List of Figures
Figure 1-1 Directions of SCARA Motions.............................................................................. 1
Figure 1-2 External Dimension of the SCARA...................................................................... 2
Figure 1-3 SCARA Motion range ........................................................................................... 3
Figure 2-1 Peripheral Device Wiring Diagram....................................................................... 7
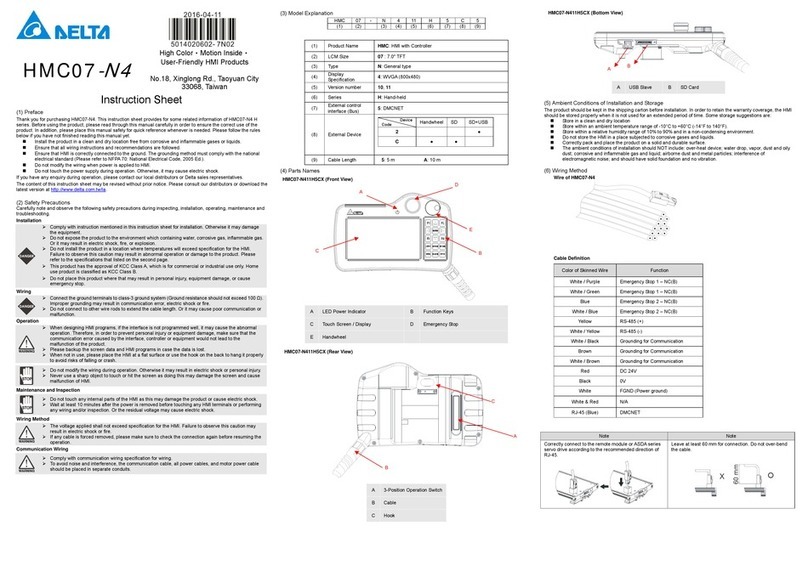
Figure 3-1 Exterior look of DCS Controller............................................................................ 8
Figure 3-2 Descriptions of external pins on the back of the controller................................. 9
Figure 3-3 Actual main circuit circuit power connector figure............................................... 11
Figure 3-4 Definition for the motor power terminal ............................................................... 11
Figure 3-5 Connector for power oncontrol circuit ............................................................................11
Figure 3-6 Definition for the control power terminal.............................................................. 11
Figure 3-7 Wiring diagram for the SCARA and MS controller............................................. 12
Figure 3-8 Motor Power Cable.............................................................................................. 12
Figure 3-9 Motor Encoder Cable .......................................................................................... 12
Figure 3-10 Motor connectors................................................................................................ 13
Figure 3-11 Connectors on motor power cable..................................................................... 13
Figure 3-12 Definitions of Encoder pins................................................................................ 14
Figure 3-13 Brake Release Button Location......................................................................... 14
Figure 3-14 Definitions of pins on motor Encoder................................................................. 15
Figure 3-15 Definitions of pins on motor Encoder................................................................. 15
Figure 3-16 External View of the Connectors ....................................................................... 16
Figure 3-17 Configuration of Rear Pins................................................................................. 16
Figure 3-18 Definitions of SYS.DIO pins............................................................................... 17
Figure 3-19 E-STOP Wiring Example.................................................................................... 18
Figure 3-20 Wiring Example of the Safety Door ................................................................... 18
Figure 3-21 MODE SELECT Wiring Example....................................................................... 19
Figure 3-22 RUN/STOP SWITCH Wiring Example............................................................... 20
Figure 3-23 Reset Wiring Example........................................................................................ 20
Figure 3-24 TP connector....................................................................................................... 22
Figure 3-25 Configurations of RS232/RS485 Pins ............................................................... 23
Figure 3-26 Ethernet Port....................................................................................................... 23
Figure 3-27 USB B-type port5............................................................................................23
Figure 3-28 USB port ............................................................................................................. 23
Figure 3-29 DMCNet port....................................................................................................... 23
Figure 3-30 Wiring Example of the Button or Inching Switch .............................................24
Figure 3-31 Wiring example of proximity switch.................................................................24
Figure 3-32 Wiring example of light signal or relay (loading positive) .................................25
Figure 3-33 Wiring example of light signal or relay (loading negative)).............................. 25
Figure 3-34 SCARA Body Connector Configuration............................................................. 26
Figure 3-35 SCARA I/O Connector Description.................................................................... 26