DGSL
Festo AG & Co. KG
Ruiter Straße 82
73734 Esslingen
Germany
+49 711 347-0
www.festo.com
Operating instructions
(Original instructions)
8067708
2017-01g
[8067710]
Mini slide DGSL English...............................................
Note
Installation and commissioning are to be carried out only by qualified personnel
in accordance with the operating instructions.
1 Further applicable documents
For all available product documentation èwww.festo.com/pk
2 Operating elements and ports
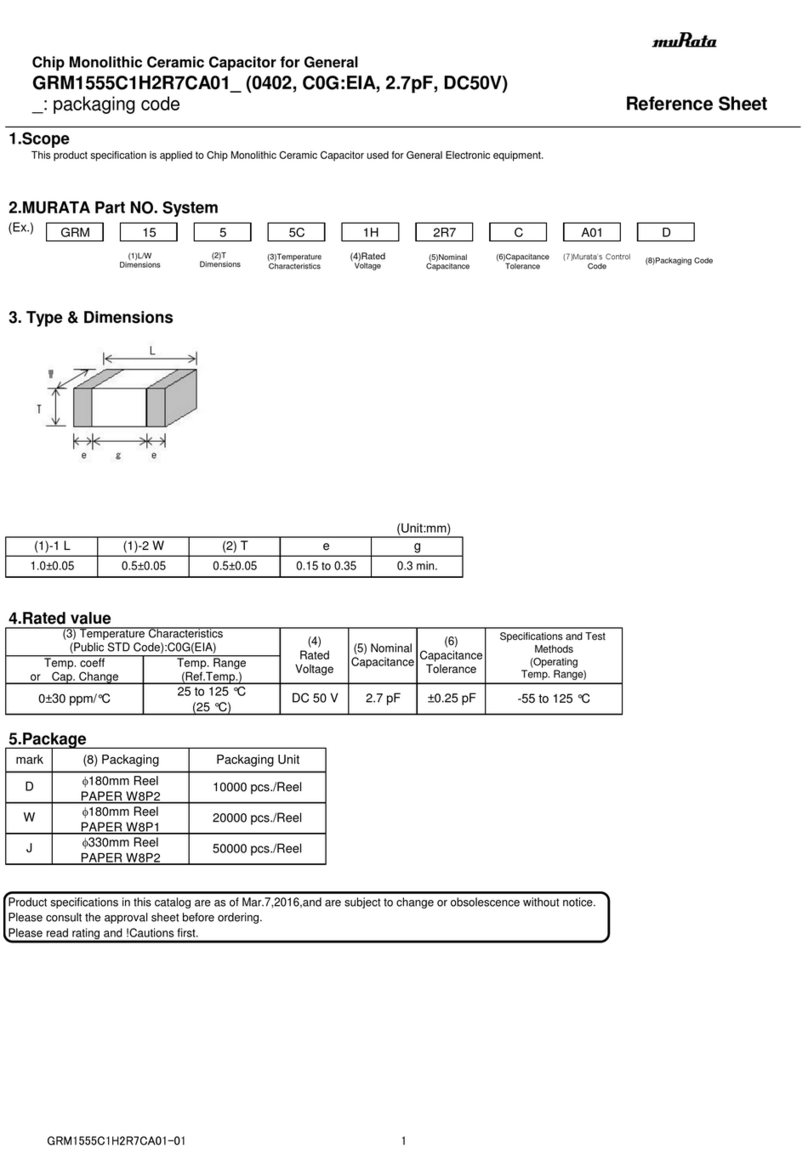
1 5
8
6
739
aJ
2 3 4
aAaBaC
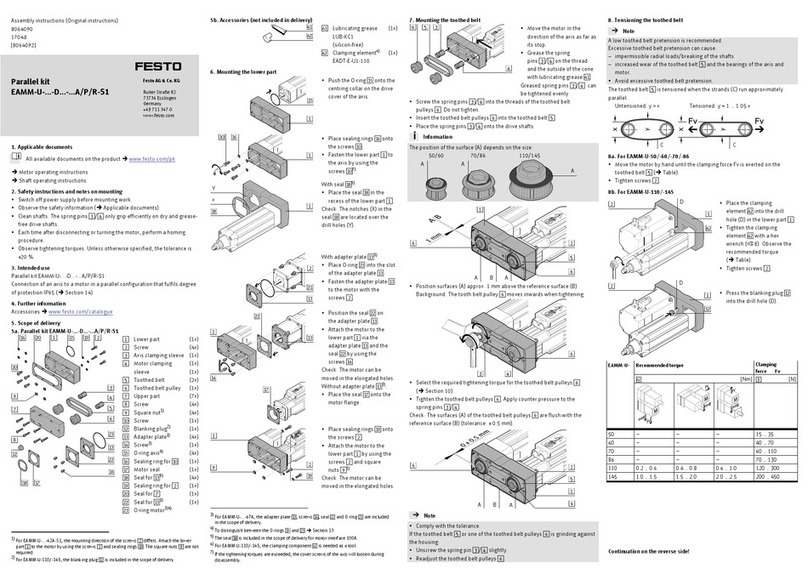
1Cushioning component:
– Elastic (DGSL-…-E/-P/-P1
– Hydraulic (DGSL-…-Y3/-Y11)
– None (DGSL-…-N)
2Drill hole for mounting the mini
slide (lies concealed)
3Thread with centring recess for
mounting the effective load
(centring sleeves included in scope
of delivery)
4Slide/bearing guide
5Yoke plate
6Fixed stop
7Thread with centring recess for
mounting the mini slide
8Piston rod
9Slots for proximity sensor
aJ Compressed air supply port
(retracting)
aA Compressed air supply port
(extending)
aB Compressed air supply port
(extending) with blanking screw1)
aC Compressed air supply port
(retracting) with blanking screw1)
1) In condition on delivery
Fig. 1
3 Function and application
The DGSL mini slide is a non-rotating single-piston drive with roller bearing guide.
When the compressed air supply ports are pressurized reciprocally, the slide
moves back and forth. The slide is braked by elastic cushioning components in the
case of DGSL-…-E/-P/-P1 and by hydraulic shock absorbers in the case of
DGSL-…-Y3/-Y11. In the case of DGSL-…-N, cushioning elements must be attached
for both end positions (è6.2 DGSL-…-N without cushioning components).
The DGSL mini slide is intended for the space-saving transport of masses. A high
degree of positioning accuracy is achieved.
4 Transport and storage
Take into account the weight of the DGSL.
Depending on the version, the DGSL can weigh up to 7 kg.
Ensure storage conditions as follows:
– Short storage times and
– Cool, dry, well-shaded, corrosion-resistant locations.
5 Requirements for product use
Note
Malfunctions will occur if the device is incorrectly used.
Make sure that the specifications contained in this chapter are adhered to at
all times.
Observe the warnings and notes on the product and in the relevant operating
instructions.
