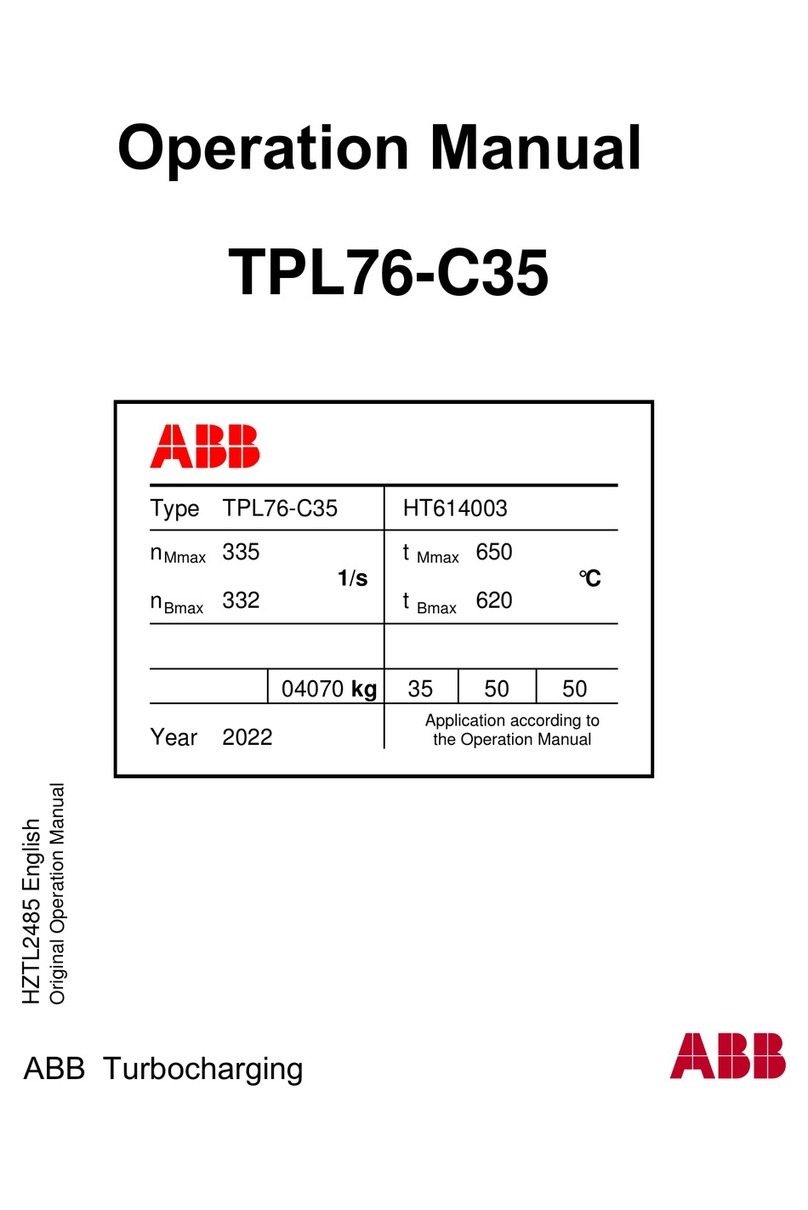
2
TRAD 350 SO DIGIT
Contents
Contents ........................................................................ "2
Ordering spare parts .................................................... "2
Guarantee ...................................................................... "2
Machine certification and identification marking .... "3
CHAPTER 1
Reference to accident-prevention regulations .......... "4
1.1 -Advice for the operator ........................................... " 4
1.2 -Location of shields against accidental contact with
the tool .................................................................... " 4
1.3 -Electrical equipment according to European
Standard "CENELEC EN 60 204-1" (1992) ........... " 4
1.4 -Emergencies according to European Standard
"CENELEC EN 60 204-1" (1992) ........................... " 4
CHAPTER 2
Recommendations and advice for use ....................... "4
2.1 -Recommendations and advice for using the machine . " 4
CHAPTER 3
Technical characteristics ............................................. "5
3.1 - Table of cutting capacity and technical details
standard model ....................................................... " 5
CHAPTER 4
Machine dimensions - Transport - Installation
Dismantling ................................................................... "5
4.1 -Machine dimensions ............................................... " 5
4.2 - Transport and handling of the machine .................. " 6
4.3 -Minimum requirements for the premises
housing the machine .............................................. " 6
4.4 -Anchoring the machine ........................................... " 6
4.5 -Instructions for electrical connection ...................... " 6
4.6 -Instructions for assembly of the loose parts and
accessories ............................................................. " 6
4.7 -Disactivating the machine ....................................... " 6
4.8 -Dismantling ............................................................. " 7
CHAPTER 5
Machine functional parts ............................................. "7
5.1 -Operating head or saw frame ................................. " 7
5.2 -Vice ......................................................................... " 7
5.3 -Bed .......................................................................... " 7
CHAPTER 6
Description of the operating cycle ............................. "8
6.1 -Starting up .............................................................. " 8
6.2 - Cycle start ............................................................... " 10
6.3 - Piece-counter .......................................................... " 10
6.4 - Cutting speed ( Option ) ......................................... " 11
6.5 - Manual mode ( Option ).......................................... " 11
6.6 - Emergency .............................................................. " 11
CHAPTER 7
Regulating the machine ............................................... " 12
7.1 -Blade tension assembly .......................................... " 12
7.2 - Restoring oil level on blade tightening cylinder ...... "12
7.3 -Blade guide blocks .................................................. " 12
7.4 -Vice ......................................................................... " 13
7.5 -Saw frame return stroke limiting device ................. " 13
