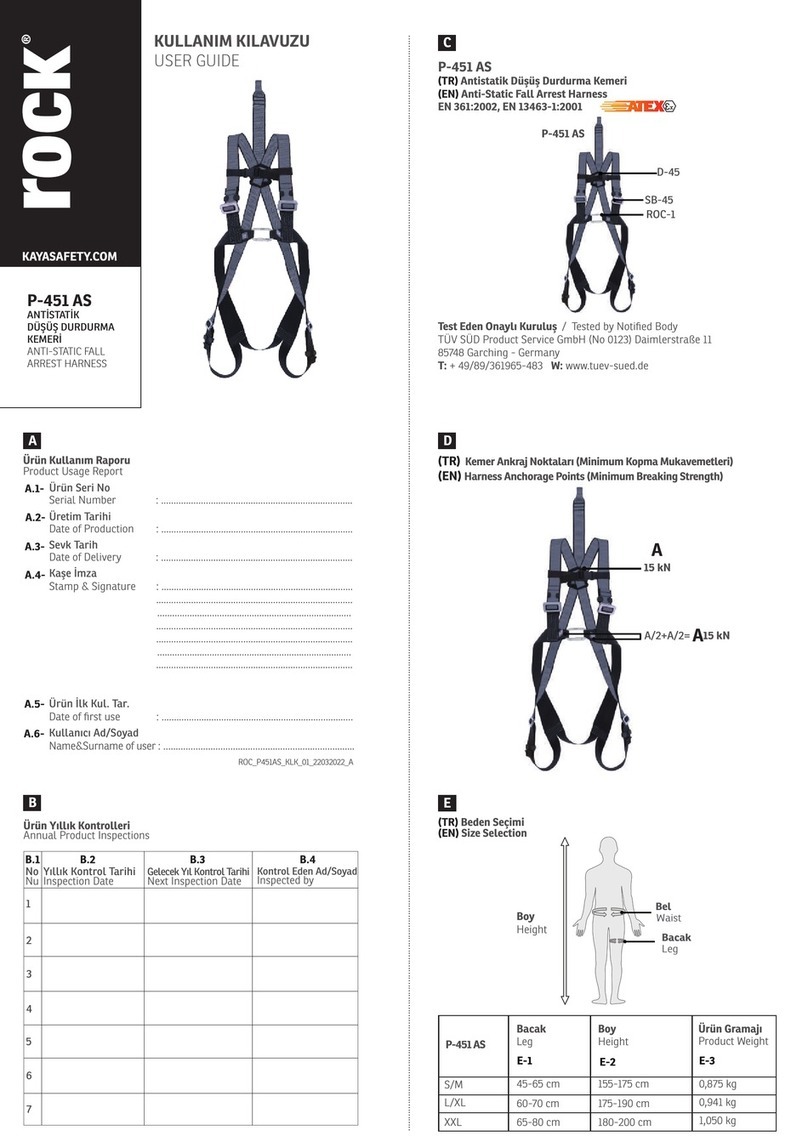
Table of contents
Leuze electronic GmbH + Co. KG MLC 530 SPG 4
7 Mounting..............................................................................................................51
7.1 Arrangement of transmitter and receiver .............................................................................. 51
7.1.1 Calculation of safety distanceS ........................................................................................51
7.1.2 Calculation of safety distance if protective fields act orthogonally to the approach direction...52
7.1.3 Calculation of safety distanceS for parallel approach to the protective field ....................57
7.1.4 Minimum distance to reflective surfaces ...........................................................................58
7.1.5 Resolution and safety distance during fixed blanking .......................................................59
7.1.6 Preventing mutual interference between adjacent devices ............................................... 60
7.2 Mounting the safety sensor................................................................................................... 61
7.2.1 Suitable mounting locations ..............................................................................................62
7.2.2 Definition of directions of movement .................................................................................63
7.2.3 Fastening via BT-NC60 sliding blocks...............................................................................63
7.2.4 Fastening via BT-2HF swivel mount..................................................................................64
7.2.5 Fastening via BT-2SB10 swiveling mounting brackets .....................................................64
7.2.6 One-sided mounting on the machine table........................................................................65
8 Electrical connection..........................................................................................66
8.1 Pin assignment transmitter and receiver .............................................................................. 67
8.1.1 MLC500 transmitter..........................................................................................................67
8.1.2 MLC530SPG receiver .....................................................................................................69
8.2 Operating mode1 ................................................................................................................. 69
8.3 Operating mode4 ................................................................................................................. 70
8.4 Operating mode5 ................................................................................................................. 71
8.5 Operating mode6 ................................................................................................................. 72
9 Starting up the device ........................................................................................74
9.1 Switching on ......................................................................................................................... 74
9.2 Aligning the sensor ............................................................................................................... 74
9.3 Acknowledgement button ..................................................................................................... 75
9.3.1 Unlocking start/restart interlock .........................................................................................75
9.3.2 Gating restart and override................................................................................................76
9.4 Teaching of fixed blanking areas .......................................................................................... 77
10 Testing .................................................................................................................78
10.1 Before commissioning and following modifications .............................................................. 78
10.1.1
Checklist for integrator – to be performed prior to commissioning and following modifications........ 78
10.2 To be performed periodically by competent persons............................................................ 80
10.3 Periodically by the operator .................................................................................................. 81
10.3.1 Checklist – periodically by the operator.............................................................................82
11 Maintenance ........................................................................................................83
12 Troubleshooting..................................................................................................84
12.1 What to do in case of failure? ............................................................................................... 84
12.2 Operating indicators of the LEDs.......................................................................................... 84
12.3 Error messages 7-segment display ...................................................................................... 85
13 Disposing.............................................................................................................90
14 Service and support ...........................................................................................91
15 Technical data .....................................................................................................92
15.1 General specifications .......................................................................................................... 92
15.2 Dimensions and weights....................................................................................................... 94
15.3 Dimensioned drawings: Accessories .................................................................................... 96