2 Getting Started
Table of Contents
1 Overview ..........................................................................................5
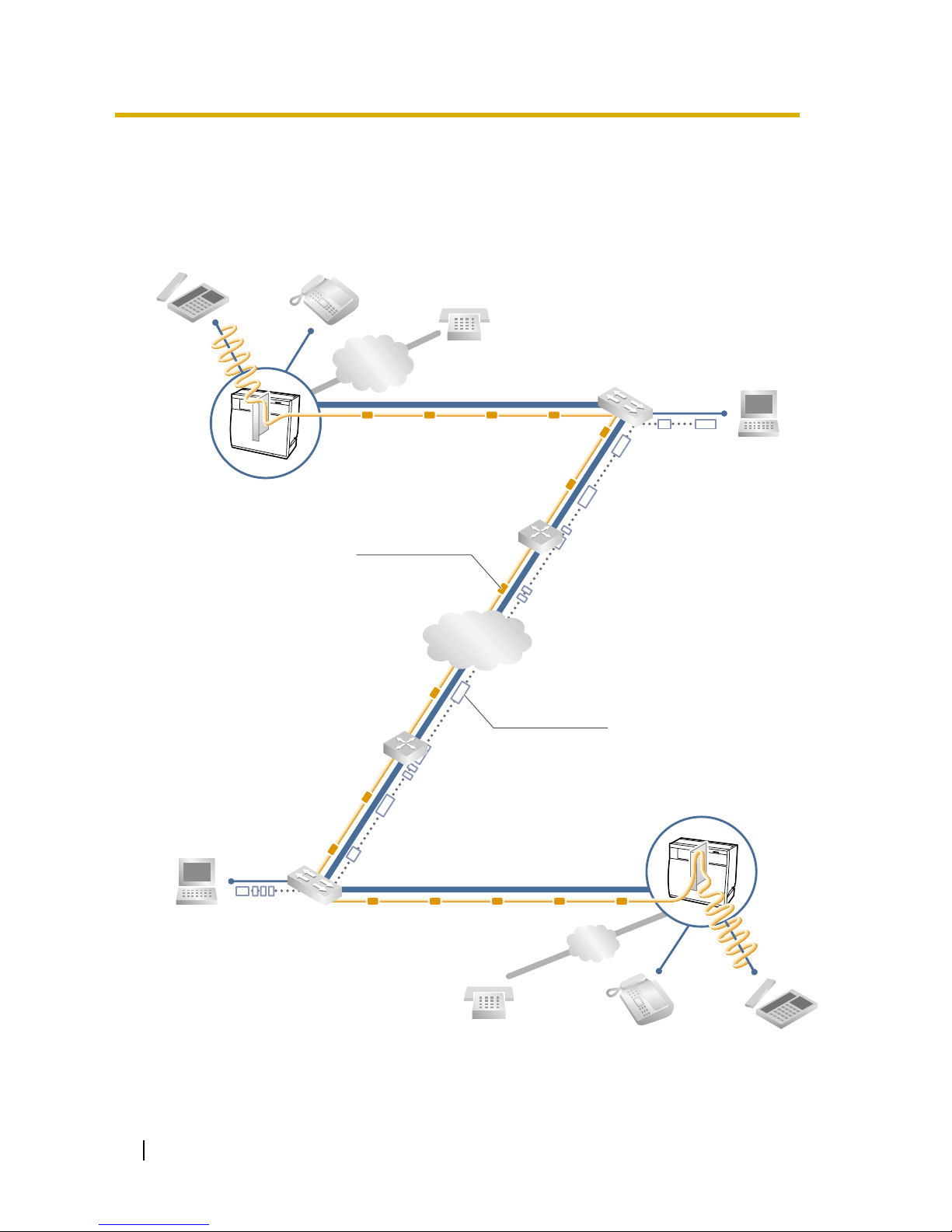
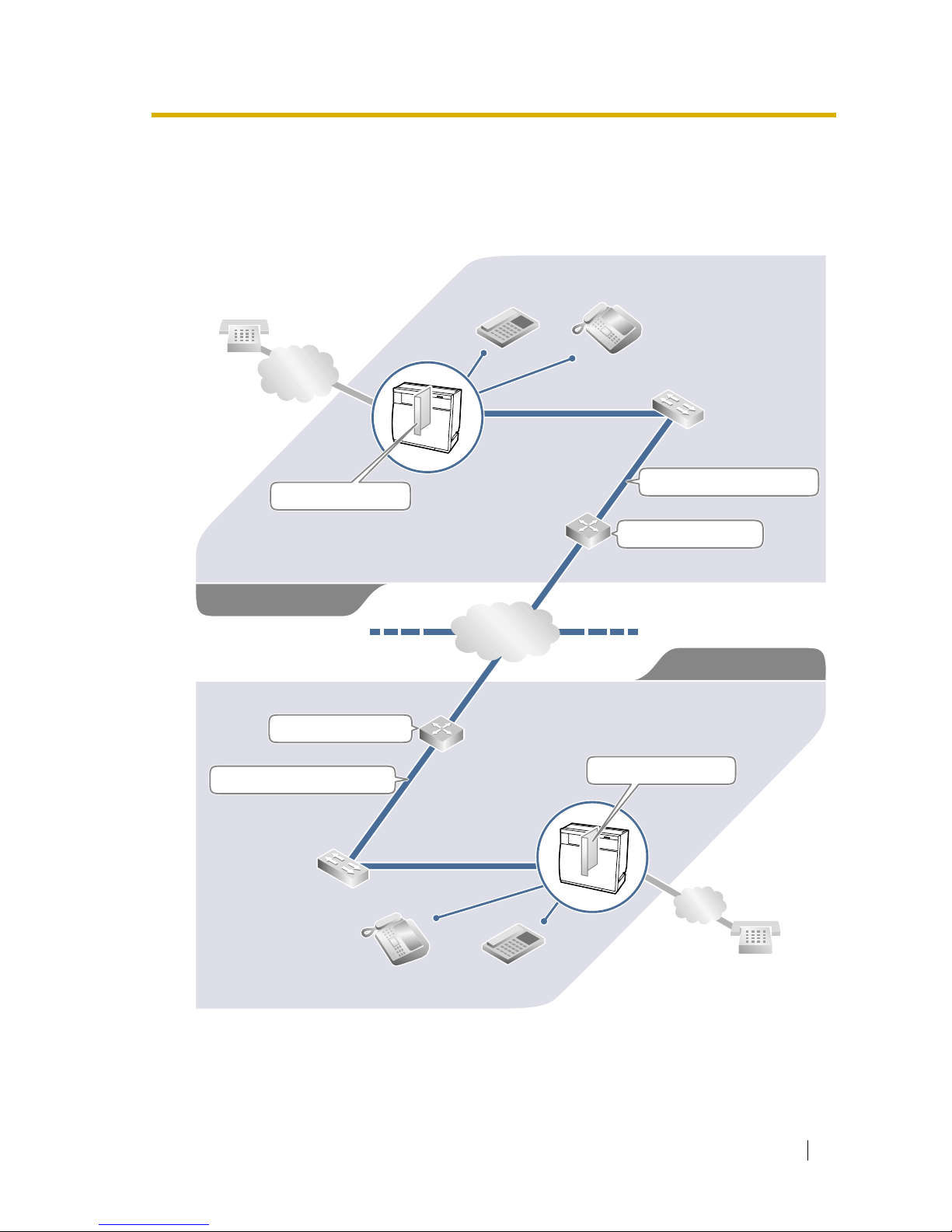
1.1 Example Network Diagram ..................................................................................... 6
1.2 Network Devices and Numbering Plan.................................................................. 7
1.2.1 Network Application................................................................................................... 8
1.2.2 Numbering Plan Example ......................................................................................... 8
1.2.3 Numbering Plan Summary ...................................................................................... 12
2 Physical Installation ......................................................................13
2.1 Installation ............................................................................................................. 14
2.1.1 Names and Locations.............................................................................................. 14
2.1.2 DIP Switch Settings................................................................................................. 14
2.1.3 Installing the VoIP Gateway Card to the Hybrid IP-PBX.......................................... 15
2.1.4 Indication Light (LED).............................................................................................. 16
2.2 Cable Connection.................................................................................................. 17
2.2.1 RS-232C Cable Connection .................................................................................... 17
2.2.2 10BASE-T Cable Connection.................................................................................. 18
3 Logical Installation (Maintenance Console Software) ...............19
3.1 The Maintenance Console Software (MCS) ....................................................... 20
3.1.1 Installing the MCS ................................................................................................... 20
3.1.2 Starting MCS and Logging In .................................................................................. 21
3.1.3 MCS Main Directory Window .................................................................................. 21
3.1.4 RS-232C Port Setting.............................................................................................. 21