7.6 -Cutting angle adjustment ........................................ " 13
7.7 -Blade cleaning brush .............................................. " 13
7.8 -Changing the blade................................................. " 14
7.9 -Replacing saw frame return spring ........................ " 14
CHAPTER 8
Routine and special maintenance .............................. " 14
8.1 -Daily maintenance .................................................. " 14
8.2 - Weekly maintenance .............................................. " 14
8.3 -Monthly maintenance ............................................. " 14
8.4 -Six-monthly maintenance ....................................... " 14
8.5 -Oils for lubricating coolant ...................................... " 14
8.6 - Oil disposal ............................................................. " 14
8.7 -Special maintenance .............................................. " 14
CHAPTER 9
Material classification and choice of tool .................. "15
9.1 -Definition of materials ............................................. " 15
9.2 -Selecting blade ....................................................... " 15
9.3 - Teeth pitch .............................................................. " 15
9.4 -Cutting and advance speed .................................... " 16
9.5 -Blade running-in...................................................... " 16
9.6 -Blade structure ....................................................... " 16
9.7 -Blade type ............................................................... " 16
Shape and angle of tooth ....................................... " 16
Set........................................................................... " 17
9.7.1 - Table of recommended cutting parameters .................. "17
CHAPTER 10
Machine components ................................................... " 18
10.1- List of spare parts .................................................. " 18
CHAPTER 11
Three-phase electric diagram ..................................... " 24
Hydraulic electric diagram .......................................... " 28
CHAPTER 12
Troubleshooting ............................................................ " 29
12.1-Blade and cut diagnosis ......................................... " 29
12.2-Electrical components diagnosis ............................ " 33
CHAPTER 13
Noise tests ..................................................................... " 34
Plates and labels .......................................................... " 35
Ordering spare parts
-When ordering spare parts you must state:
MACHINE MODEL
SERIAL NUMBER
PARTREFERENCE NUMBER
Without these references WE WILL NOT SUPPLYthe spares. See point 10.1 - list of spare parts -
Guarantee
-The Company guarantees that the machine, described in this manual, has been designed to meet safety requirements. As for
machine functionality, inspection has been successful.
-The machine is guaranteed for 12 months: the guarantee does not cover the electric motors, electric components, pneumatic
components or any damage due to dropping or to bad machine management, the failure to observe maintenance standards or bad
handling by the operator.
-The buyer has only the right to replacement of the faulty parts, while transport and packing costs are at his expense.
-The serial number on the machine is a primary reference for the guarantee, for after-sales assistance and for identifying the
machine for any necessity.