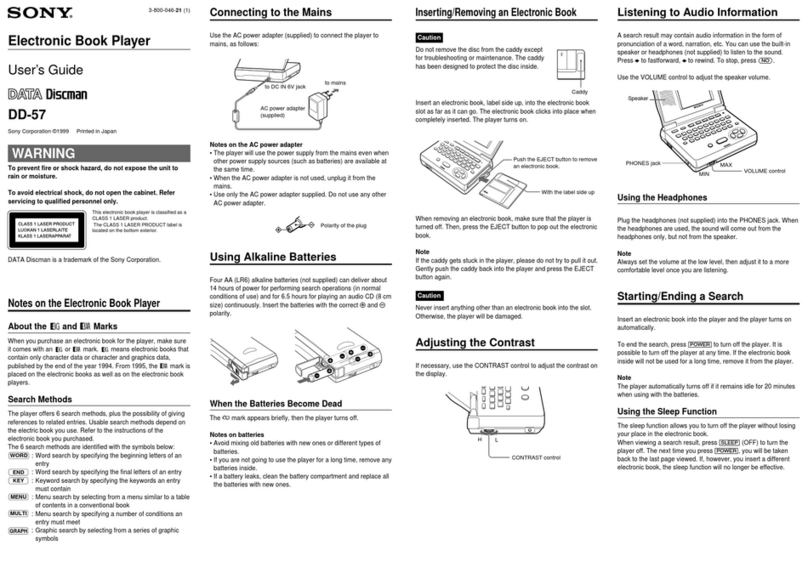
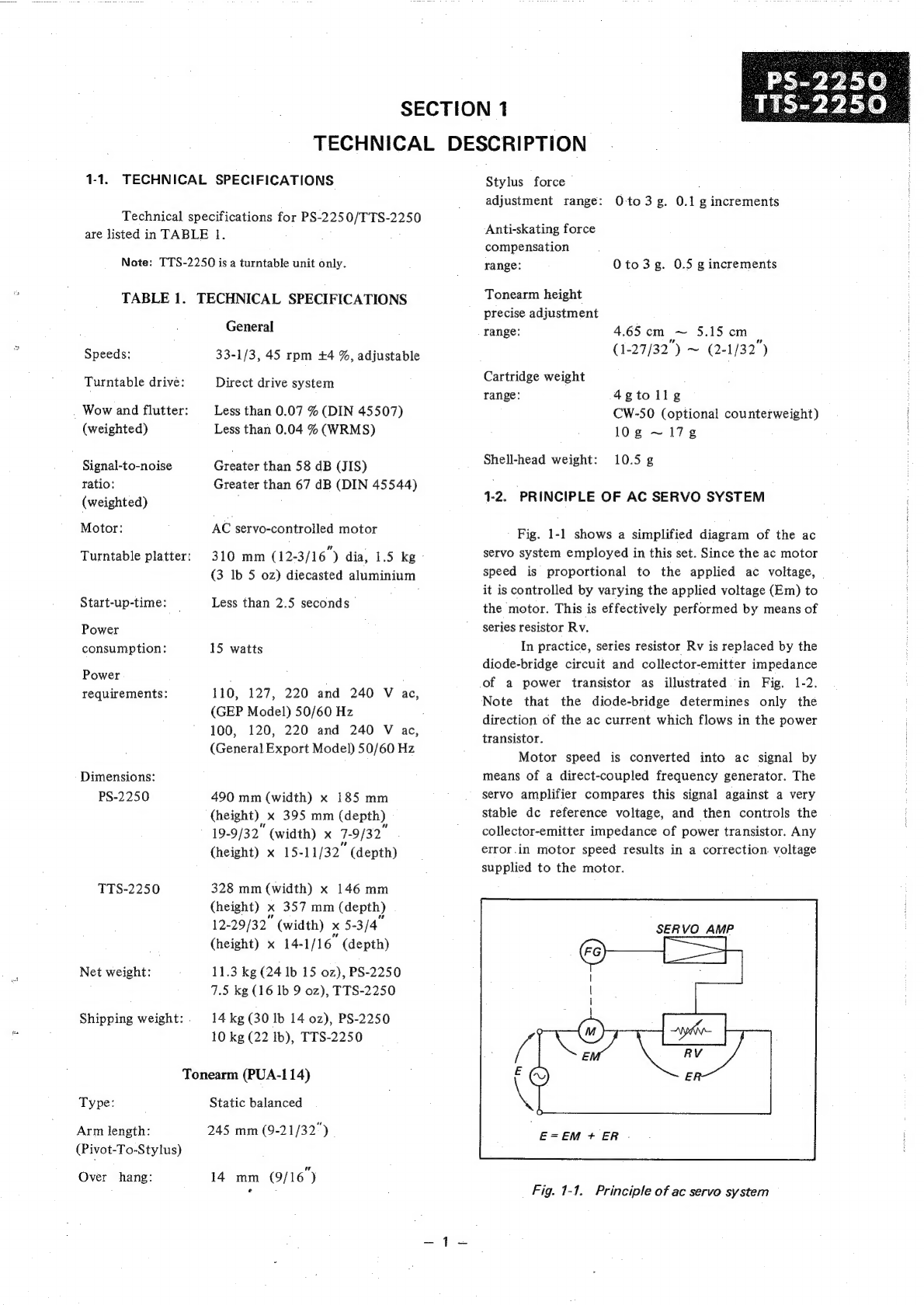
