2
SAR460SAG
Contents
Contents ........................................................................ " 2
Ordering spare parts .................................................... " 2
Guarantee ...................................................................... " 2
Machine certification and identification marking ...... " 3
CHAPTER 1
Reference to accident-prevention regulations........... " 4
1.1 - Advice for the operator ..........................................." 4
1.2 - Location of shields against accidental contact with
the tool ...................................................................." 4
1.3 - Electrical equipment according to European
Standard "CENELEC EN 60 204-1"......................." 5
1.4 - Emergencies according to European Standard
"CENELEC EN 60 204-1"......................................." 5
CHAPTER 2
Recommendations and advice for use ....................... " 5
2.1 - Recommendations and advice for using the machine." 5
CHAPTER 3
Technical characteristics ............................................. " 6
3.1 - Table of cutting capacity and technical details
standard model......................................................." 6
CHAPTER 4
Machine dimensions -Transport - Installation
Dismantling.................................................................... " 6
4.1 - Machine dimensions .............................................." 6
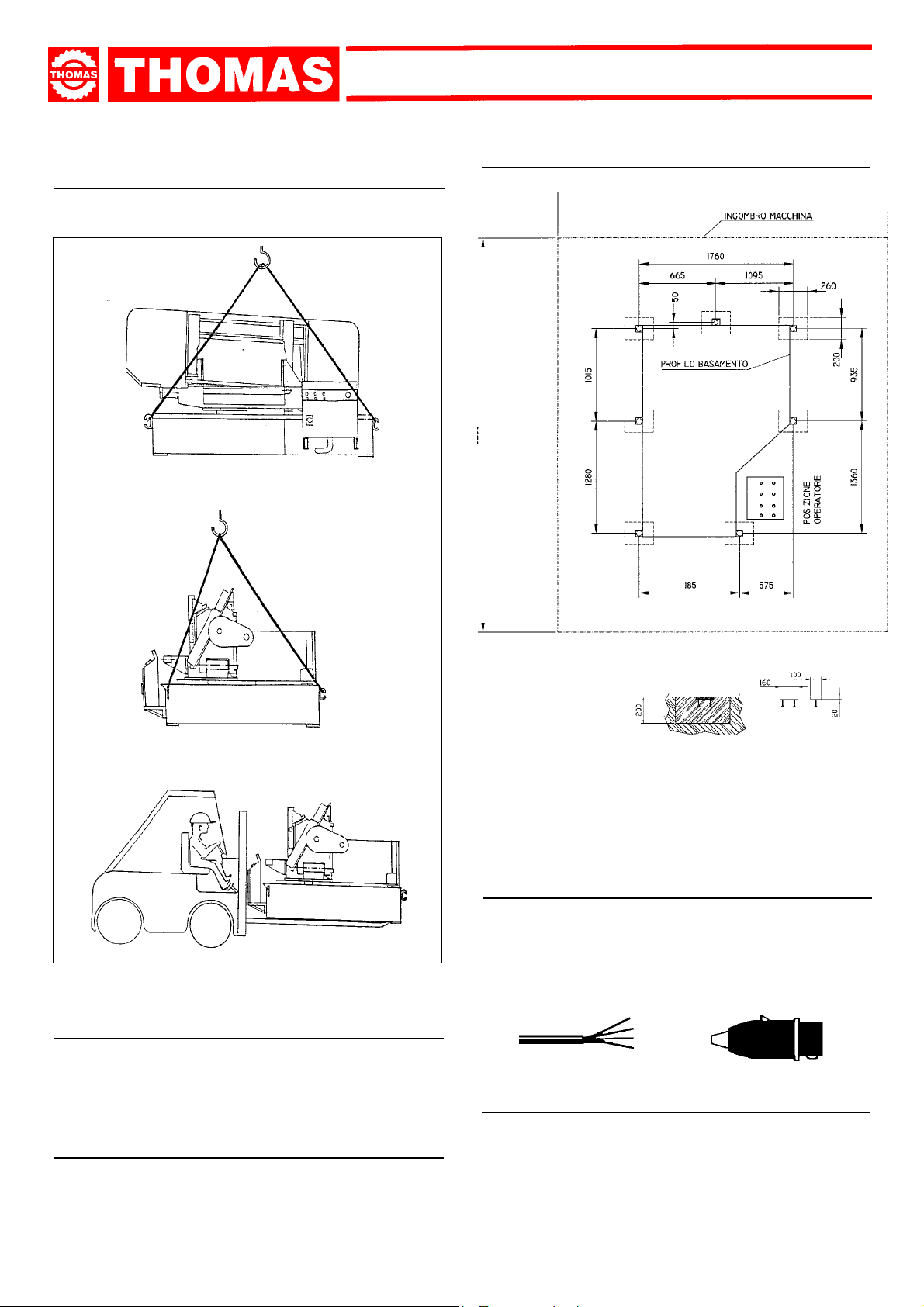
4.2 - Transport and handling of the machine ................." 7
4.3 - Minimum requirements for the premises
housing the machine.............................................. " 7
4.4 - Anchoring the machine .........................................." 7
4.5 - Instructions for electrical connection ......................" 7
4.6 - Disactivating the machine ......................................" 7
4.7 - Dismantling............................................................." 8
CHAPTER 5
Machine functional parts .............................................. " 8
5.1 - Operating head or sawframe.................................." 8
5.2 - Vice........................................................................." 8
