Inclinometer
B1N360V-Q20L60-2LU3-H1151/3GD
Edition • 2014-04-11T21:43:30+02:00
1 / 4
Hans Turck GmbH & Co.KG
ñ D-45472 Mülheim an der Ruhr
ñ Witzlebenstraße 7
ñ T
el. 0208 4952-0
ñ Fax 0208 4952-264
ñ [email protected] ñ www
.turck.com
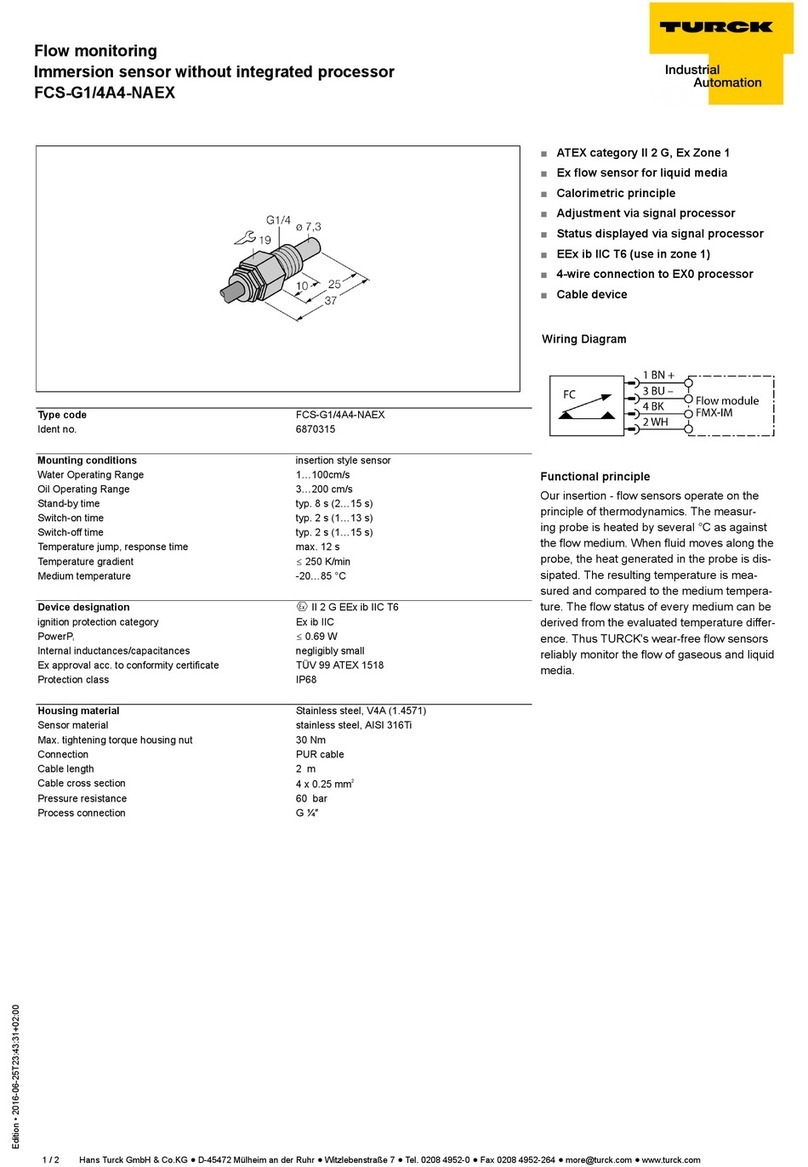
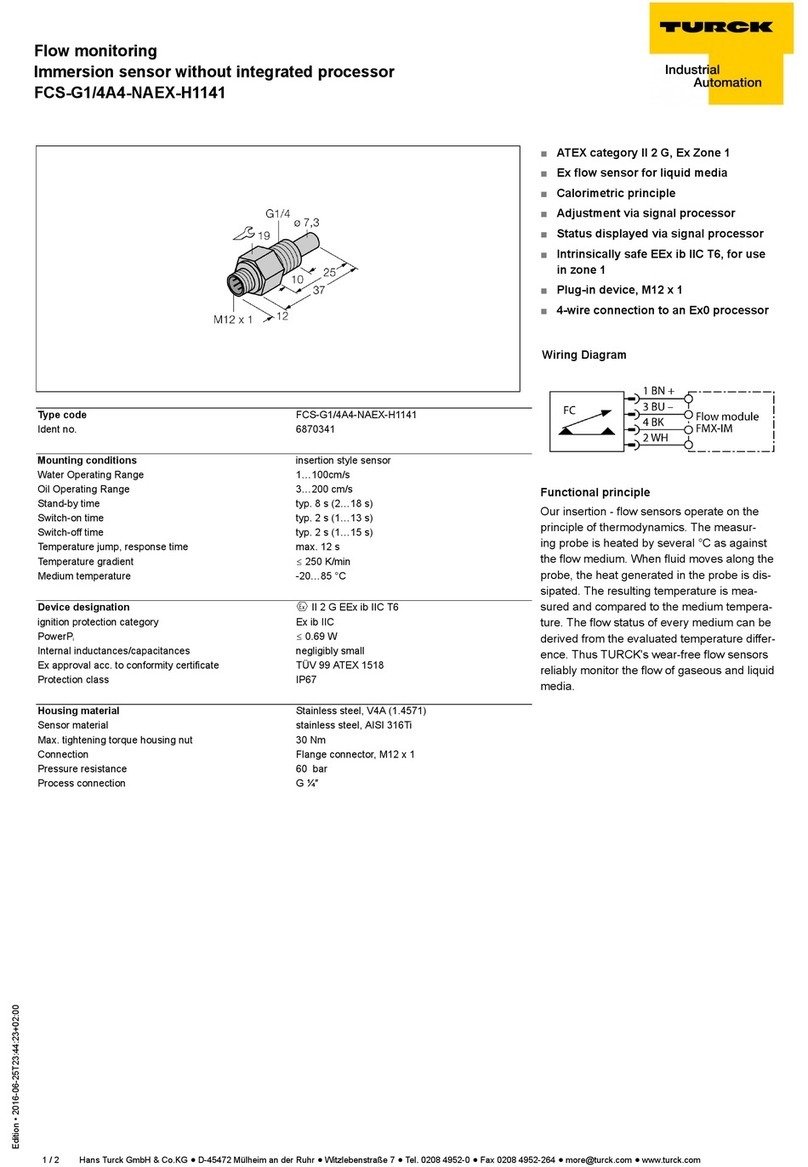
Type code B1N360V-Q20L60-2LU3-H1151/3GD
Ident no. 1534114
Measuring range 0…360°
Repeatability ð 0.2 % of measuring range |A - B|
ð 0.1 %, after warm-up 0.5 h
Temperature coefficient typical 0.03 °/K
Resolution ð 0.14 °
Ambient temperature -30…+70 °C
in the explosion hazardous area see instruction
leaflet
Operating voltage 10…30VDC
Rated insulation voltage ð 0.5 kV
Short-circuit protection yes
Wire breakage / Reverse polarity protection yes/ complete
Output function 5-wire, analog output
