Introduction...............................................................................................................................................5
1.1. Description.........................................................................................................................................5
1.2. Validity of documentation ..............................................................................................................5
1.3. Who should use this documentation..............................................................................................5
1.4. Use of the product............................................................................................................................5
1.5. Safety precautions ...........................................................................................................................5
1.7. Acronyms............................................................................................................................................6
Product......................................................................................................................................................7
2.1. Main features....................................................................................................................................7
2.2. Type selection...................................................................................................................................7
2.3. Operating modes.............................................................................................................................8
2.3.1. SIO mode.....................................................................................................................................8
2.3.2. IO-Link mode...............................................................................................................................8
2.3.3. Process data ...............................................................................................................................9
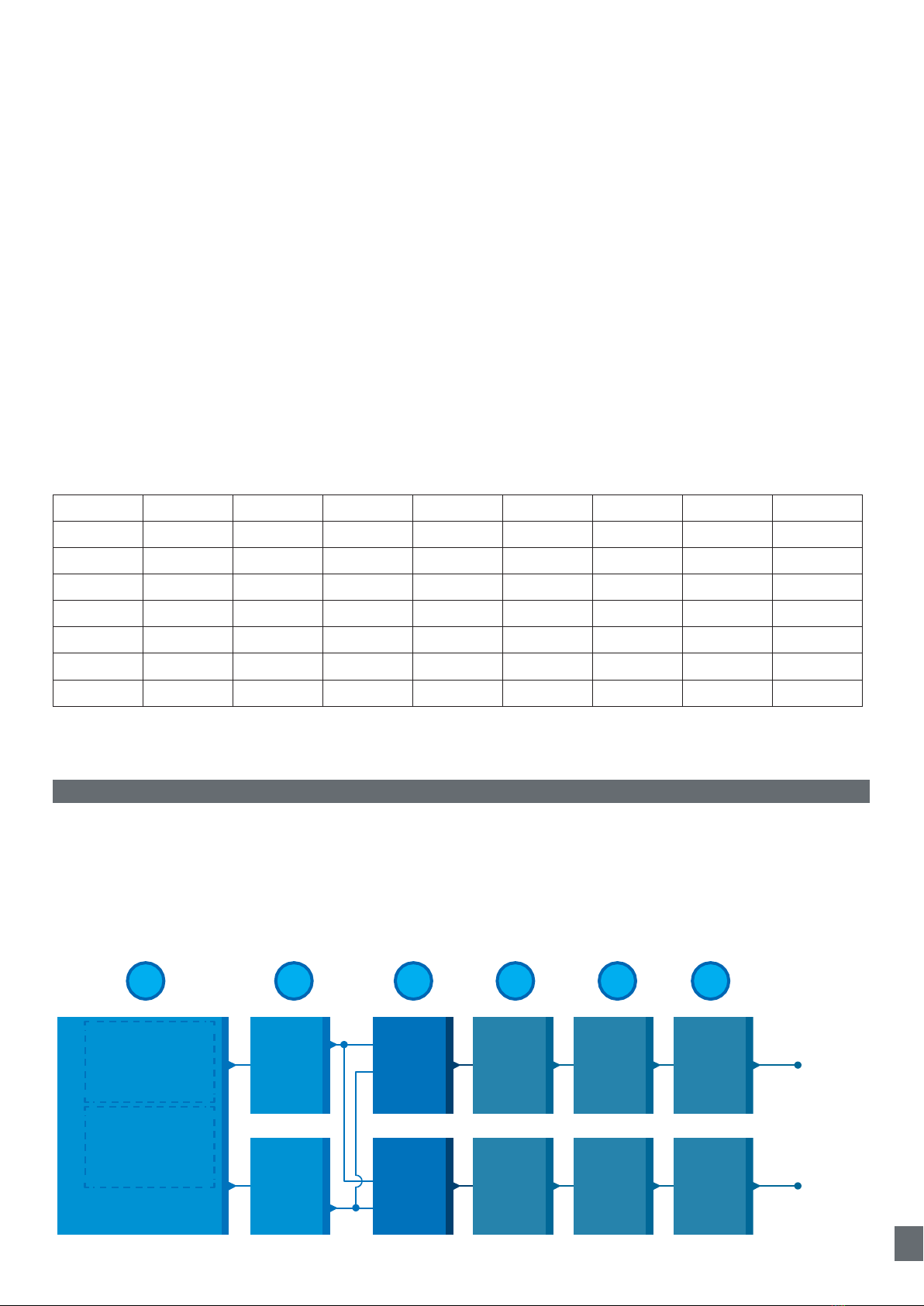
2.4. Output Parameters...........................................................................................................................9
2.4.1. Sensor front................................................................................................................................10
2.4.1.1. SSC (Switching Signal Channel)........................................................................................10
2.4.1.2. Switchpoint mode:.............................................................................................................10
2.4.1.3. Hysteresis Settings ...............................................................................................................11
2.4.1.4. Temperature alarm (TA).....................................................................................................11
2.4.1.5. External input ......................................................................................................................11
2.4.2. Input selector ............................................................................................................................12
2.4.3. Logic function block ................................................................................................................12
2.4.4. Timer (Can be set individually for Out1 and Out2)...............................................................14
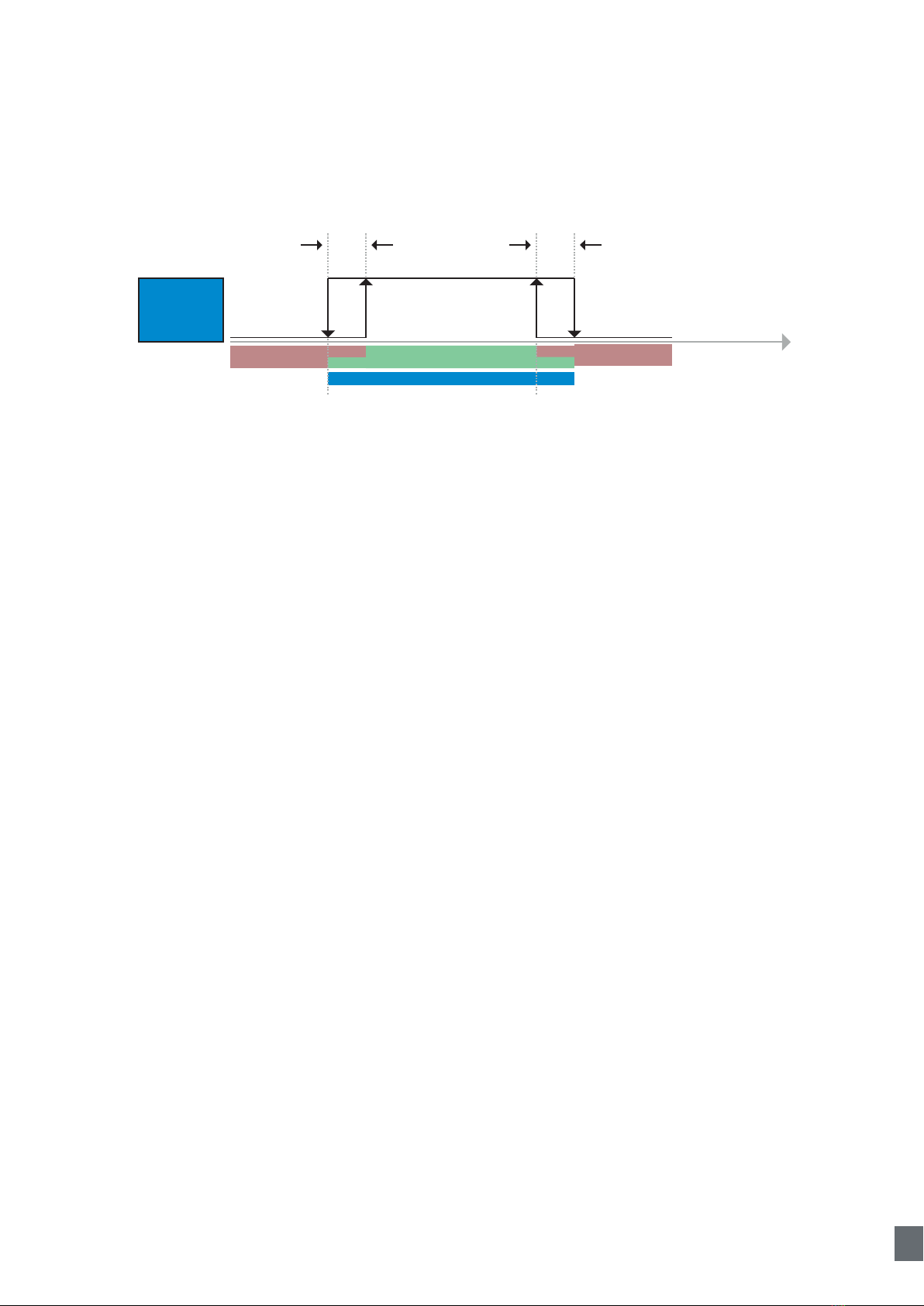
2.4.4.1. Timer mode .........................................................................................................................14
