Texas Instruments ADS1282 User manual
Other Texas Instruments Media Converter manuals

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments DAC 3202 Series User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments UCC28782EVM-030 User manual
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TVP5147M1PFP Installation and user guide

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments DAC 300 Series User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments HPA070 User manual
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TPS549B22EVM-847 User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments LM5157 Q1 Series User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TMS320 Series User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments ADS5102 EVM User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments ADS1230REF User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TPS40003 User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments MSC1211 User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments ADS79 EVM-PDK Series User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TPS543C20EVM-054 User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments EUROTEXT CF70200 User manual
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TPS62840-1YBGEVM56 User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TPS61092 User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TPS6103 Series User manual
Texas Instruments
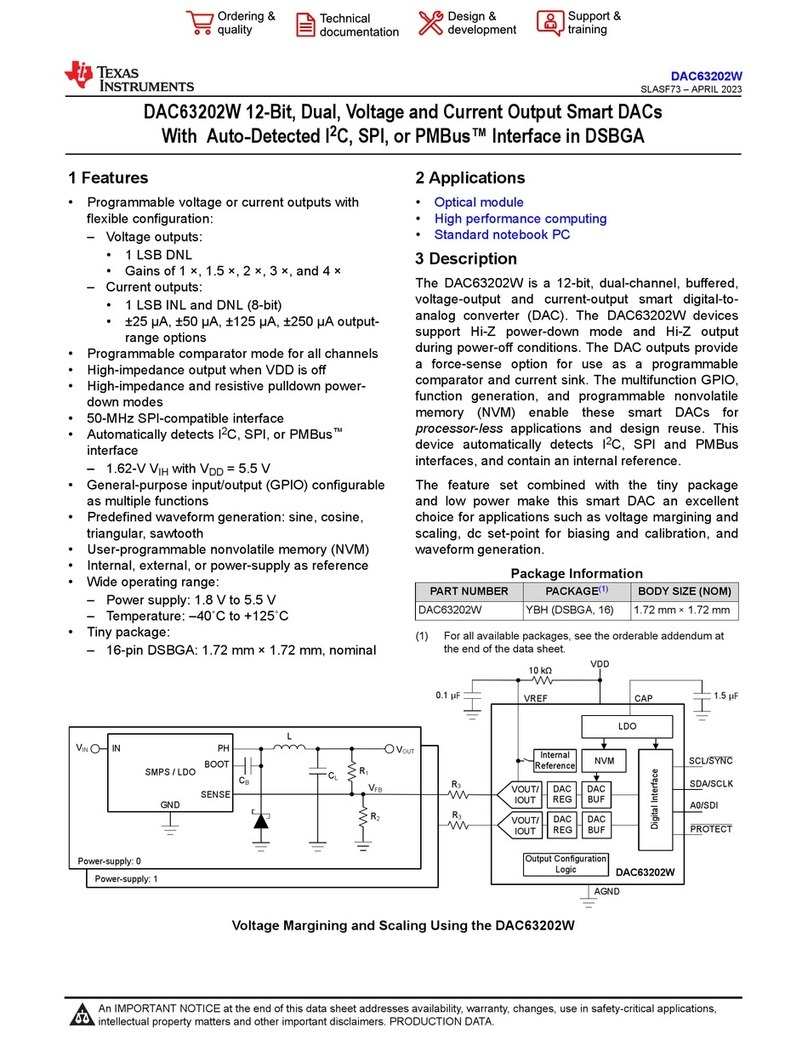
Texas Instruments DAC63202W User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TPS54320 User manual






























