3. Protection functions
The generator protection relay offers protection functionality for
synchronous generators and their prime mover against internal
faults and abnormal conditions of external systems. The main
feature in the standard configuration D is the differential
protection. The main feature in the standard configuration C is
the 3rd harmonic-based stator earth-fault protection
completing the detection coverage with the other earth-fault
protection provided. The generator protection relay also
features reverse power and directional overpower protection
against delivering excessive power beyond the generator's
capacity and against the generator running like a motor. The
underpower protection protects generators and prime movers
against the effects of very low power outputs. A dedicated
protection function detects any loss of synchronism (out-of-
step condition) between the generator and the rest of the power
system. The generator relay also includes back-up overcurrent
protection featuring voltage dependent overcurrent and, in the
standard configuration D, directional overcurrent protection
and, in the standard configuration C, underimpedance
protection. Overexcitation protection (U/f) protects the
generators against excessive flux density. Underexcitation (X<)
protects the synchronous machine against the underexcitation
or loss of excitation condition. Frequency and voltage based
protection, thermal overload and unbalance protection are also
included in both standard configurations C and D intended for
generator protection.
The relay for the interconnection point of the power grid and
distributed power generation is provided with the standard
configuration A where the main features are low-voltage ride-
through protection, directional reactive power undervoltage
protection (QU) and the voltage vector shift protection. The
main features of the interconnection relay can be used to
support utility grid stability and to detect islanding. The
