BQ25157 I2C Controlled 1-Cell 500-mA Linear Battery Charger With 10-nA Ship Mode,
Power Path With Regulated System (PMID) Voltage, ADC, LDO and 6.2-V OVP
1 Features
• Linear battery charger with 1.25-mA to 500-mA
fast charge current range
– 0.5% Accurate I2C programmable battery
regulation voltage ranging from 3.6 V to 4.6 V in
10-mV steps
– Configurable termination current supporting
down to 0.5 mA
– 20-V Tolerant input with typical 3.4-V to 6.2-V
input voltage operating range
– Programmable thermal charging profile, fully
configurable hot, warm, cool and cold
thresholds
• Power Path management for powering system and
charging battery
– Dynamic power path management optimizes
charging from weak adapters
– Advanced I2C control allows host to disconnect
the battery or adapter as needed
• I2C Configurable load switch or up to 150-mA LDO
output
– Programmable range from 0.6 V to 3.7 V in
100-mV steps
• Ultra low Iddq for extended battery life
– 10-nA Ship mode battery Iq
– 400-nA Iq While powering the system (PMID
and VDD on)
• One push-button wake-up and reset input with
adjustable timers
– Supports system power cycle and HW reset
• 16-Bit ADC
– Monitoring of charge current, battery thermistor
and battery, input and system (PMID) voltages
– General purpose ADC input
• Always on 1.8-V VDD LDO supporting loads up to
10 mA
• 20-Pin 2-mm x 1.6-mm CSP package
• 12-mm2 Total solution size
2 Applications
•Headsets, earbuds and hearing aids
•Smart watches and smart trackers
•Wearable fitness and activity monitors
•Blood glucose monitors
3 Description
The BQ25157 is a highly integrated battery charge
management IC that integrates the most common
functions for wearable, portable and small medical
devices, namely a charger, a regulated output voltage
rail for system power, ADC for battery and system
monitoring, a LDO, and push-button controller. The
BQ25157 has the Input Supply Over Voltage
Threshold (VOVP) threshold set to 6.2 V.
The BQ25157 IC integrates a linear charger with
Power Path that enables quick and accurate charging
for small batteries while providing a regulated voltage
to the system. The regulated system voltage (PMID)
output may be configured through I2C based on the
recommended operating condition of downstream IC's
and system loads for optimal system operation.
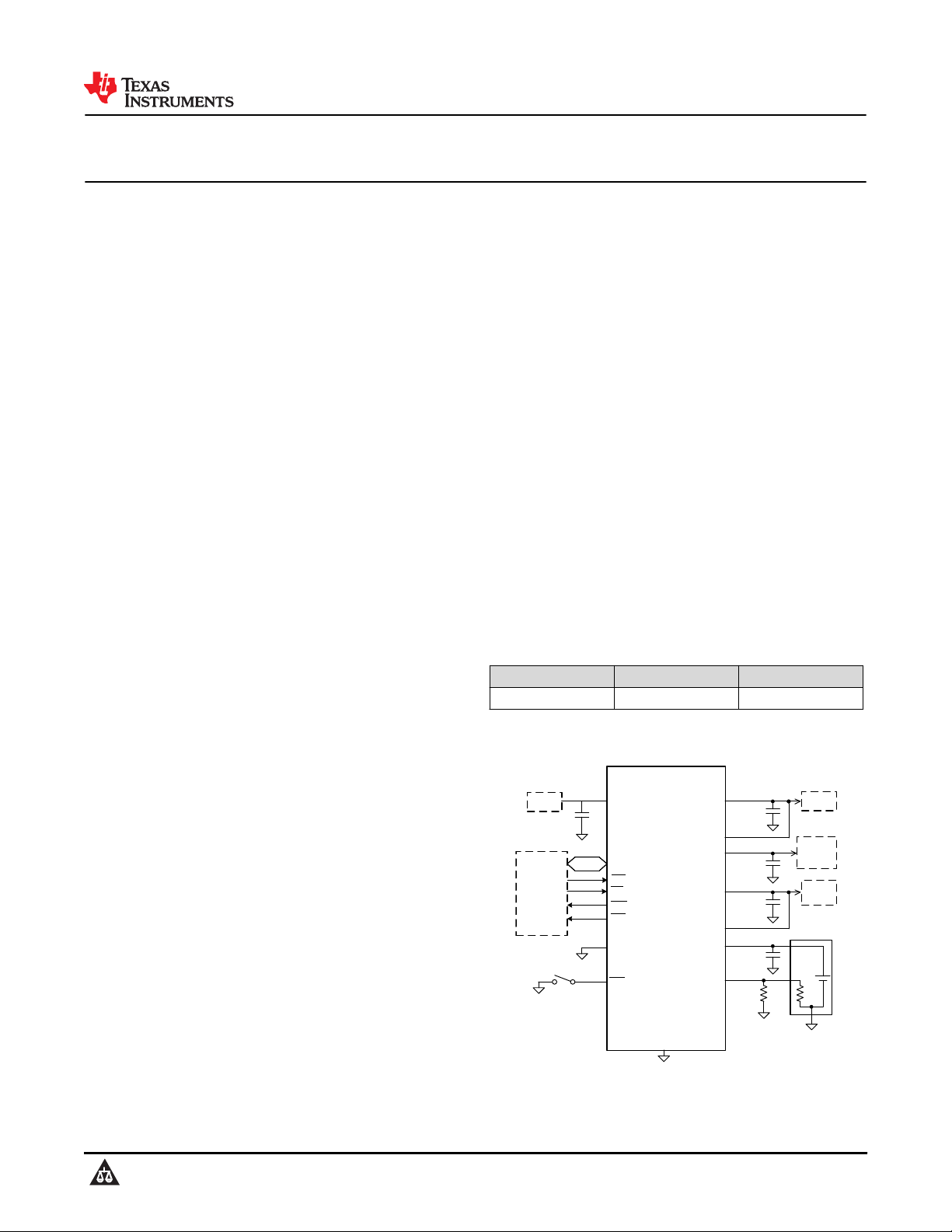
Device Information (1)
PART NUMBER PACKAGE BODY SIZE (NOM)
BQ25157 DSBGA (20) 2.00 mm x 1.60 mm
(1) For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at
the end of the data sheet.
BQ25157
VINLS
PMID
LS/LDO
VDD
BAT
TS +
±
NTC
GND
IN
VIO
Host
USB
I2C Bus
<150mA
Load
<10mA
Load
System
ADCIN
MR
PG
INT
LP
CE
C4
C5
C3
C2
C1
Simplified Schematic
www.ti.com
BQ25157
SLUSEC5 – DECEMBER 2020
Copyright © 2020 Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Document Feedback 1
Product Folder Links: BQ25157
BQ25157
SLUSEC5 – DECEMBER 2020
An IMPORTANT NOTICE at the end of this data sheet addresses availability, warranty, changes, use in safety-critical applications,
intellectual property matters and other important disclaimers. PRODUCTION DATA.