10
Sensor Calibration
All Apogee oxygen sensors respond to absolute oxygen concentration in air, where common units of absolute gas
concentration are partial pressure (e.g., kilopascals, kPa), mass per unit volume (e.g., grams per liter, g l-1), and number of
molecules per unit volume (e.g., moles per liter, mol l-1). The absolute amount of oxygen in air is dependent on absolute
(barometric) pressure and temperature, in addition to oxygen content of air. Therefore, Apogee oxygen sensors are not
calibrated at the factory and must be calibrated by the user.
The output of Apogee oxygen sensors is a linear function of absolute oxygen concentration. A simple linear calibration is
generally used to derive a calibration factor used to convert sensor output to relative oxygen concentration. The calibration
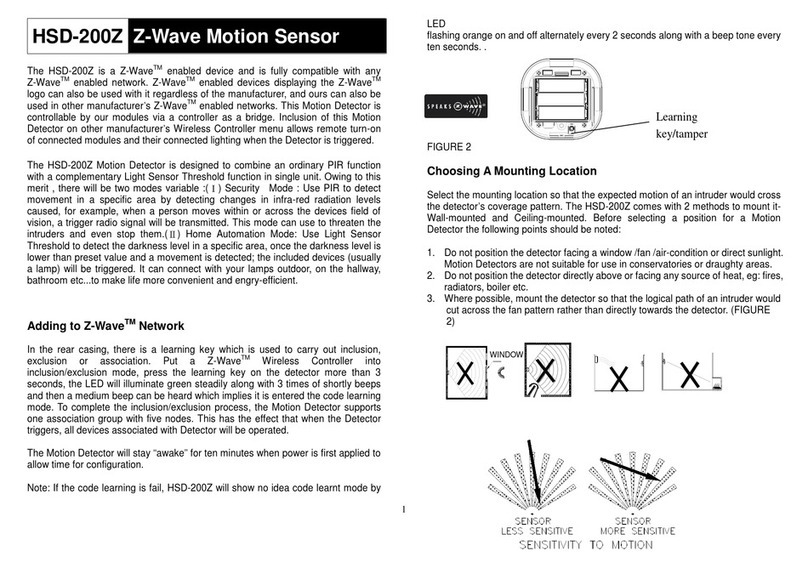
factor (CF, in kPa O2mV-1) is derived by dividing ambient oxygen partial pressure (21.23 kPa at sea level assuming standard
pressure of 101.325 kPa) by the measured voltage output from the sensor under ambient conditions (in air or over water in a
sealed chamber) minus the measured voltage output under conditions of zero oxygen (0 kPa O2):
(2)
where PBis barometric pressure [kPa], 0.2095 multiplied by PBequals partial pressure of oxygen under ambient conditions
[kPa], mVCis sensor voltage output [mV] during calibration, mV0is sensor voltage output [mV] under zero oxygen (0 kPa O2),
and CF is a linear multiplier that converts voltage measurements from the sensor to partial pressure of oxygen [kPa] using the
equation:
(3)
where mVMis measured voltage output [mV] and Offset is derived by multiplying CF by mV0. The voltage output during
calibration, mVC, should be measured in a well-ventilated area. Do not breathe on the sensor, as exhaled breath has a much
lower oxygen concentration than ambient air. If mV0is not measured, it can be estimated to be 3.0 mV for SO-100 series
sensors and 0.30 mV for SO-200 series sensors. It is recommend that mV0be measured (in pure nitrogen gas) for applications
where low values of oxygen (less than 10 kPa) will be measured. Precise measurements of hypoxic and anaerobic conditions
can be made by making a periodic zero calibration of the sensor with ultra-pure nitrogen gas.
To convert sensor voltage output to partial pressure of oxygen (in kPa), multiply the measured voltage signal by the
calibration factor, and then subtract the offset. For example, at sea level and 20.95 % O2:
Calibration Factor [kPa O2per mV] * Sensor Output Signal [mV] - Offset [kPa] = Oxygen [kPa]
0.379 * 59.0 -1.14 = 21.23
The calibration factor and offset are variable from sensor to sensor (those listed above are examples), and a sensor-specific
calibration factor should be derived for each individual sensor. For routine oxygen measurements, the generic offset
described above can be used. For measurements in air with less than 10 kPa (approximately 10 %) oxygen, a sensor-specific
offset should be derived for each individual sensor.
Sensors can also be calibrated to measure relative oxygen concentration. The same procedure described for calibration to
absolute oxygen is used, except ambient oxygen is set equal to 20.95 % (instead of 0.2095 multiplied by barometric pressure)
to derive the calibration factor [% O2mV-1]:
(4)
where mVCand mV0are as described above. The offset is also derived in the same manner, where mV0is multiplied by the
calibration factor calculated from equation (4). Equation (3) is then used to produce relative oxygen measurements, when the
calibration factor and offset derived from 20.95 % are used.