Compare the limit values in these operating instructions with those of your
application (e.g. forces, torques, temperatures, loads, speeds).
Operation of the product in compliance with the relevant safety regulations is
contingent on adherence to the load limits.
Take into consideration the ambient conditions at the location of use.
Corrosive environments will reduce the service life of the product (e.g., ozone).
Comply with the regulations of the workers’ compensation trade association,
the German Technical Control Board (TÜV), of the VDE or relevant national
regulations.
Use the product in its original status, without any unauthorised product
modifications.
Remove all transport packaging, such as foils, caps, cardboard.
Exception:
– possibly covers in the pneumatic connections.
The material used in the packaging has been specifically chosen for its
recyclability (exception: oiled paper = residual waste).
Make sure there is a supply of correctly prepared compressed air
(è13 Technical data).
Maintain the selected medium for the total service life of the product. Example:
Always use non-lubricated compressed air.
Pressurize your entire system slowly. There will then be no uncontrolled
movements.
For slow start-up pressurisation, use on-off valve HEL.
Take the tolerance of the tightening torques into account. Unless otherwise
specified, the tolerance is ± 20 %.
6 Installation
Note
For vertical installation:
Make sure that the slide has reached a stable position when it comes to
astop (e.g., the lowest point or secured with external stops).
6.1 Installation, mechanical
Handle the DGSL with care so that the slide guide is not damaged.
This could impair the roller bearing function.
Leave all screws and threaded bolts in their original states, unless you are
requested to modify them in these instructions.
For safety reasons, they are fixed with a screw locking agent.
Make sure there is sufficient space
for the pneumatic connections, the
control sections and for possible
replacement of the cushioning
component and proximity switches.
Fig. 2
Make sure that the device is installed
free of distortion and deflection.
Fig. 3
Installing the effective load
Note
If pins strike against the yoke plate, the
mechanical connector can be destroyed.
Push a metal plate between the yoke plate and
the housing as a counterholder.
Then press the required pins into the yoke
plate. Fig. 4