Calibration system overview RM0345
6/38 Doc ID 024080 Rev 3
1 Calibration system overview
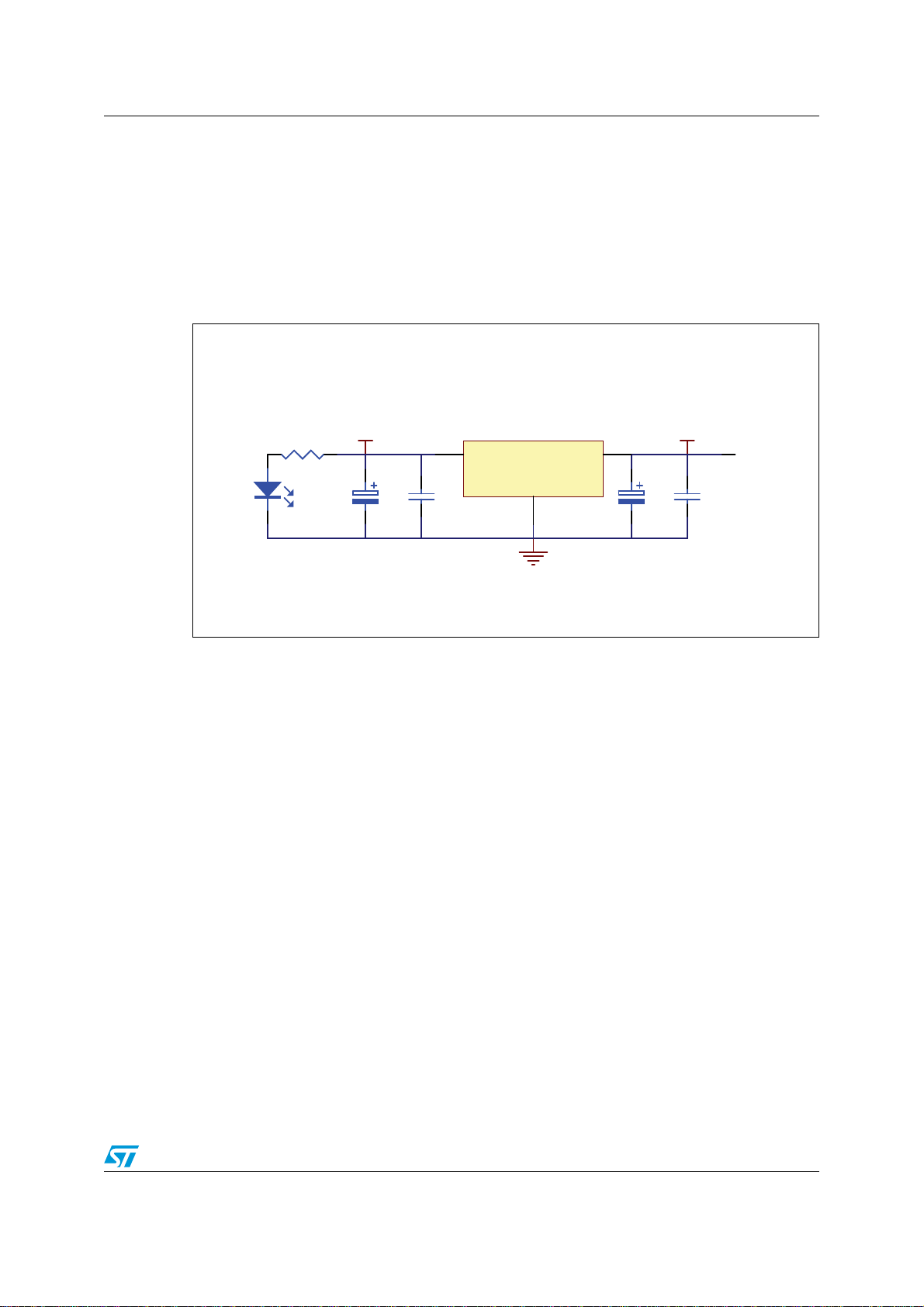
The Calibration Adapter board features 2 Mbytes of SRAM in order to substitute to the
SPC563M64xx internal Flash during calibration.
A voltage regulator is also integrated upon the board to generate, from selectable 5 V
source, the 3.3 V voltage for the RAM and the calibration bus interface.
Development connector (Mictor AMP38) is providing the interface for the debug and trace
tools.
A calibration connector (ERNI 154819) is providing an interface optimized for calibration
usage.
A high speed CAN transceiver is connected to the FlexCAN of the mcu device.
The components chosen in the design of this board are automotive qualified to allow system
evaluation over the full automotive evaluation range (-40 °C to 125 °C).
1.1 Features overview
calibration systems include these distinctive features:
●
Use 100% production silicon, ensuring full hardware and software compatibility
between production and calibration systems;
●
Support LQFP144 MCU production package allowing calibration systems to be built
without requiring modifications to the standard production system housing;
●
2MByte static RAM organized as 1024K words by 16 bits;
●
On-board latch providing a 16-bit de-multiplexed bus interface from the SPC563M64xx
16-bit multiplexed calibration interface;
●
Support for Nexus-based debug tools even if application PCB does not include Nexus
connector;
●
Nexus functionality with 12 Message Data Out (MDO) signals;
●
Support for full-feature calibration tools, via availability of comprehensive set of device
signals available on the connectors;
●
ERNI 154819 connector optimized for calibration;
●
High speed CAN transceiver with signals protection;
●
Allows system calibration without impacting standard MCU I/O resources;
●
Allows system calibration regardless of availability of standard MCU external bus;
●
Uses tried and tested technology.