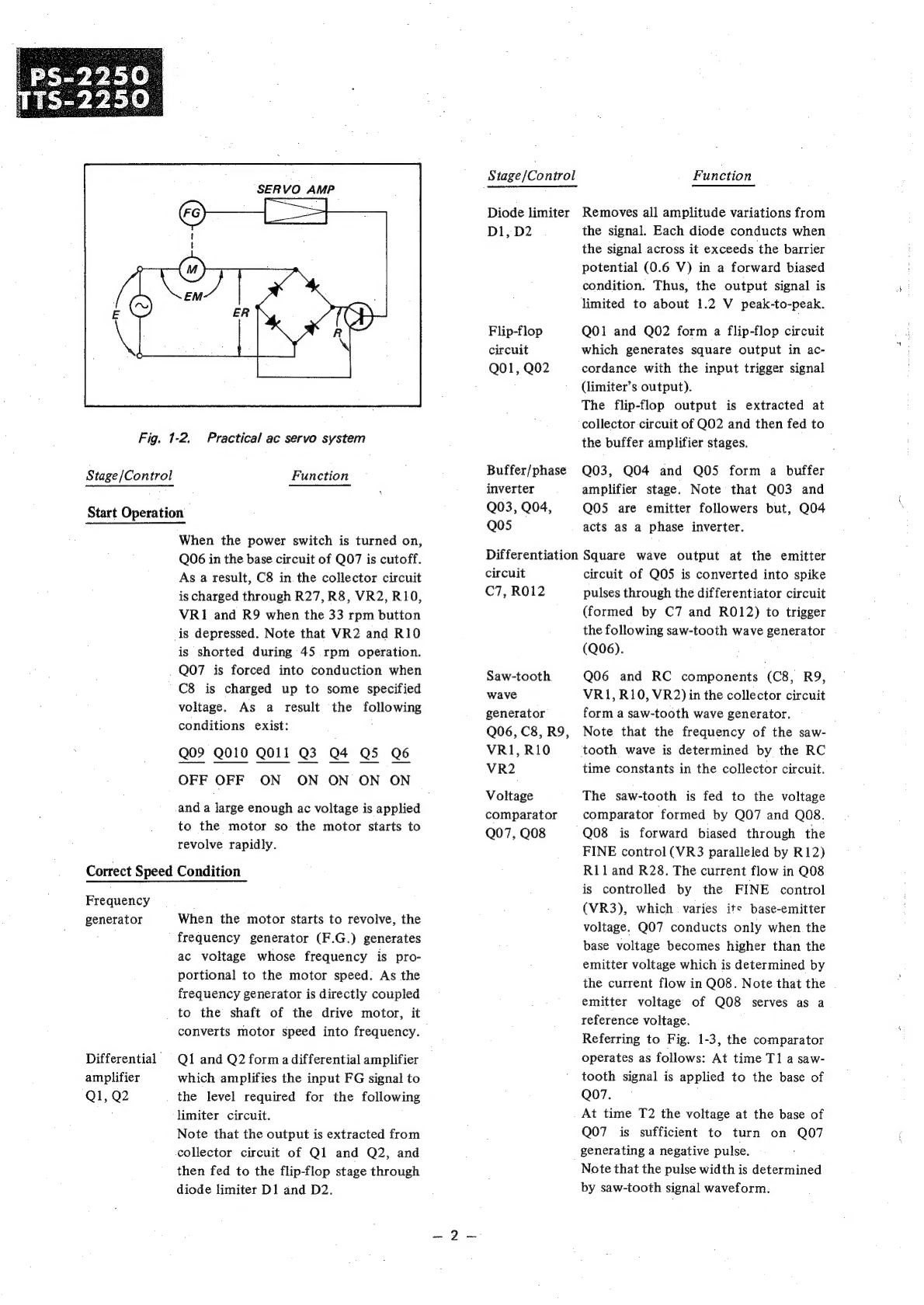
