Texas Instruments TMS320DM357 User manual
Other Texas Instruments Microcontroller manuals
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments CC110 Series Guide

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TIDA-00204 User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Errata MSP430FG6426 User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments CC1110 User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments MSP430 series User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments MSP430F67621 User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments PGA460-Q1 User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments MSP430F67471 User manual
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments LOGIC PD ZOOM DM3730 SOM-LV User manual
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments MSP430F6730 User manual
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments CC3220 User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments CC3235MODSF SimpleLink User manual
Texas Instruments
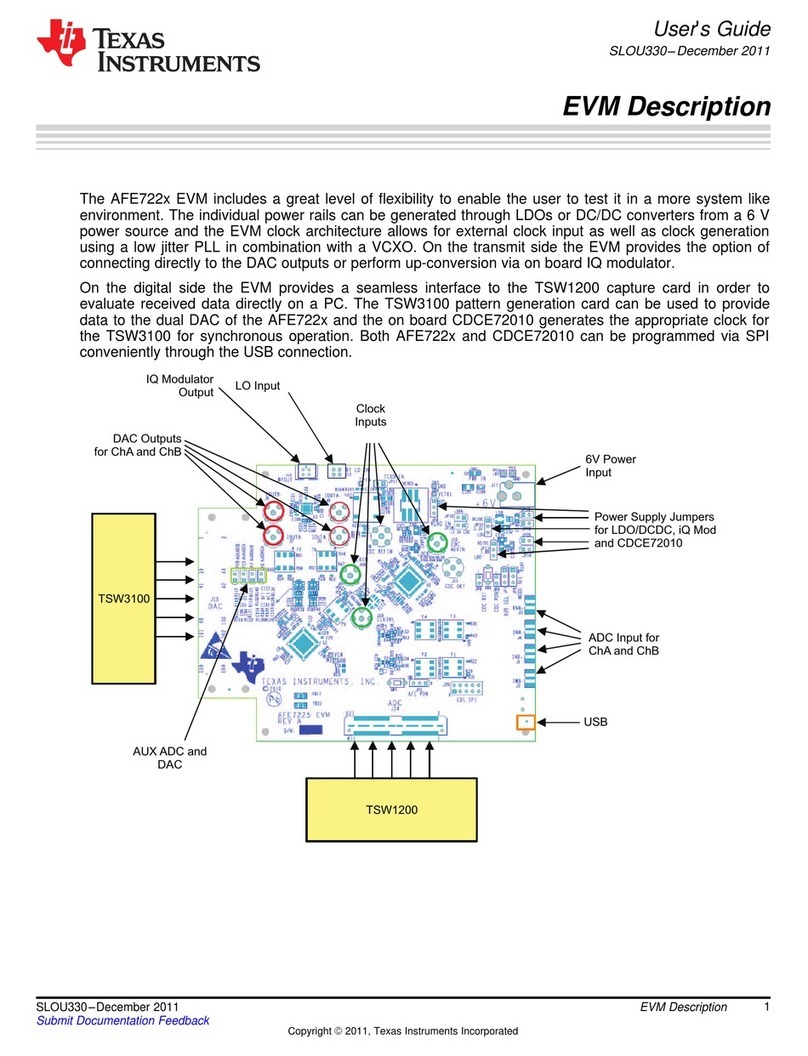
Texas Instruments AFE722 Series User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments LaunchPad MSP-EXP430F5529LP User manual
Texas Instruments
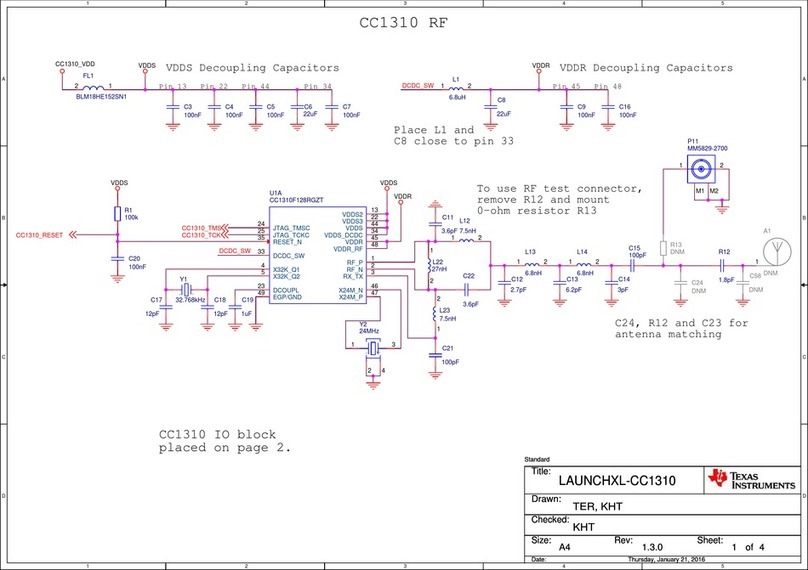
Texas Instruments LAUNCHXL-CC1310 Manual
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments SimpleLink Ethernet MSP432E401Y User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments CC1110 Programming manual
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments C2000 LAUNCHXL-F280049C User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments REF70EVM User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments MSP430F6720A User manual
Popular Microcontroller manuals by other brands

Novatek
Novatek NT6861 manual

Espressif Systems
Espressif Systems ESP8266 SDK AT Instruction Set

Nuvoton
Nuvoton ISD61S00 ChipCorder Design guide

STMicrolectronics
STMicrolectronics ST7 Assembler Linker user manual

Lantronix
Lantronix Intrinsyc Open-Q 865XR SOM user guide

NEC
NEC 78GK0S/K 1+ Series Application note