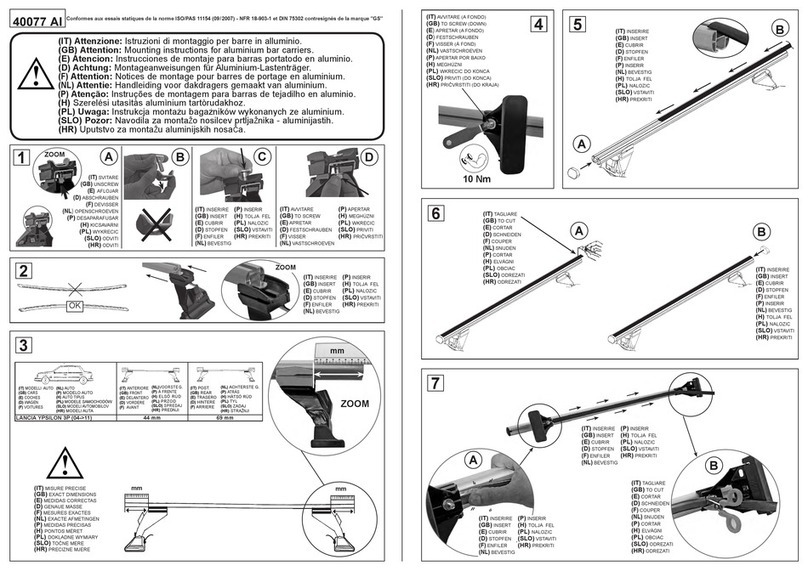
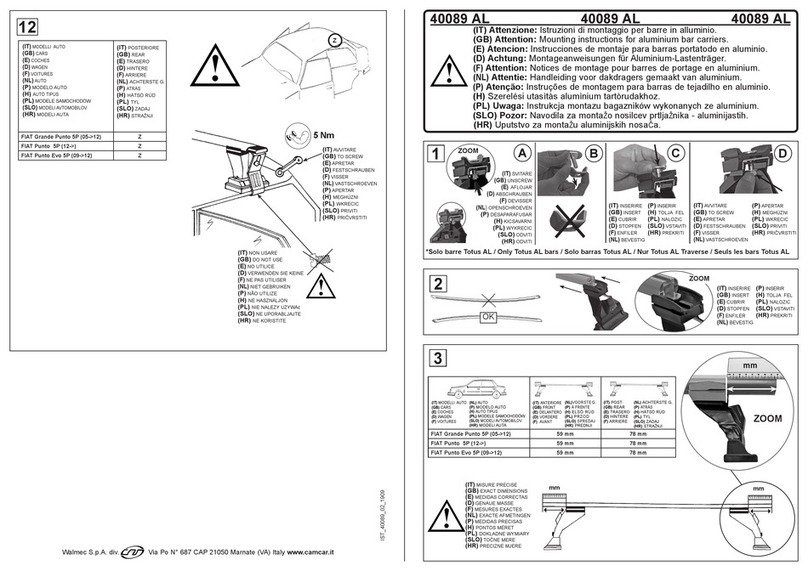
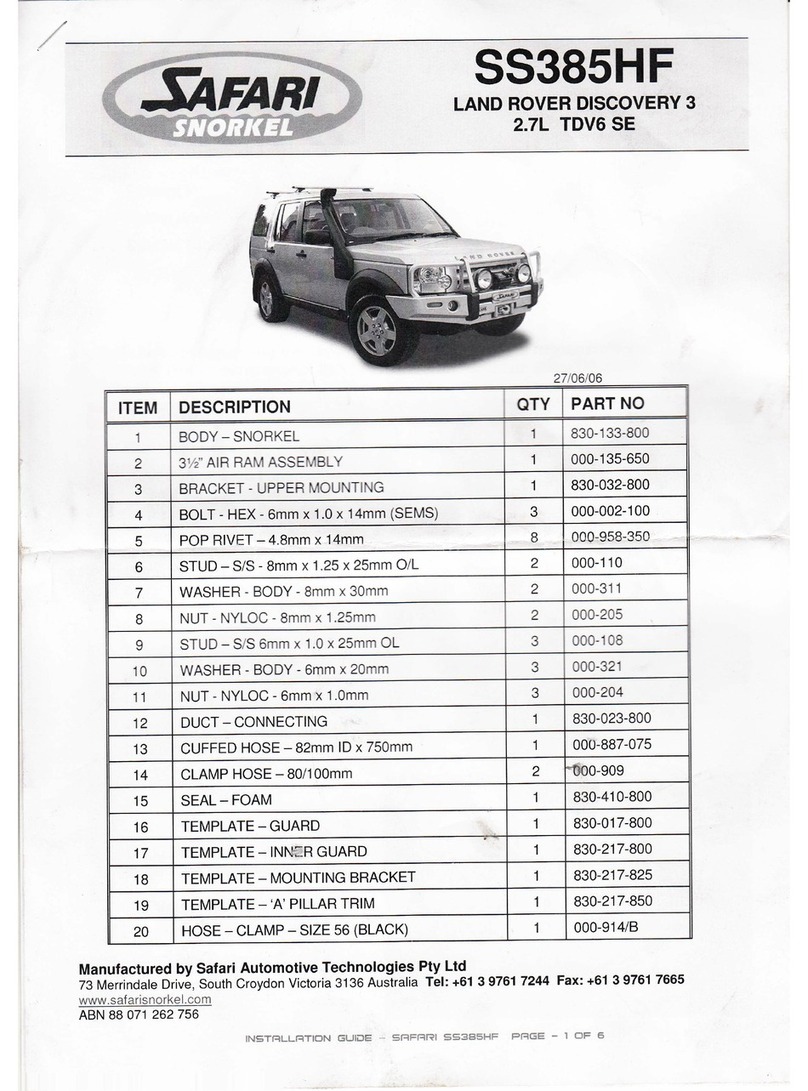
8 9
2.6 OBD II Definitions
Power-train Control Module (PCM) - OBD n
terminology for the on-board Computer that
controls engine and drive train.
Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL) -
Malfunction Indicator Light (Service Engine
Soon, Check Engine) is a term used for the
light on the instrument panel. It is to alert the
driver and/or the repair technician that there
is a problem with one or more of vehicle’s
systems and may cause emissions to exceed
federal standards . If the MIL illuminates
with a steady light, it indicates that a problem
has been detected and the vehicle should be
serviced as soon as possible. Under certain
conditions, the dashboard light will blink or
flash. This indicates a severe problem and
flashing is intended to discourage vehicle
operation. The vehicle onboard diagnostic
system can not turn the MIL off necessary re
airs are completed or the condition no longer
exists.
DTC - Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) that
identify which section of the emission control
system has malfunctioned.
Enabling Criteria -Also termed Enabling
Conditions. They are the vehicle-specific
events or conditions that must occur within
the engine before the various monitors will
set» or run. Some monitors require the
various to follow a prescribed “drive cycle”
routine as part of the enabling criteria . Drive
cycles vary among vehicles and for each
monitor in any particular vehicle .
OBD Drive Cycle — A specific mode of
vehicle operation that provides conditions
required set all the readiness monitors
completing and OBD II drive cycle is to force
the vehicle to run its onboard diagnostics.
Some from the PCM’s memory or after the
battery has been disconnected。 Running
through a vehicle’s complete drive cycle will
“set” the readiness monitors so that future
faults can be detected。Drive cycles vary
depending on the vehicle and the monitor
that needs to be reset。 For vehicle specific
drive cycle, consult the vehicle’s Owner’s
Manual.
Freeze Frame Data — When an emissions
related fault occurs, the OBD II system not
only sets a code but also records a snapshot
of the vehicle operating parameters to help
in identifying the problem. This set of values
is referred to as Freeze Frame Data and may
include important engine parameters such as
engine RPM, vehicle speed, airflow, engine
load, fuel pressure, fuel trim value> engine
coolant temperature, ignition timing advance,
or closed loop status.
2.7 OBD II Modes of Operation
Here is a basic introduction to the OBD n
communication protocols Mode byte : The
first byte in the stream is the mode number.
There are 10 modes for diagnostic requests
. The first byte in the response data bytes
is this same number plus 64.For example,a
mode 1 request would have the first data
byte =1, and the response would have the
first data byte=65.
Mode $01 - Identifies the Power train
information and shows current data available
to the scan tool. This data includes: DTC set,
status of on-board tests, and vehicle data
such as engine RPM, temperatures, ignition
advance, speed, air flow rates, and closed
loop status for fuel system.
Mode $02 - Displays Freeze Frame data.
Same data as in mode 1, but it was captured
and stored when a malfunction occurred and
a DTC was set. Some of the PIDs for mode
one are not implemented in this mode.
Mode $03 - Displays the type of power train
or emission related DTCs stored by a 5 digit
code identifying the faults. There may be
more than one response message if there
are more trouble codes than will fit in the
data bytes of the response message, or
it there are more than one ECU computer
responding.
Mode $04 - Used to clear DTCs and Freeze
Frame data. This clears all diagnostic trouble
codes that may be set including freeze frame
data and readiness monitors.
Mode $05 - Oxygen Sensor Test Results. This
mode displays the oxygen sensor monitor
screen and the test results gathered about
the oxygen sensor.
There are ten numbers available for
diagnostics:
1. $01 Rich-to-Lean 02 sensor threshold
voltage.
2. $02 Lean-to-Rich 02 sensor threshold
voltage.
3. $03 Low sensor voltage threshold for
switch time measurement.
4. $04 High sensor voltage threshold for
switch time measurement.
5. $05 Rich-to-Rich switch time in ms.
6. $06 Lean-to-Rich switch time in ms.
7. $07 Minimum voltage for test.
8. $08 Maximum voltage for test.
9. $09 Time between voltage transitions in
ms.
Mode $06 - Non-continuously Monitored
Systems test results. There are typically
a minimum value, a maximum value, and
a current value for each non-continuous
monitor. This data is optional, and it is
defined by a given vehicle maker if it’s used.
Mode $07 - Request for DTCs (pending)
from Continuously Monitored Systems after
a single driving cycle has been performed to
determine if repair has fixed a problem. This
is used by service technicians to verify repair
was performed properly and after clearing
diagnostic trouble codes.
Mode $08 - This special Control Mode
requests control of the on-board system,
test or component bi-directionally (where
applicable). This mode is manufacturer
specific.