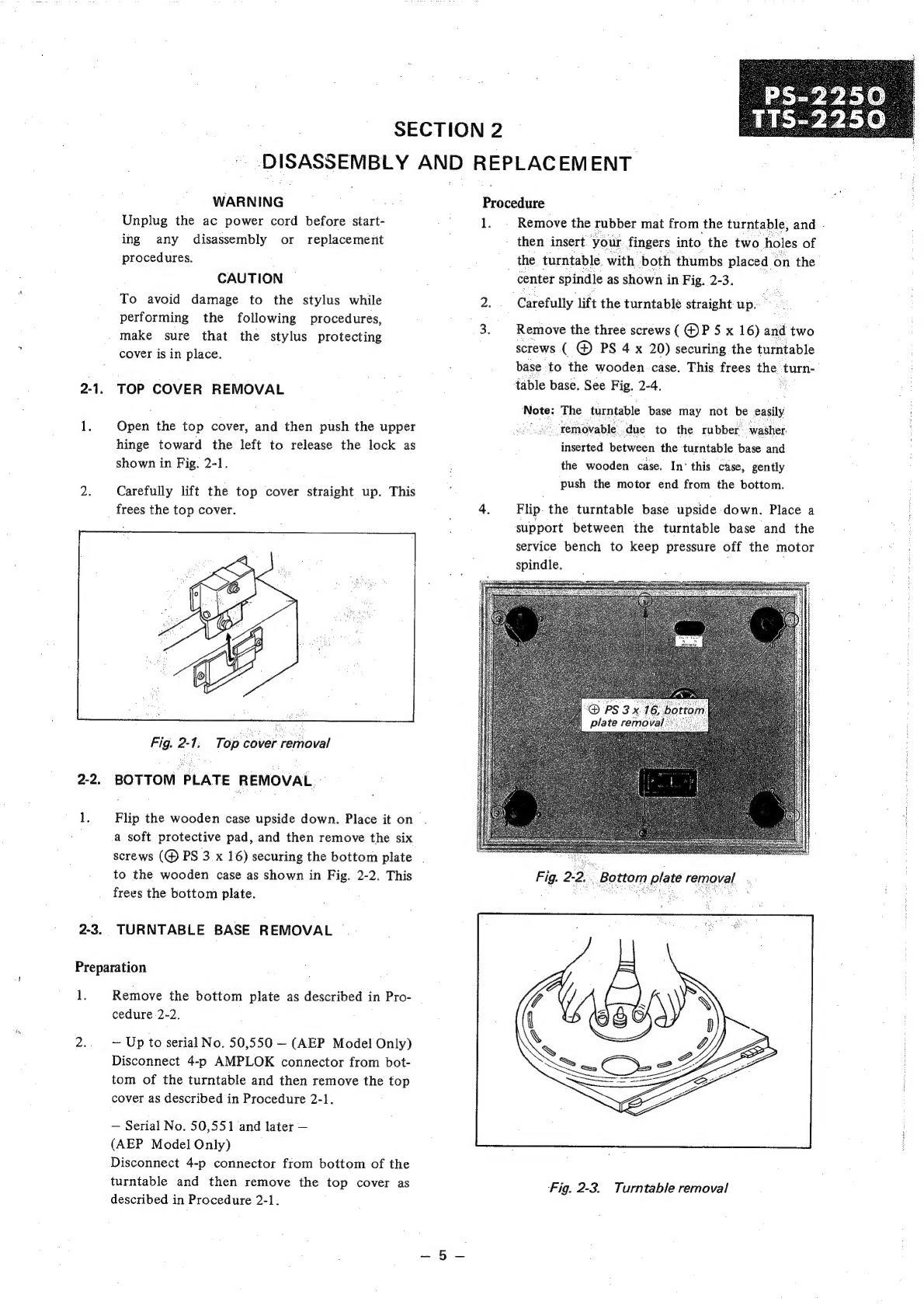
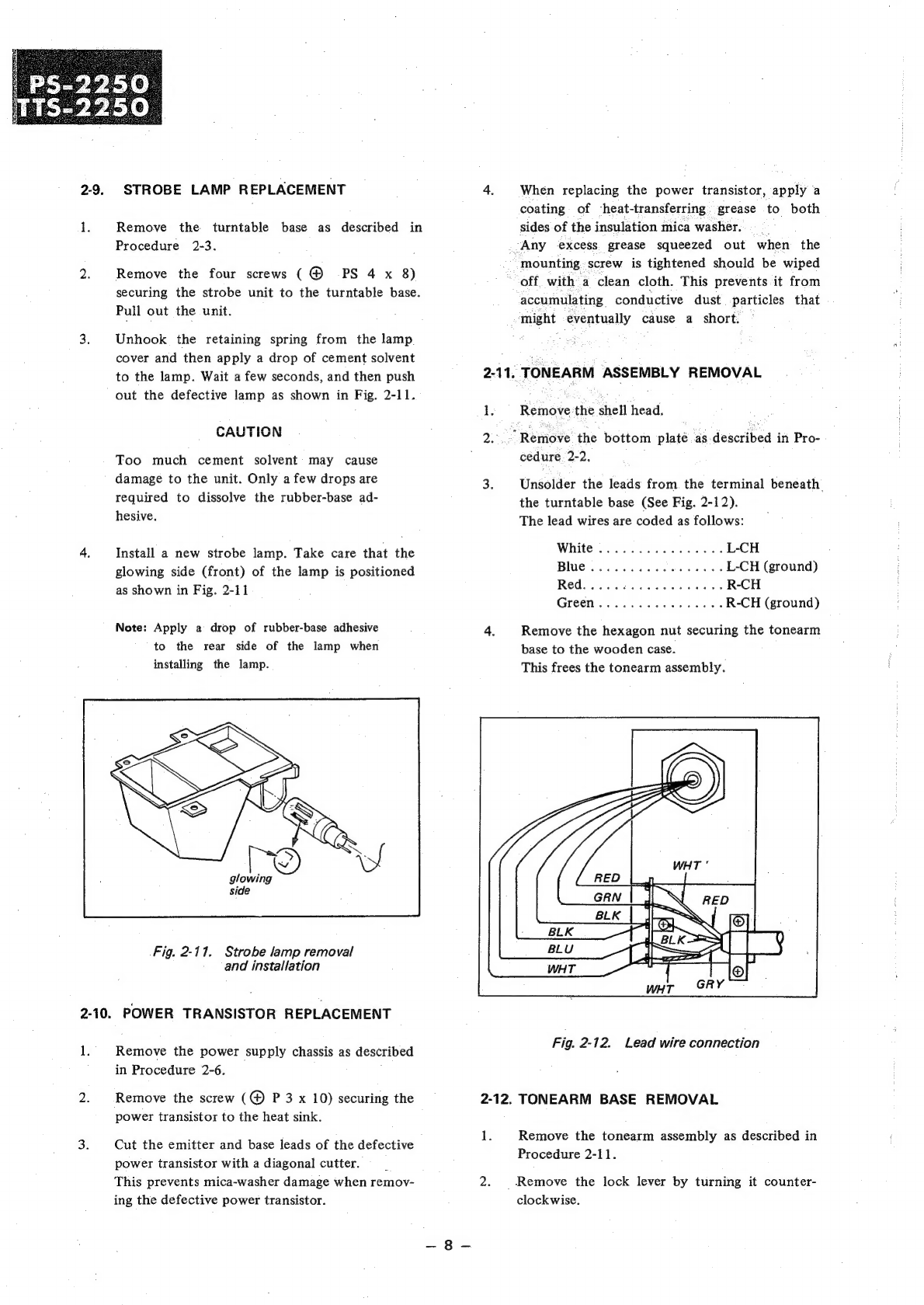
Sony PS-2250 User manual
Other Sony Turntable manuals

