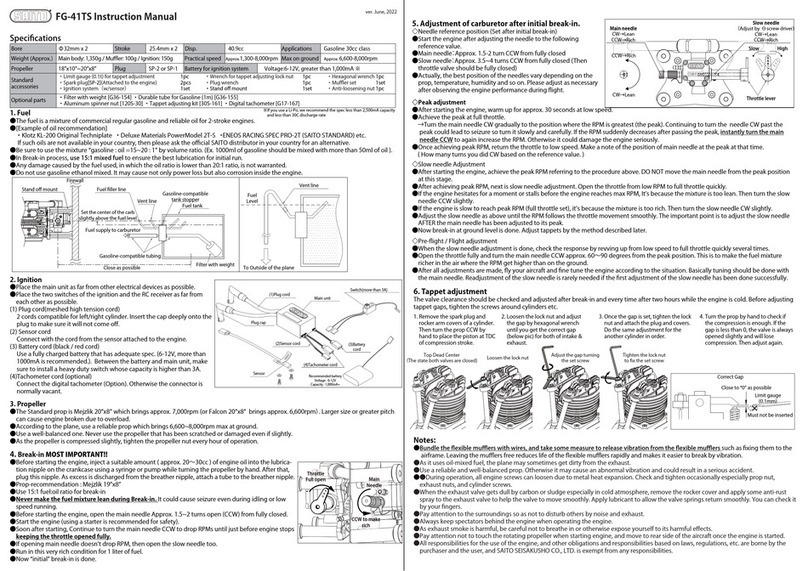
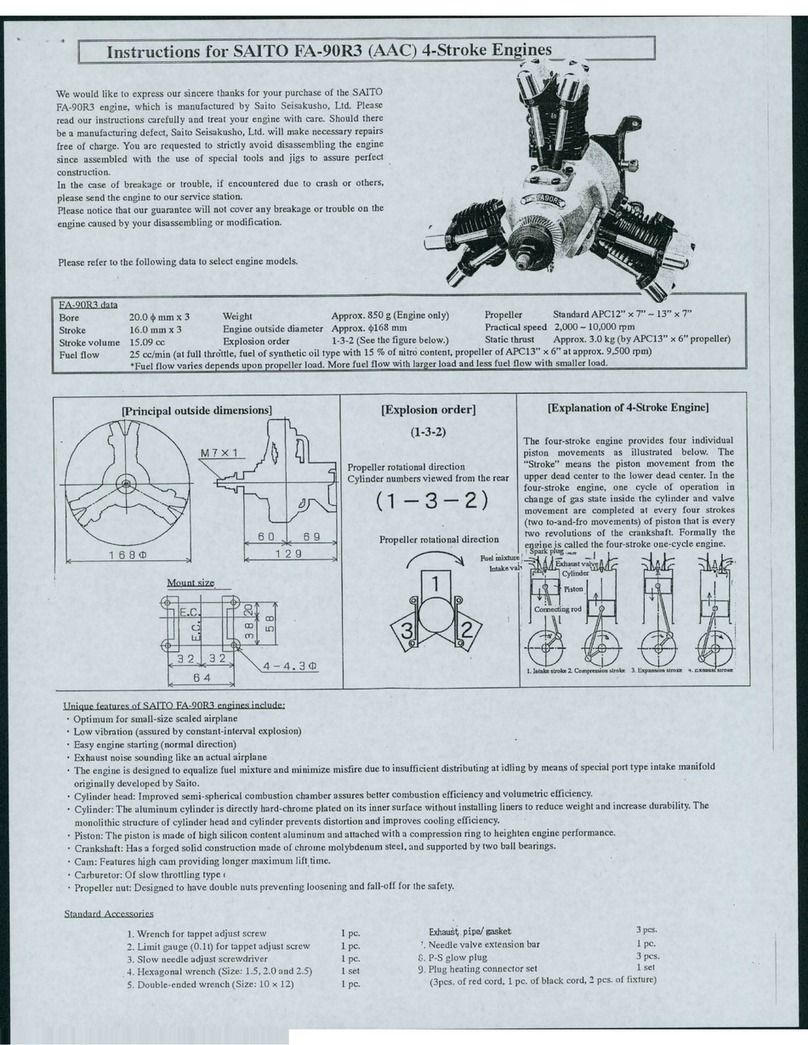
STARTING THE ENGINE
4
Break-In
The first run on any engine, whether
2-cycle or 4-cycle, is critical to the
future of the engine itself. During this
time, metal mating parts (piston and
cylinder, ball bearings, etc.) wear in.
Care must be taken that the engine is
clean and free of any dust or grit that
may have accumulated while
building the model.
There are two accepted methods for
breaking in a new engine: test stand
mounted and run or aircraft mounted
and run. Either method is acceptable,
however, mounting the engine to a test
stand allows the engine to be observed
throughout its operation, as well as
elevating it above the ground and away
from harmful dust and dirt.
NOTE: Because your engine may
have been sitting for an extended
period of time prior to running it, a few
drops of light oil applied through the
crankcase breather nipple (19 on the
exploded view),if applicable,and down
the pushrod tubes (40) will ensure
proper lubrication for the first run.
Regardless of the mounting method
chosen for break-in, the following
procedures are applicable:
1. Use a break-in fuel as described
in the “Support Equipment” Section
on page 3 of this manual.
2. Use the proper glow plugs.Your
engine includes the Hangar 9/McCoy
MC-4C (HAN3010) glow plugs,
which are also the standard
replacement glow plugs for these
engines.
3. Select the correct propeller. To do
so, refer to the Propeller Selection
Chart on page 18 of this manual.
4. Make sure that the high speed
needle valve(s) (85) are opened
(turned counterclockwise) five full
turns. This guarantees a very rich
setting.
Do not adjust the low-speed needle
valve(s) or airbleed screws (89) at
this time. The low speed needle
valve(s), or airbleed screws, are pre-
adjusted at the factory for initial
break-in.
5. The use of a tachometer is highly
recommended since the adjustment
of a 4-cycle engine, while similar to
that of a 2-cycle engine, is more
difficult to “set by ear,” therefore
making it easier to damage the
engine by “over leaning.”