Voltage output 0.1…4.9V
2 outputs, one for CW and one for CCW
Load resistance voltage output ï 40 kò
Response time 0.1 s
Time for the output signal to reach 90% of the ad-
justed measuring range
Current consumption 50…105 mA (voltage-dependent)
Approval acc. to ATEX declaration of conformity TURCK Ex-12002H
X
Device designation Ex II 3 G Ex nA IIC T5 Gc/II 3 D Ex tc IIIC T85°C Dc
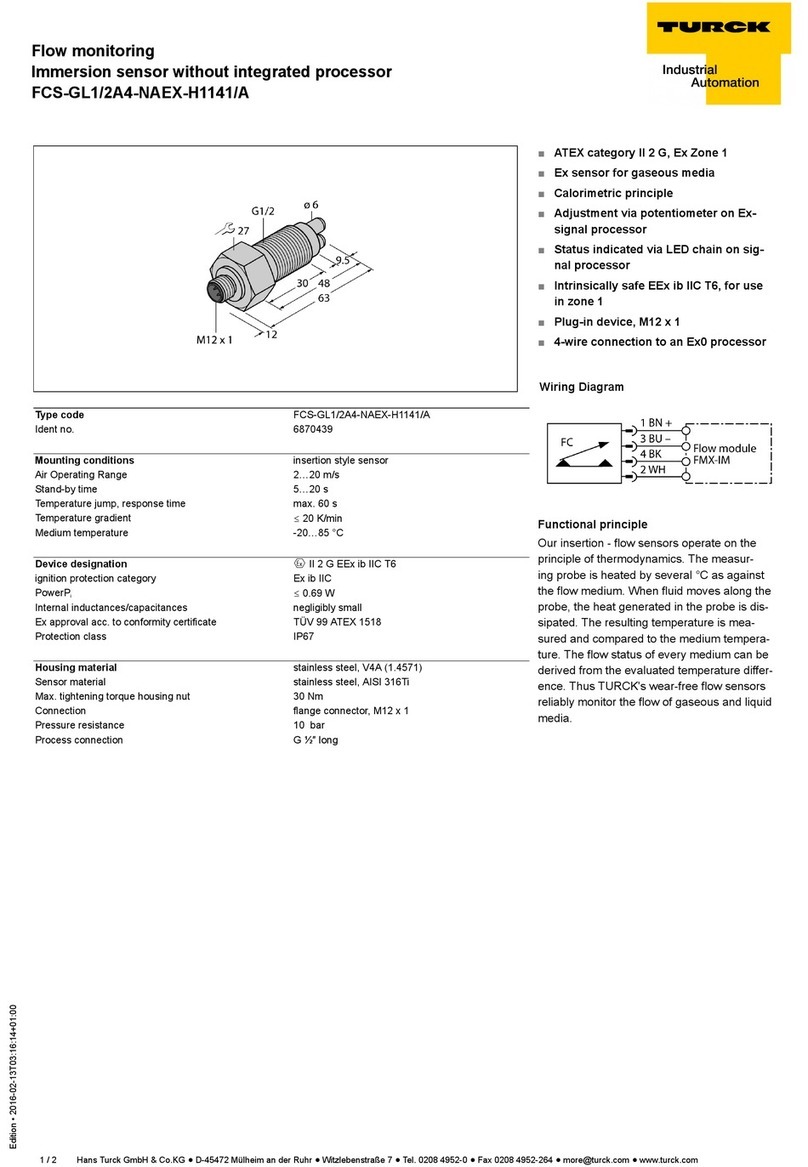
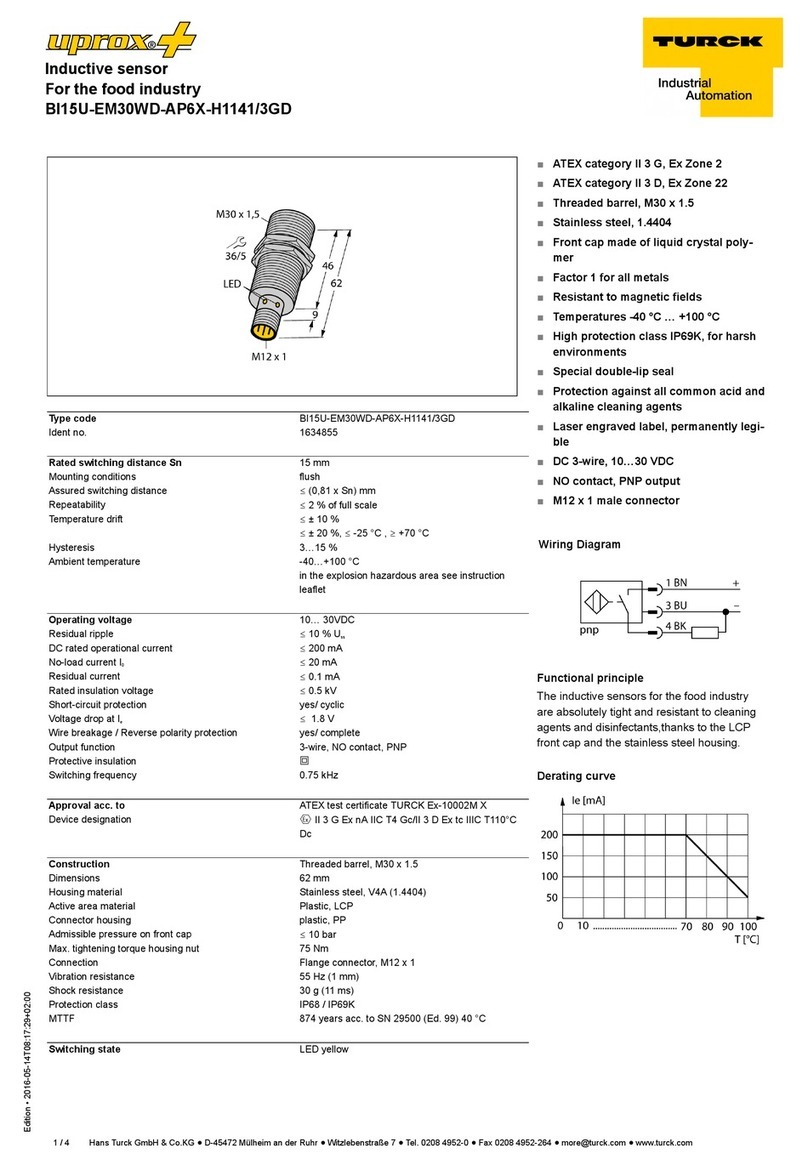
Design rectangular, Q20L60
Dimensions 60 x 30 x 20 mm
Housing material plastic, PC
Connection male, M12 x 1
Vibration resistance 55 Hz (1 mm)
Shock resistance 30 g (11 ms)
Protection class IP68 / IP69K
MTTF 203 years acc. to SN 29500 (Ed. 99) 40 °C
Included in scope of supply Security clip SC-M12/3GD
■ATEX category II 3 G, Ex Zone 2
■ATEX category II 3 D, Ex Zone 22
■Rectangular, plastic, PC
■Compact housing
■Connection via M12x1 plug connectors
■12 bit resolution
■5-wire, 10…30 VDC
■0.1 … 4.9 V analog output for clockwise
(CW) rotation
■0.1 … 4.9 V analog output for counter-
clockwise (CCW) rotation
Wiring diagram
Functional principle
The TURCK inclinometers incorporate a mi-
cromechanical pendulum, operating on the
principle of MEMS technology (Mikro Elektro
Mechanic Systems).
The pendulum basically consists of two 'plate'
electrodes arranged in parallel with a dielec-
tric placed in the middle. When the sensor is
inclined, the dielectric in the middle moves,
causing the capacitance ratio between both
electrodes to change.
The downstream electronics evaluates this
change in capacitance and generates a corre-
sponding output signal.