3.1.5 Changing the Password .......................................................................................... 23
3.2 Creating New Group and Gateway....................................................................... 24
3.2.1 Creating a New Unit Group (Network)..................................................................... 24
3.2.2 Creating New Gateways (VoIP Gateway Card) ....................................................... 24
3.3 Configuring Domain Name System (DNS) Data ................................................. 27
3.3.1 Creating DNS Data.................................................................................................. 27
3.4 Configuring Office Data........................................................................................ 29
3.4.1 Editing Office Data .................................................................................................. 29
3.5 Transferring Data to the Units.............................................................................. 32
3.5.1 Transferring Data ..................................................................................................... 32
3.6 Synchronising Time and Date of the Units ......................................................... 33
3.6.1 Synchronising Time and Date ................................................................................. 33
4 Programming the Hybrid IP-PBX .................................................35
4.1 PC Programming ................................................................................................... 36
A Additional Information ..................................................................39
A1 Numbering Plan Example Alternative ................................................................. 40
A1.1 Extension Number Method...................................................................................... 40
A2 Firewalls ................................................................................................................. 43
A2.1 Firewalls .................................................................................................................. 43
A3 Optimising Performance....................................................................................... 45
A3.1 Voice Volume........................................................................................................... 45
A3.2 Transmission Delays................................................................................................ 45