2.4.4.1.1. Disabled........................................................................................................................14
2.4.4.1.2. Turn On delay (T-on)....................................................................................................14
2.4.4.1.3. Turn Off delay (T-off)....................................................................................................15
2.4.4.1.4. Turn ON and Turn Off delay (T-on and T-off) ............................................................15
2.4.4.1.5. One shot leading edge..............................................................................................16
2.4.4.1.6. One shot trailing edge................................................................................................16
2.4.4.2. Timer scale...........................................................................................................................16
2.4.4.3. Timer Value..........................................................................................................................16
2.4.5. Output Inverter .........................................................................................................................17
2.4.6. Output stage mode .................................................................................................................17
2.5. Teach procedure............................................................................................................................18
2.5.1. External Teach (Teach-by-wire)..............................................................................................18
2.5.2. Teach from IO-Link Master.......................................................................................................18
2.5.2.1. Single point mode procedure...........................................................................................18
2.5.2.2. Two point mode procedure..............................................................................................19
2.5.2.3. Windows mode procedure...............................................................................................20
2.6. Sensor Specific adjustable parameters .......................................................................................21
2.6.1. Selection of local or remote adjustment...............................................................................21
2.6.2. Trimmer data.............................................................................................................................21
2.6.3. Process data configuration.....................................................................................................21
2.6.4. Sensor application setting.......................................................................................................21
2.6.5. Temperature alarm threshold..................................................................................................21
2.6.6. Event configuration..................................................................................................................22
2.6.7. Quality of run QoR....................................................................................................................22
2.6.8. Quality of Teach QoT ...............................................................................................................22
2.6.9. Filter Scaler ................................................................................................................................23
Rs Components Ltd