5/45
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION ..................................................................................................................7
1.1. Applicability.....................................................................................................................7
1.2. Acronyms........................................................................................................................7
1.3. Symbols..........................................................................................................................8
1.4. Referenced documents...................................................................................................8
2. UNPACKING AND INSPECTION.........................................................................................9
2.1. Battery characteristics...................................................................................................11
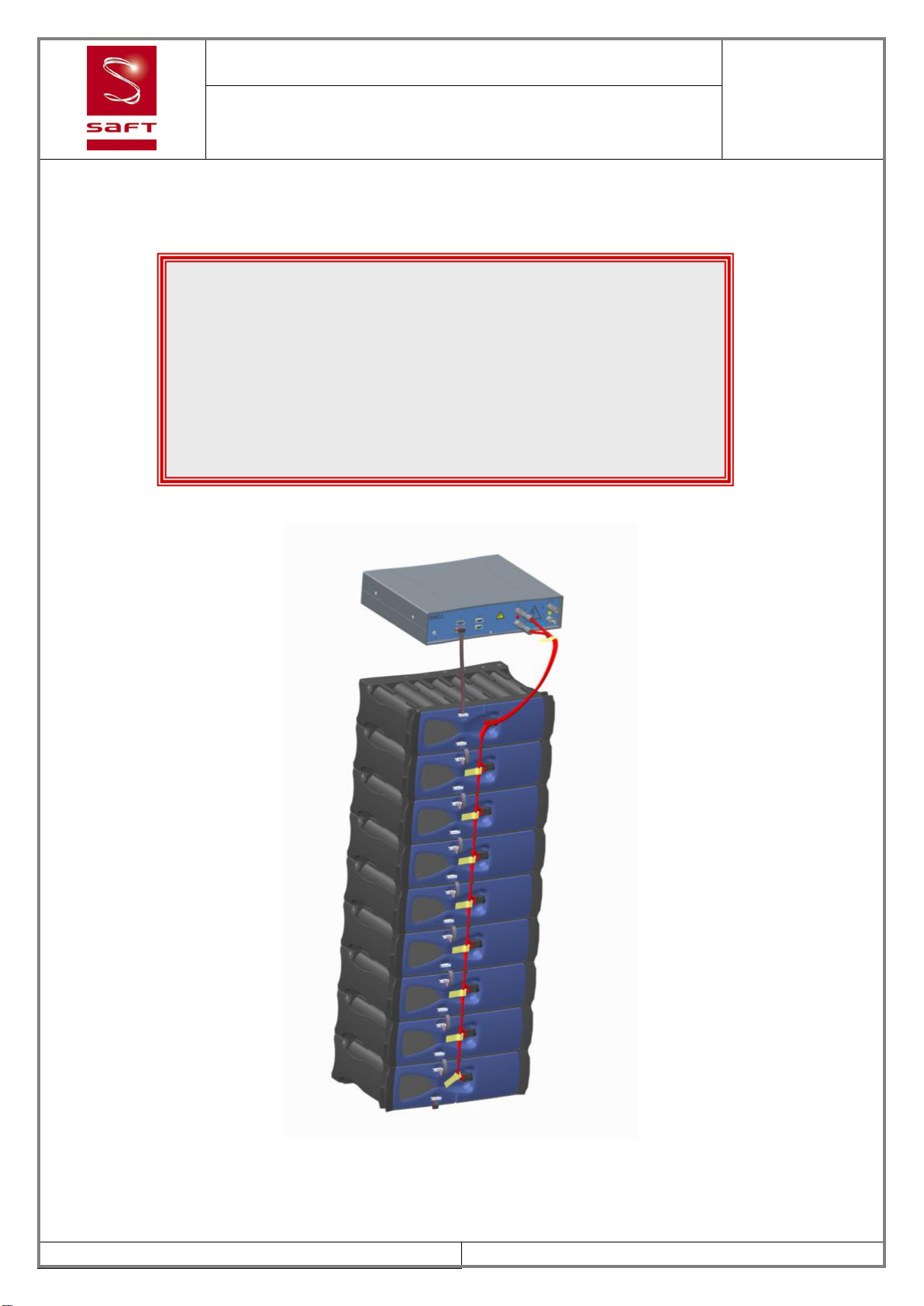
3. GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF THE BATTERY SYSTEM.................................................13
3.1. Synoptic........................................................................................................................13
3.2. Battery system..............................................................................................................14
3.2.1. Li-ion Modules........................................................................................................14
3.2.2. BMM.......................................................................................................................14
3.3. HMI...............................................................................................................................15
3.4. Assembly installation ....................................................................................................16
3.5. Battery start-up.............................................................................................................16
3.6. Battery shutdown..........................................................................................................16
3.7. Gas exhaust..................................................................................................................16
3.8. Electrical interfaces.......................................................................................................17
3.8.1. Power connection...................................................................................................17
3.8.2. Electrical connection ..............................................................................................17
3.8.3. Communication connector......................................................................................19
3.8.4. Power supply connector.........................................................................................19
3.8.5. Earth connection ....................................................................................................19
3.8.6. Diagnostic interface................................................................................................20
4. BATTERY MANAGEMENT and Operating instructions.................................................21
4.1. General principle...........................................................................................................21
4.2. Safety functions ............................................................................................................21
4.2.1. Over charge protection...........................................................................................21
4.2.2. Over-discharge protection......................................................................................22
4.2.3. Over temperature protection...................................................................................22
4.2.4. Over current protection...........................................................................................22
4.3. Communication.............................................................................................................23
4.4. Operation during storage & maintenance .....................................................................23
4.5. Operational states.........................................................................................................24
4.6. Precharge .....................................................................................................................25
4.7. Battery charging............................................................................................................26
4.8. Charge profile description.............................................................................................26
4.9. Battery discharging.......................................................................................................28
4.10. Complete discharge & sleep mode............................................................................28
4.11. Alarms and warnings.................................................................................................28
4.12. Balancing...................................................................................................................29
4.13. Displayed information................................................................................................29
4.14. Communication with application................................................................................29
4.14.1. Data sent by BMM to EMS..................................................................................29
4.14.2. Data received by BMM from EMS.......................................................................30
4.15. SOH and EOL definitions...........................................................................................31
4.16. SOC definitions..........................................................................................................31
5. COMMISSIONING AFTER LONG STORAGE...................................................................31
6. HANDLING & STORAGE OF THE BATTERY MODULES................................................33
6.1. Handling........................................................................................................................33
6.2. Storage.........................................................................................................................33
6.2.1. Storage location .....................................................................................................33