ABB 15VHK500 User manual
Other ABB Circuit Breaker manuals

ABB
ABB DEH41820 User manual

ABB
ABB Sace Emax UL Listed Manual

ABB
ABB SACE Tmax XT5 User manual

ABB
ABB SACE Emax 2 User manual
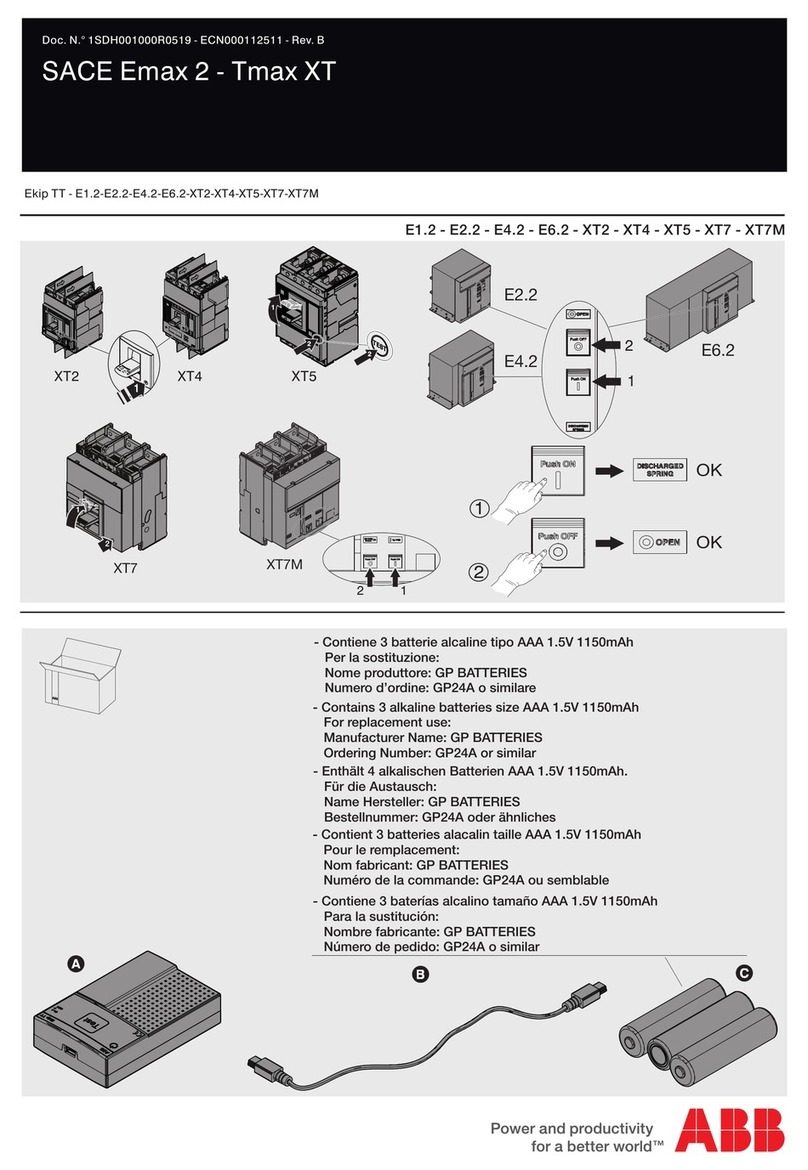
ABB
ABB SACE Emax 2 - Tmax XT User manual

ABB
ABB SACE Emax 2 User manual

ABB
ABB VD4 12.06.16 p150 Quick guide

ABB
ABB S201-K5 User manual
ABB
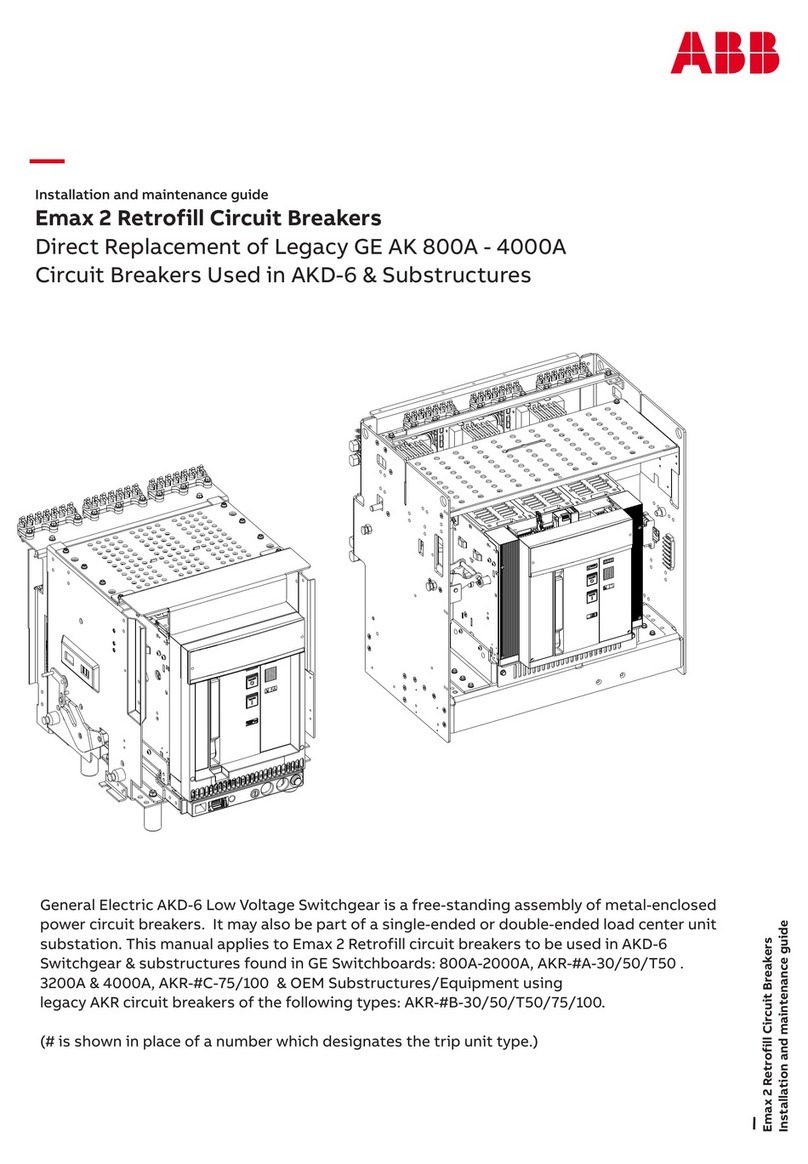
ABB Emax 2 Retrofill AKR-30-800A Product manual

ABB
ABB AF40 User manual
Popular Circuit Breaker manuals by other brands

Eaton
Eaton Power Defense PDG2 Instruction leaflet
Bticino
Bticino L4412CM2 quick start guide

Eaton
Eaton S-T0 Instruction leaflet

OEZ
OEZ 3VA9-RS-4VBH1 Installation, service and maintenance instructions

Siemens
Siemens PSR Instructions, Installation, Operation, Maintenance
Rockwell Automation
Rockwell Automation Allen-Bradley 140G-G manual