5.3 - Bed ........................................................................." 8
CHAPTER 6
Description of the operating cycle .............................. " 9
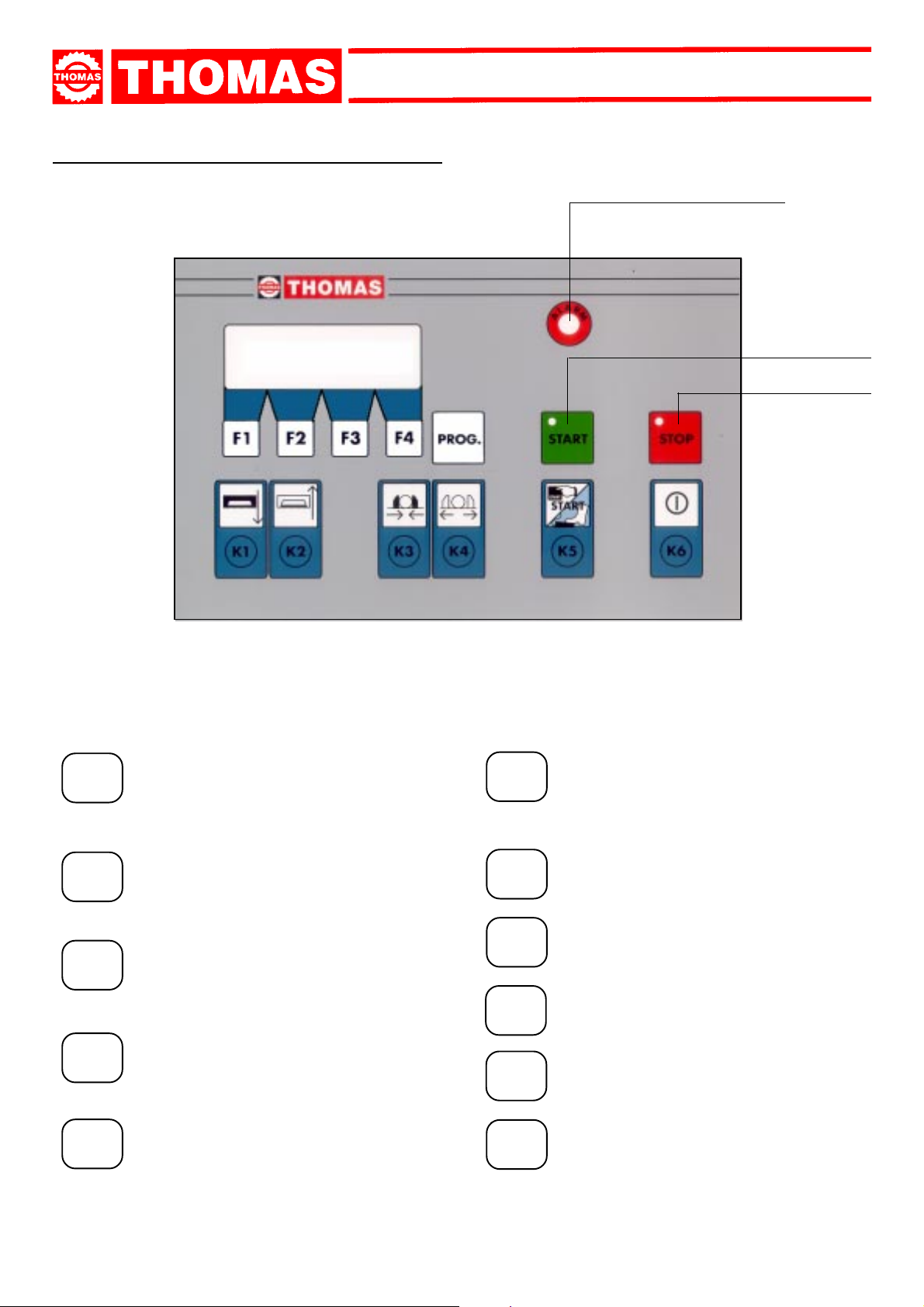
6.1 - Starting up .............................................................." 9
6.2 - Cutting speed INVERTER ......................................" 9
6.3 - Piece-counter ........................................................." 10
6.4 - Cutting cycle ..........................................................." 10
6.5 - Sawframe return stroke limit (option) ....................." 10
6.6 - Alarm ......................................................................" 12
Orderingspareparts
- Whenorderingsparepartsyoumuststate:
MACHINE MODEL
SERIAL NUMBER
PART REFERENCE NUMBER
WithoutthesereferencesWEWILLNOTSUPPLYthespares.Seepoint10.1-listofspareparts-
Guarantee
- TheCompanyguaranteesthatthemachine,describedinthismanual,hasbeendesignedtomeetsafetyrequirements.Asformachinefunctionality,inspectionhasbeen
successful.
- Themachineisguaranteedfor12months:theguaranteedoesnotcovertheelectricmotors,electriccomponents,pneumaticcomponentsoranydamageduetodropping
ortobadmachinemanagement,thefailuretoobservemaintenancestandardsorbadhandlingbytheoperator.
- Thebuyerhasonlytherighttoreplacementofthefaultyparts,whiletransportandpackingcostsareathisexpense.
- Theserialnumberonthemachineisaprimaryreferencefortheguarantee,forafter-salesassistanceandforidentifyingthemachineforanynecessity.
CHAPTER 7
Regulating the machine ................................................ " 12
7.1 - Blade tension assembly ........................................." 12
7.2 - Blade-guides .........................................................." 13
7.3 - Vice........................................................................." 14
7.4 - Cutting angle adjustment ......................................." 14
7.5 - Vice pressure regulation ........................................" 14
7.6 - Blade cleaning brush ............................................." 14
7.7 - Changing the blade................................................" 15