Sony
Sony XD-AX10 User manual

Sony
Sony PS-J11 Primary User manual

Sony
Sony PS-LX2C User manual

Sony
Sony PS-1350 User manual

Sony
Sony Walkman WM-EX162 User manual

Sony
Sony DVW-522 User manual
Sony
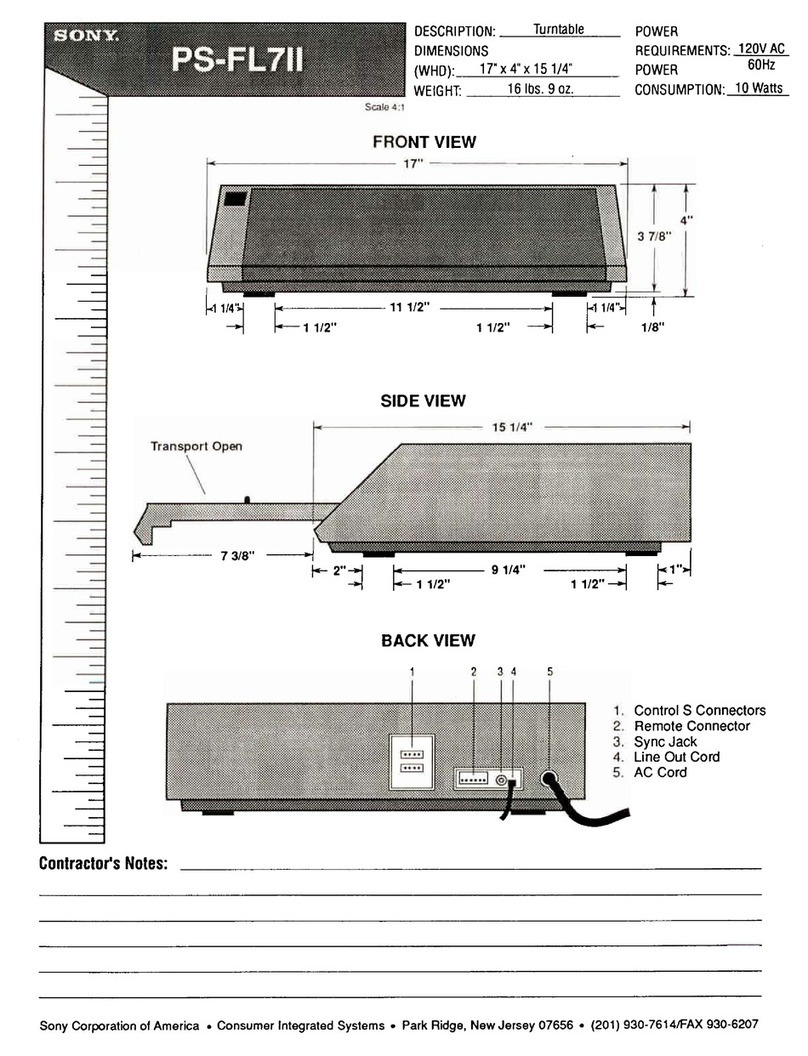
Sony PS-FL7II - Stereo Turntable Parts list manual

