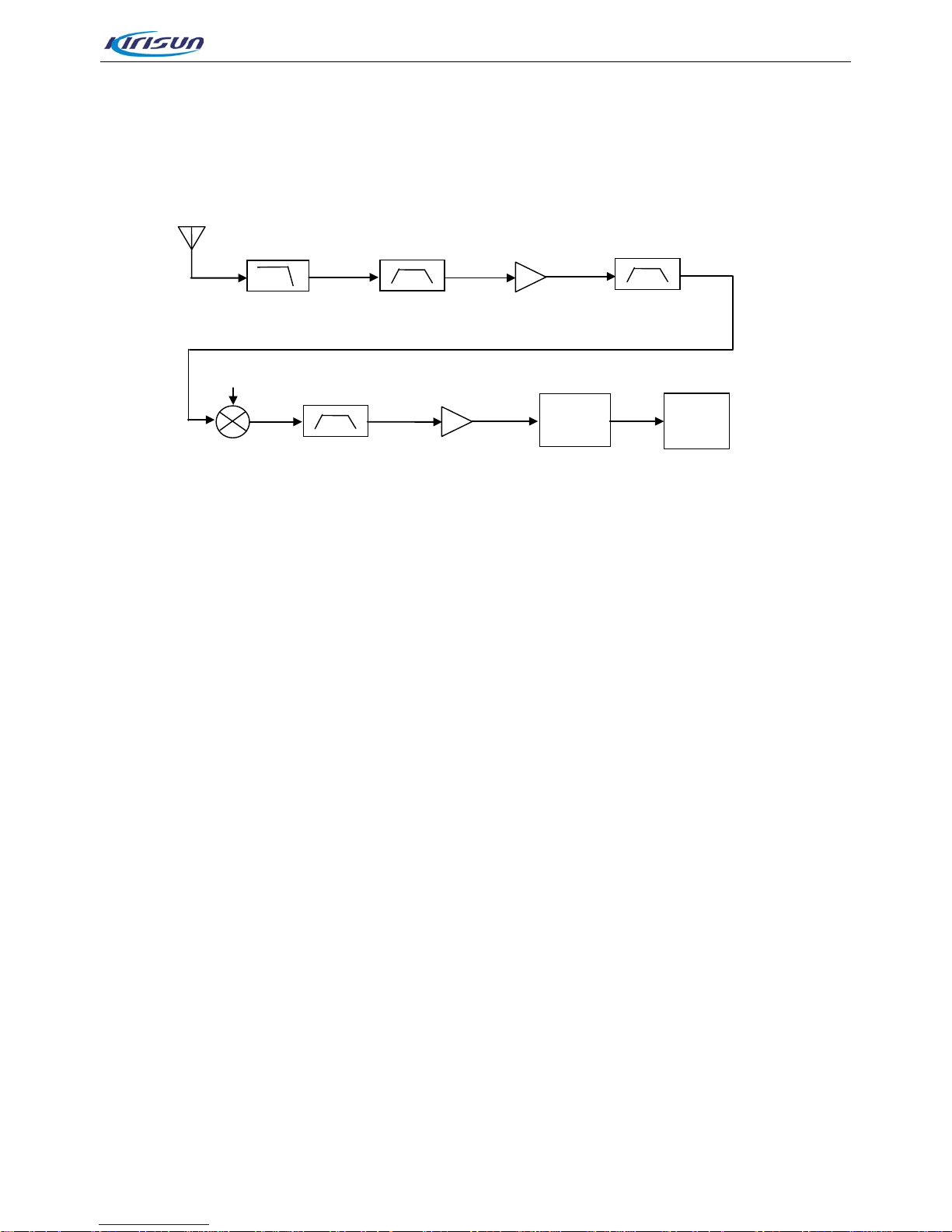
3.1.2. Receiver Circuit .....................................................................................................................................8
3.1.3. Frequency Generation Unit ...................................................................................................................9
3.1.4. GPS Circuit..........................................................................................................................................10
3.2. Baseband Section................................................................................................................................................11
3.2.1. Power Section...................................................................................................................................... 11
3.2.2. Audio Section....................................................................................................................................... 11
4.Function Instruction and Parameters Setting .......................................................................................13
4.1. General Functions................................................................................................................................................13
4.2. Parameters Setting..............................................................................................................................................14
5.Assembly and Disassembly ....................................................................................................................17
5.1. Attaching and Detaching the Battery.................................................................................................................17
5.2. Attaching and Detaching theAntenna...............................................................................................................18
5.3. Attaching and Detaching the Belt Clip...............................................................................................................19
5.4. Detaching the Chassis.........................................................................................................................................19
5.5. Removing the PCB board from the Chassis....................................................................................................20
5.6. Detaching the Keypad Board from the Case....................................................................................................20
5.7. Exploded View......................................................................................................................................................22
6.Tune Mode .................................................................................................................................................25
6.1. Required parts in adjustment..............................................................................................................................25
6.2. Adjusting and checking method.........................................................................................................................25
Page 1 of 102