CHAPTER 8
Routine and special maintenance ............................... " 15
8.1 - Daily maintenance ................................................." 15
8.2 - Weekly maintenance.............................................." 15
8.3 - Monthly maintenance ............................................." 15
8.4 - Six-monthly maintenance......................................." 15
8.5 - Oils for lubricating coolant......................................" 15
8.6 - Oil disposal ............................................................." 15
8.7 - Special maintenance.............................................." 15
CHAPTER 9
Material classification and choice of tool.................... " 16
9.1 - Definition of materials............................................." 16
9.2 - Selecting blade......................................................." 16
9.3 - Teeth pitch .............................................................." 16
9.4 - Cutting and advance speed ..................................." 17
9.5 - Blade running-in....................................................." 17
9.6 - Blade structure ......................................................." 17
9.7 - Blade type..............................................................." 17
Shape and angle of tooth ......................................." 17
Set..........................................................................." 18
9.7.1 - Table of recommended cutting parameters .............. " 18
CHAPTER 10
Machine components ................................................... " 19
10.1- List of spare parts ................................................... " 19
CHAPTER 11
Three-phase electric diagram...................................... " 30
Hydraulic electric diagram........................................... " 35
CHAPTER 12
Troubleshooting ............................................................. " 37
12.1-Blade and cut diagnosis........................................." 37
CHAPTER 13
Noise tests..................................................................... " 41
Plates and labels ........................................................... " 42