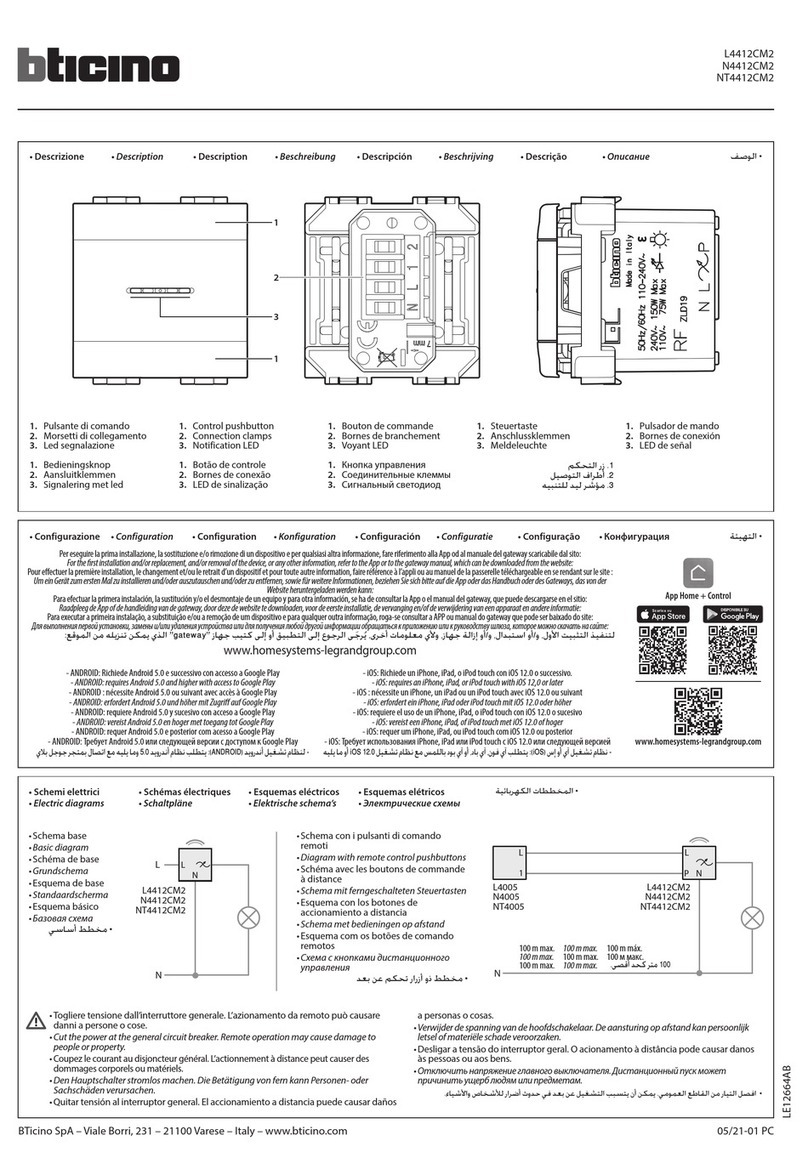
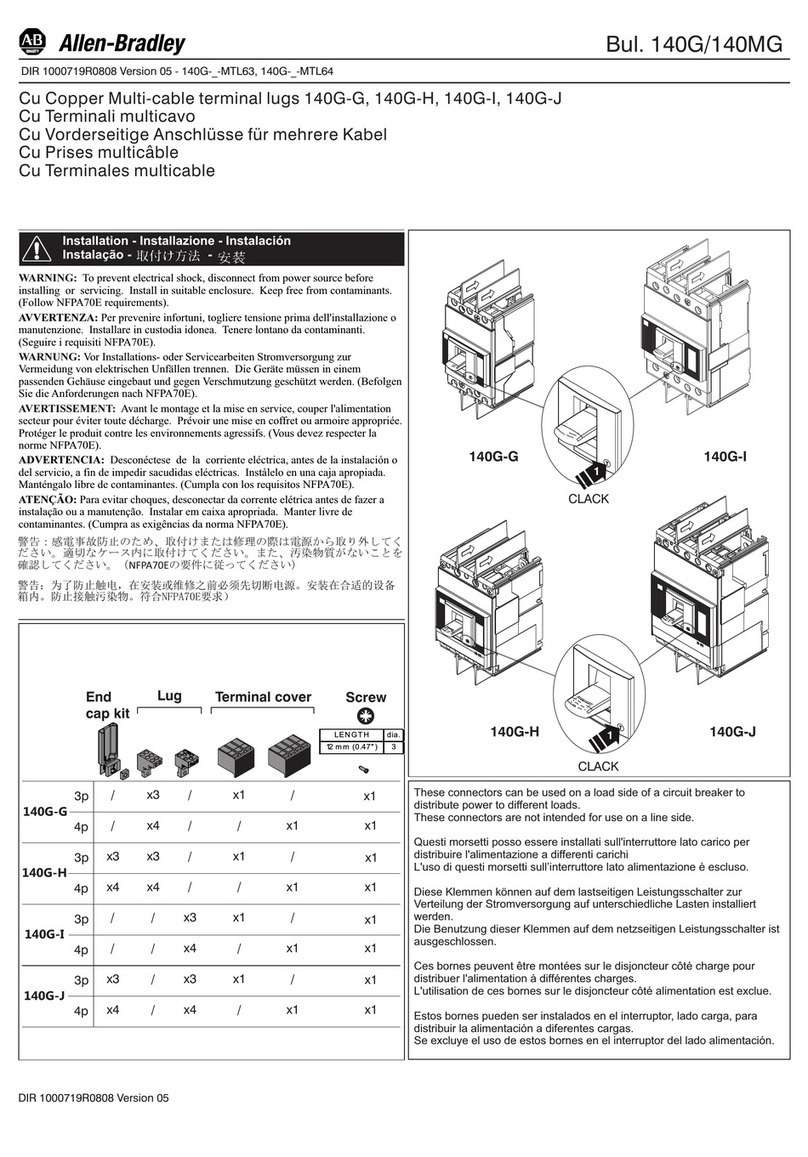
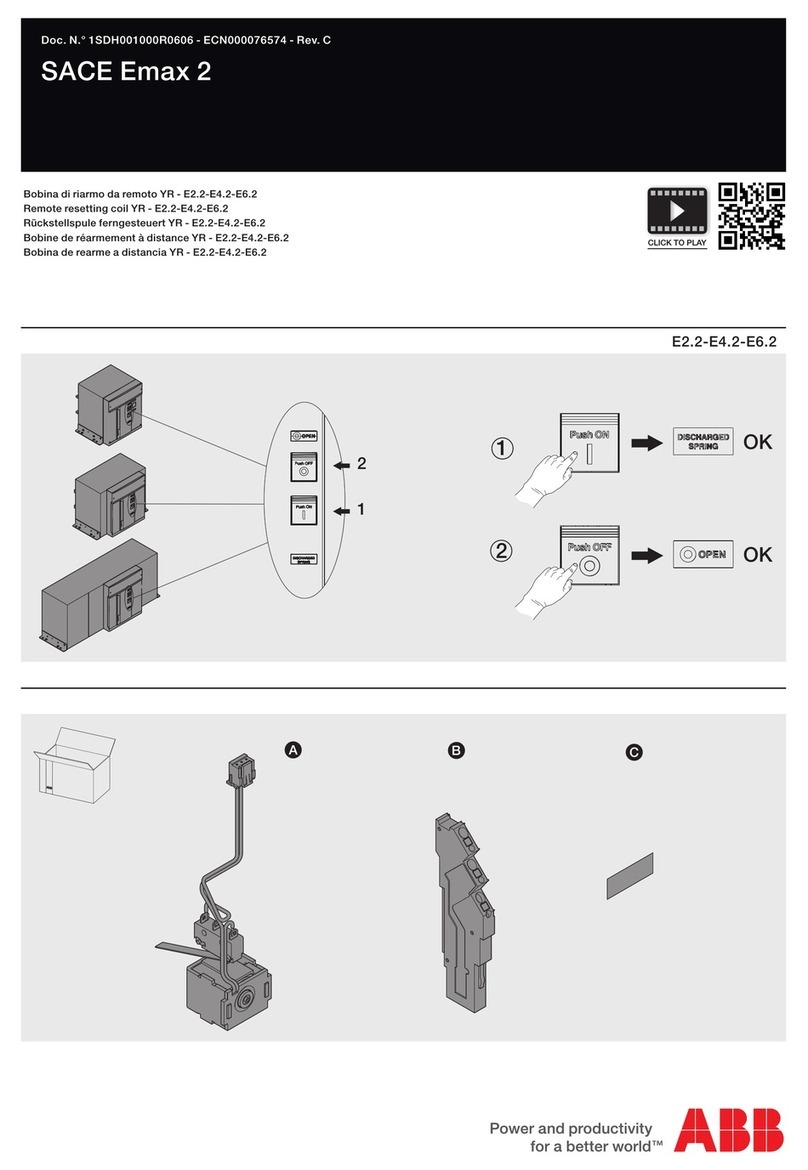
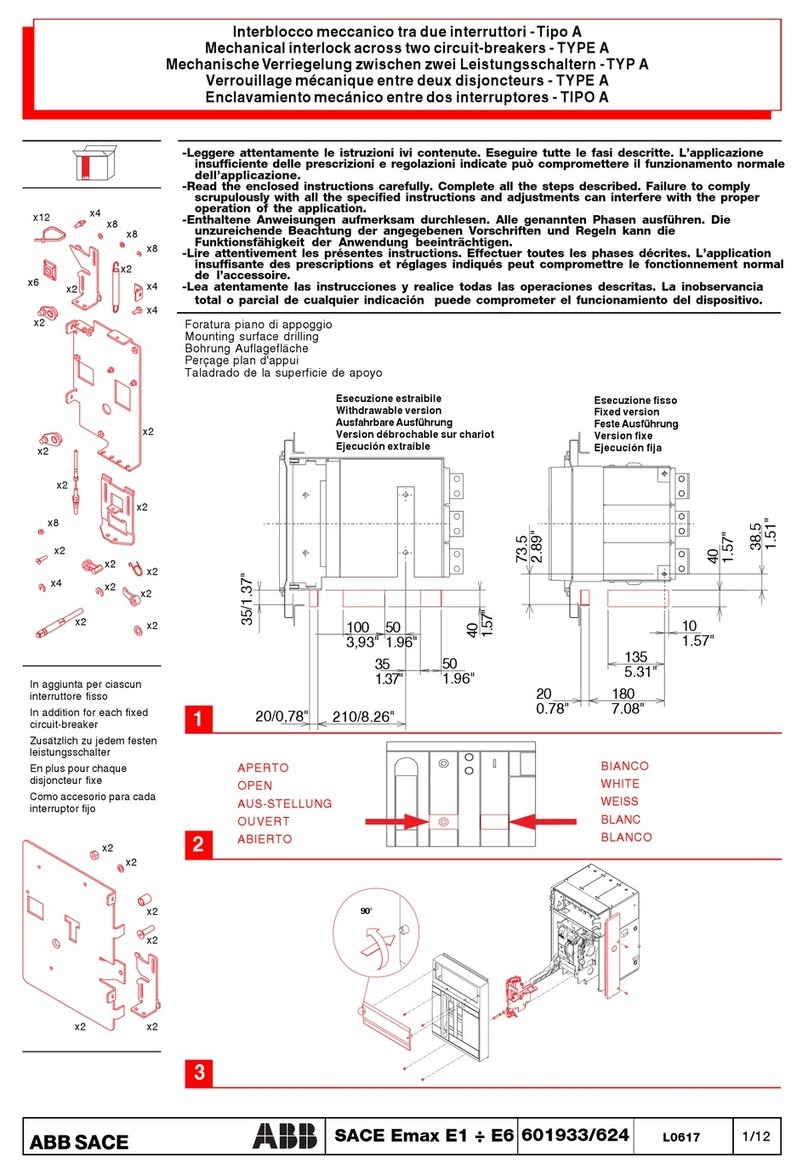
4.4 Magnetic Actuator
The magnetic actuator incorporates a very powerful permanent magnet assembly. When the
armature is in contact with the upper plate, the magnet produces a holding force in excess of
1500 lbs. Attached to the armature are two stainless steel guide rods.The upper guide rod
attaches to the lower end of the main operating rod, which connects directly to the moving
contacts of the vacuum interrupters.The lower guide rod mounts to the manual trip assembly.
Disassembly of the magnetic actuator is not necessary nor recommended. Lubrication or
maintenance is not required. Should an actuator fail to operate, contact ABB for service.The
permanent magnet inside the actuator is extremely powerful with the potential to trap fingers.
4.5 Standard Control (ED2.0)
The standard control package of the R-MAG is the ED2.0.The ED2.0 consists of a power
