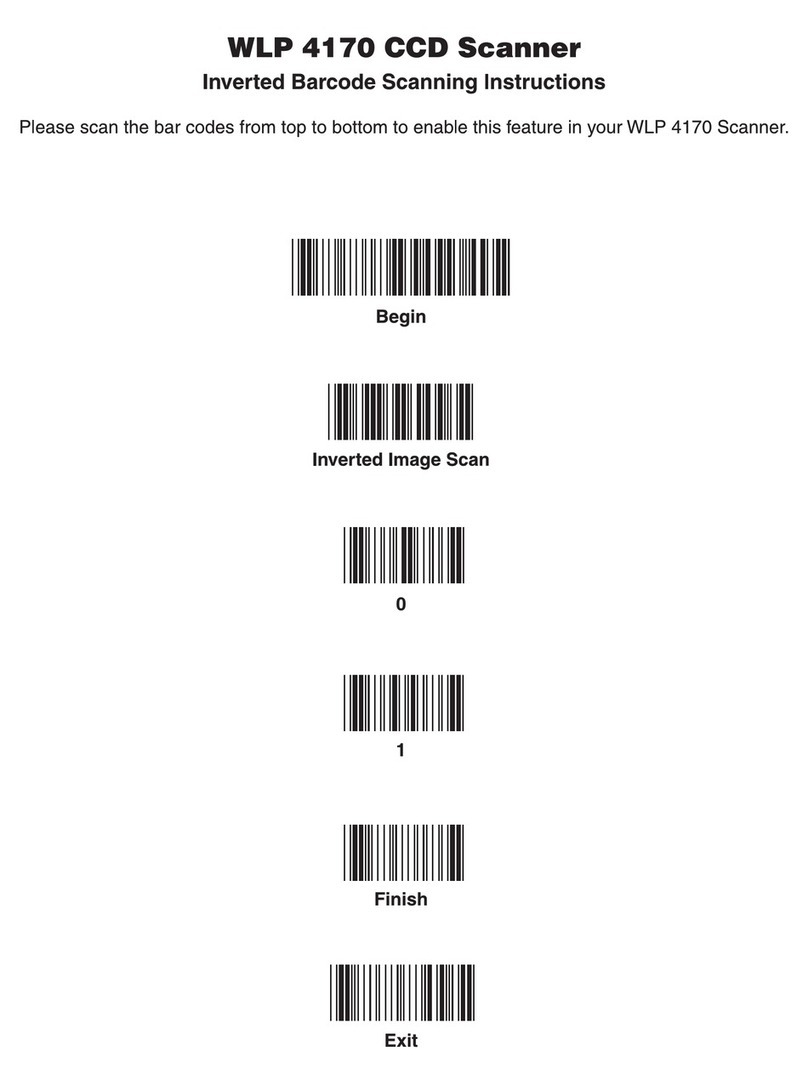
4
Chapter 3 QUICK START
Quick Start
1. Unpack.
Open the box and remove all the pieces from their protective packaging.
2. Charging the WWS150i.
You must charge the scanner for 4 hours before first using it. To charge the
scanner plug the power supply in to the bottom of the scanner.
3. Setting up Bluetooth.
If you already have Bluetooth setup on your PC or device, please continue
to the next step.
To setup Bluetooth on your PC you will need to insert the CD with the Bluetooth software on it. Follow the instruction on the CD
for installing the Bluetooth software.
4. Connecting the scanner to a Bluetooth device.
The scanner will connect to most Bluetooth devices that support HID connection.
You will need to open your Bluetooth software and search for Bluetooth devices. The Bluetooth software can be found by clicking
the Bluetooth symbol on the start bar near the computer time. If the Bluetooth symbol is
not found, there could be a problem
with the Bluetooth installation.
Once you have the Bluetooth software open you will need to scan the Set Connection
barcode (pg 7). This will make the scanner
ready
to be detected by the Bluetooth software.
The following screens are Microsoft’s standard Bluetooth wizard.
*Most Bluetooth wizards will have similar steps. Instructions for XP users are displayed below. Instructions for Win7 users
begin on page 5
Check the “My device is setup and ready to be found.” and click Next.
The scanner will show up in the list of Bluetooth devices found. Select the Wasp Barcode Bluetooth
Keyboard and click Next.
If Wasp Barcode Bluetooth Keyboard does not show up in the available devices please check the
following:
1. Make sure the scanner is on by pressing the trigger.
2. If you are using a pre-installed Bluetooth
adapter, make sure the adapter supports HID.
The next step will ask you to setup a passkey for the device. By default the scanner will not have a
passkey set. Please select “Don’t use a passkey” and click Next.
You can set a passkey later if you prefer,see Start/Stop Pin on page 8 for details.