D
Group 20
•“Engine Does Not Start” page 5
•“Engine Difficult to Start” page 5
•“Engine Starts But Will Not Continue to Run” page 5
•“Engine Unexpectedly Shuts Down During
Deceleration” page 6
•“Engine Cuts Out Intermittently” page 6
•“Engine Does Not Shut Off” page 6
“Start and Stop Problems, Fault Tracing” page 4
Engine Does Not Start
There is no ignition in any of the cylinders during repeated
attempts. This can be caused by:
•Fuel not properly injected into cylinders.
•Power/ground and electrical problems in the EECU
and related systems.
•Abnormal conditions on the exhaust or intake systems.
The following checks should be performed in order until
the fault is found. These checks also can help exclude
components with no faults or malfunctions. The amount
and sequence of checks depend on results from Basic
Checks (including active or inactive fault codes noted),
vehicle conditions, vehicle service and repair history,
other symptoms, and information from the driver.
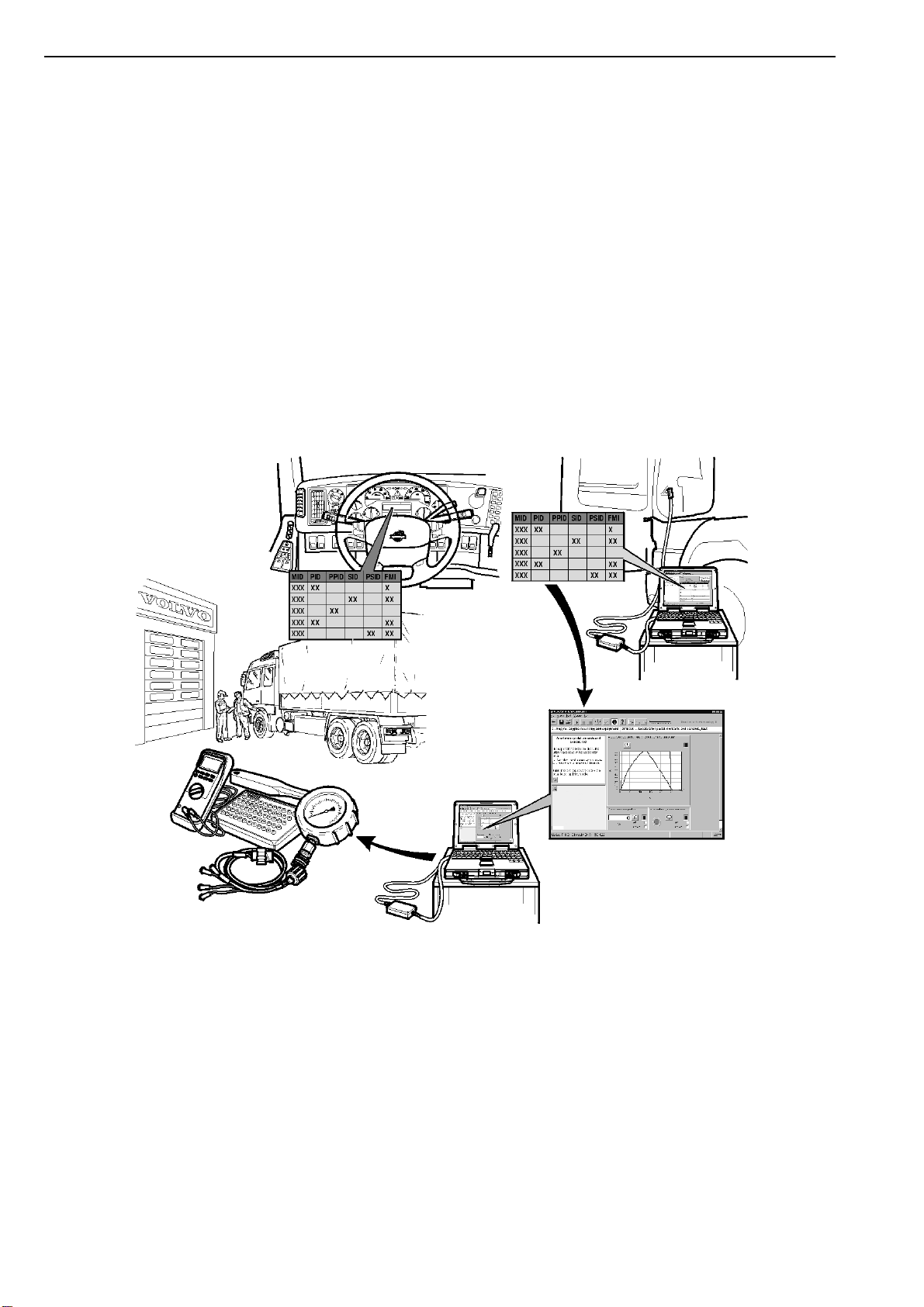
•“Step 1: Fault Code Readings” page 7
•“Step 2: Visual Inspection (System Checks)” page 7
•“Step 3: VCADS Pro Tests” page 9
•“Step 4: Component and Function Checks” page 10
“Start and Stop Problems, Fault Tracing” page 4
Engine Difficult to Start
The engine only starts after extended cranking or engine
idling speed is irregular immediately after starting. This
can be caused by:
•Incorrect fuel grade or bad fuel quality.
•Power/ground or electrical problems in EMS-related
components.
•Malfunctions in fuel system components.
•Faults in the inlet or exhaust systems.
•Preheater not functioning properly
The following checks should be performed in order until
the fault is found. These checks also can help exclude
components with no faults or malfunctions. The amount
and sequence of checks depend on results from Basic
Checks (including active or inactive fault codes noted),
vehicle conditions, vehicle service and repair history,
other symptoms, and information from the driver.
•“Step 1: Fault Code Readings” page 11
•“Step 2: Visual Inspection (System Checks)” page 11
•“Step 3: VCADS Pro Tests” page 12
•“Step 4: Component and Function Checks” page 13
“Start and Stop Problems, Fault Tracing” page 4
Engine Starts But Will Not Continue to Run
The engine starts but stalls after running for a short time.
This can be caused by:
•Fuel not being injected into the cylinders.
•Air in the fuel.
•An Engine ECU parameter is incorrectly set.
The following checks should be performed in order until
the fault is found. These checks also can help exclude
components with no faults or malfunctions. The amount
and sequence of checks depend on results from Basic
Checks (including active or inactive fault codes noted),
vehicle conditions, vehicle service and repair history,
other symptoms, and information from the driver.
•“Step 1: Fault Code Readings” page 14
•“Step 2: Visual Inspection (System Checks)” page 15
•“Step 3: VCADS Pro Tests” page 15
•“Step 4: Component and Function Checks” page 16
“Start and Stop Problems, Fault Tracing” page 4
5