supply, position indication and capacitor charging/discharging system. Refer to Appendix A for
an extensive overview of the ED2.0.
5.0 STANDARD PRODUCTION TESTS
Standard production tests include:
1. Verification of all wiring per connection diagrams.
2. Electrical operation: Close and trip. Overcurrent response and automatic closing, with
relaying control option.
3. Check on functioning of all manual controls: Local/remote, non-reclosing, ground fault
bypass, etc.
4. Three readings are made on each phase of the breaker using a Biddle “Ductor.”Typical
values do not exceed 150 micro ohms.
5. Voltage Withstand:The complete breaker is tested (a) between live parts and tank, (b)
across open contacts, and (c) between phases. In compliance with ANSI C37.09 & IEC
an AC dielectric withstand test at 50 kV is performed.Test duration is one minute.
6. Wiring Insulation: The terminal block connections are given an over-potential test of 1500
volts AC to ground.
6.0 OPERATION
6.1 Closing
In the open position, the magnetic actuator’s armature rests against the bottom plate in the
actuator assembly.The armature is held there by the force developed by the magnet.When
the top coil is energized, the magnetic flux generated is in the same direction as the magnet
assembly.The armature is drawn into the coil and brought into contact with the upper plate. In
this position, the coil is de-energized and the armature is held in position by the magnet
alone. As the armature is drawn into the coil, the operating rod, which is attached to the top
guide rod, moves the moving contact of the vacuum interrupter towards the closed position.
The actuator has more stroke than the vacuum interrupter and the interrupter contacts make
contact before the actuator has completed the stroke.The additional movement of the
operating rod after the contact closing causes the contact pressure spring to compress at the
top of the operating rod.This “over-travel” allows for contact wear in service.
Page 4