Sony
Sony D-F181 - Fm/am Portable Cd Player User manual
Sony
Sony WALKMAN NW-WM1A User manual
Sony
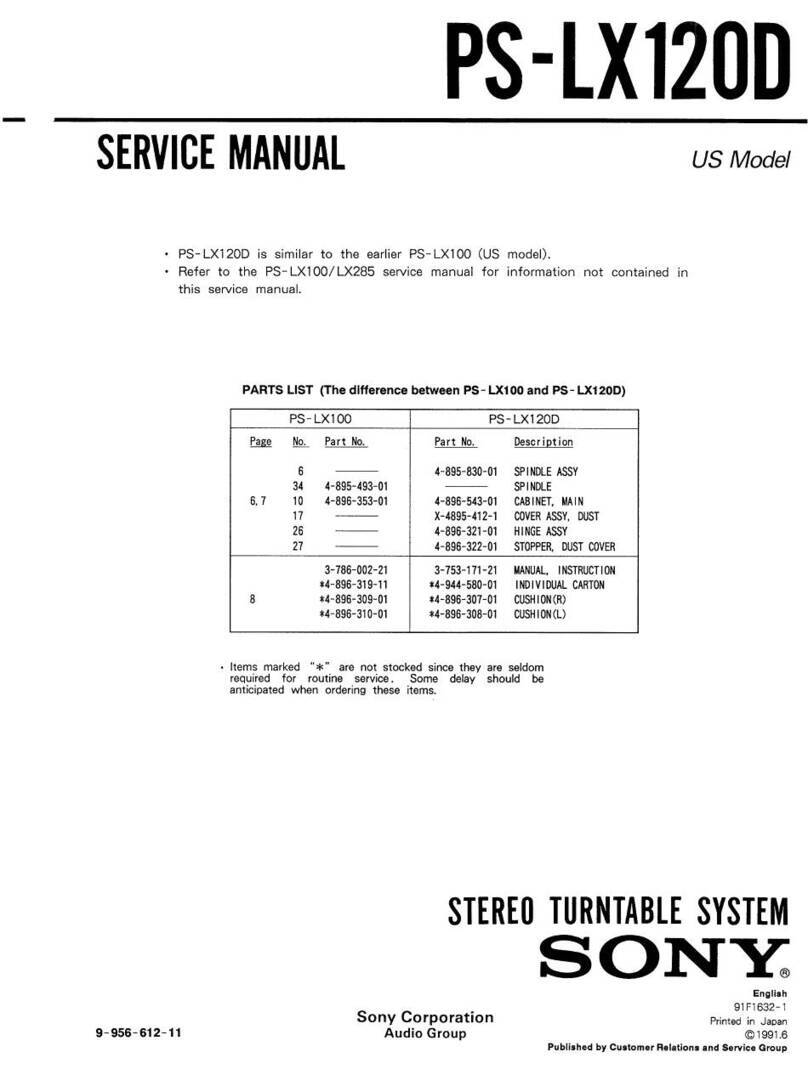
Sony PS-LX120D User manual

Sony
Sony DD-10EX User manual

Sony
Sony PS-LX110 User manual

Sony
Sony PS-LX250H User manual

Sony
Sony PS-DJ9000 - Stereo Turntable System User manual

Sony
Sony PS-LX55 User manual
Sony
Sony PS-LX76 User manual

Sony
Sony PS-F5 User manual

Sony
Sony MDH-10 User manual

Sony
Sony PS-LX110 User manual

Sony
Sony NW-A45 User manual