protection allows the monitoring of distributed generation
during low-voltage or fault ride through to determine whether
and when to disconnect from the grid. The voltage vector shift
protection detects islanding from the grid by measuring
continuously the duration of the voltage cycle and it can be
further secured with the provided frequency and voltage based
protection. Standard configuration A additionally offers
directional overcurrent protection, directional earth-fault
protection and reverse power and directional overpower
protection.
The RTD/mA inputs are offered as an option for the default
configuration. They can be used with Multipurpose protection
function for tripping and alarm purposes. Multipurpose
protection function uses RTD/mA measuring data or analog
values via GOOSE messages.
Enhanced with optional hardware and software, the relay also
features three light detection channels for arc fault protection of
the circuit breaker, busbar and cable compartment of metal-
enclosed indoor switchgear.
The arc-fault protection sensor interface is available on the
optional communication module. Fast tripping increases staff
safety and security and limits material damage in an arc fault
situation. A binary input and output module can be selected as
an option - having three high speed binary outputs (HSO) it
further decreases the total operate time with typically 4...6 ms
compared to the normal power outputs.
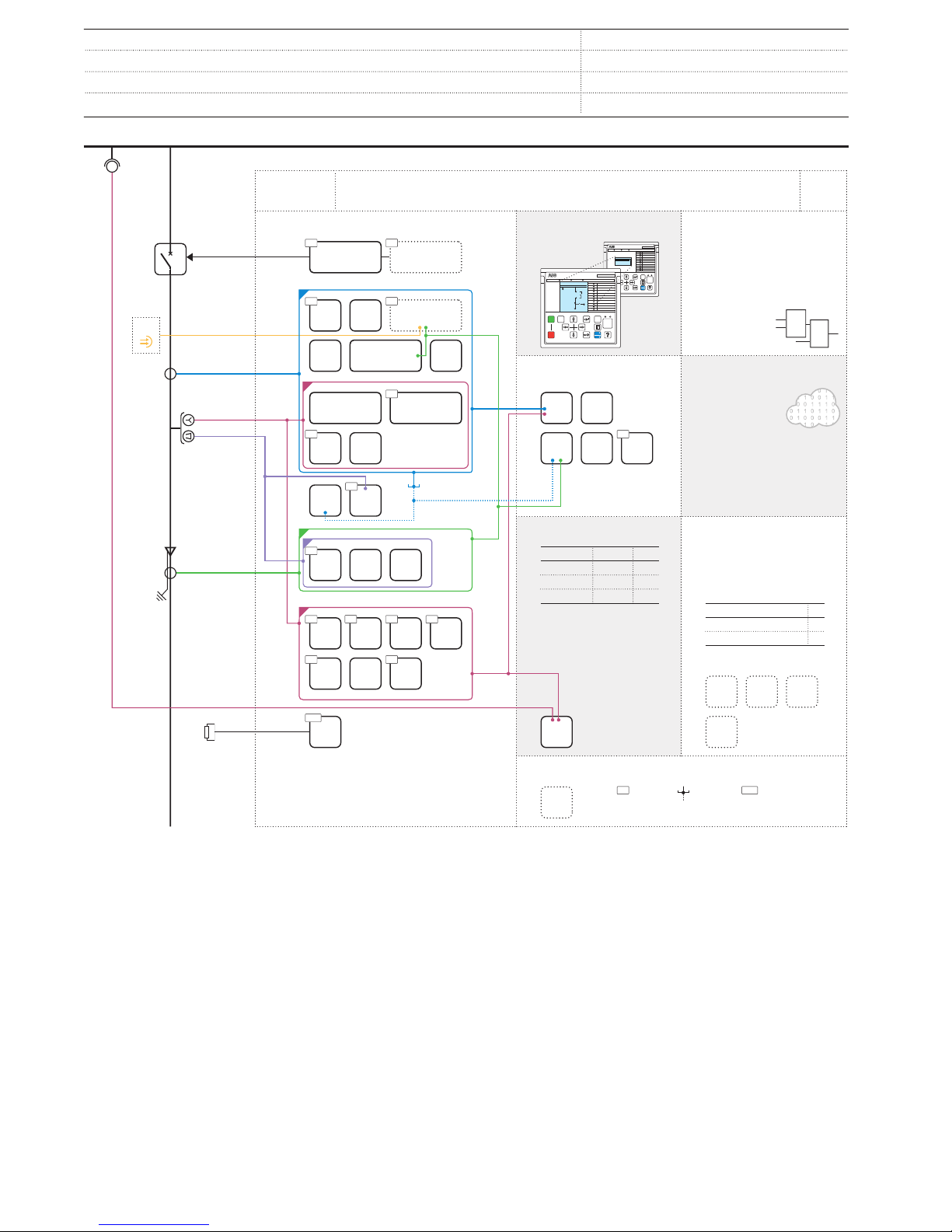
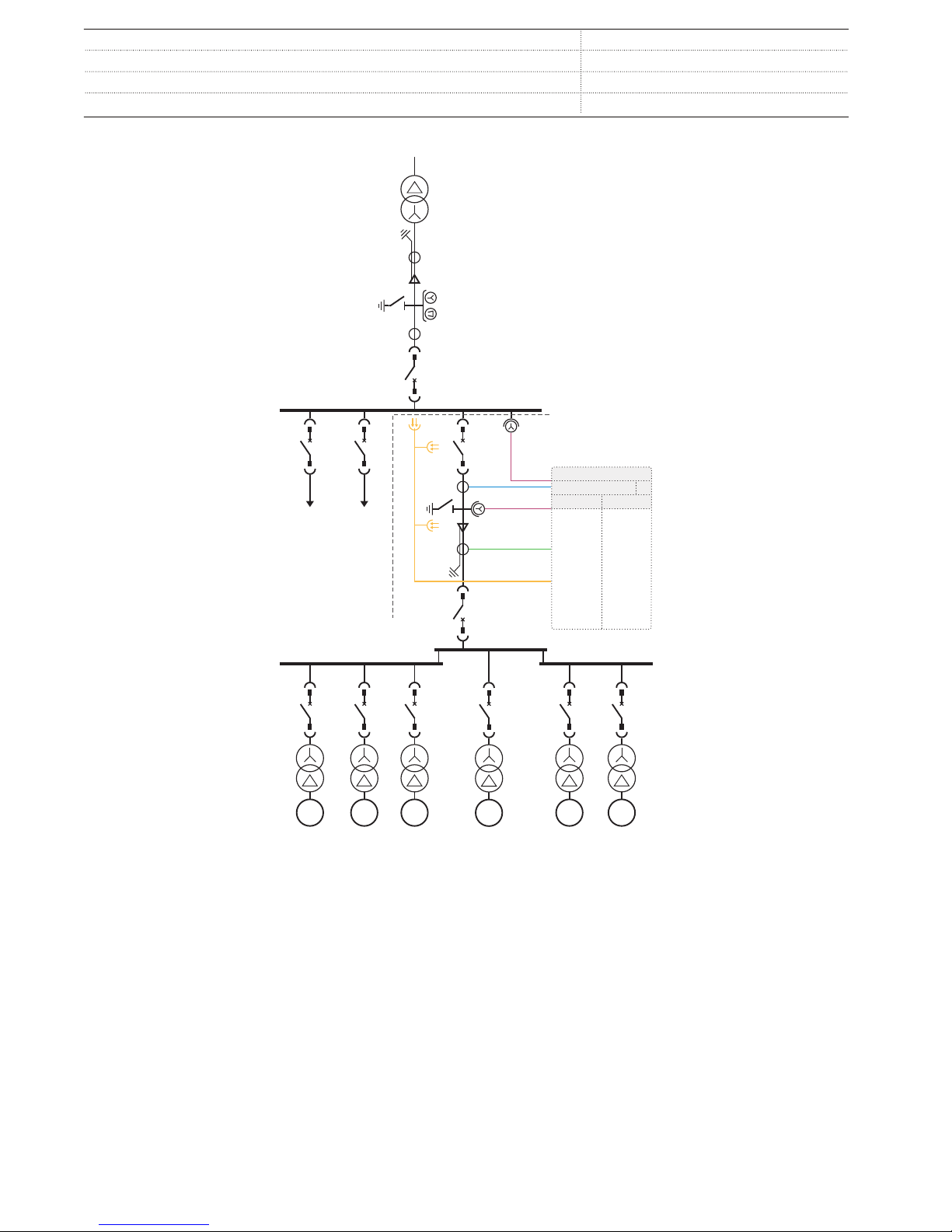
4. Application
Standard configuration A is intended to be used in the common
point of coupling distributed power generation into the utility
network. It ensures the grid stability and reliability according to
given grid codes and by determining whether and when to
disconnect according to defined settings. A typical application
example of the distributed power generation is a wind power
plant or a solar power plant but it can also be a combined heat
and power or hydroelectric power plant.