GE AKR User manual
Other GE Circuit Breaker manuals
GE
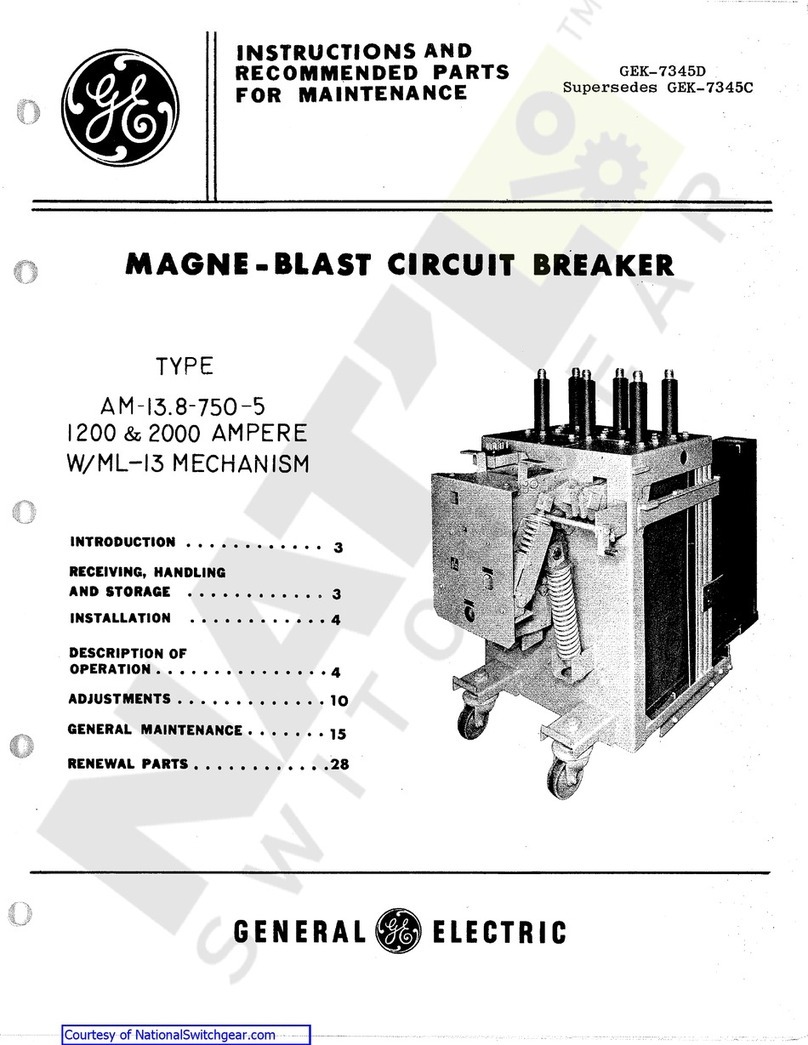
GE AM-13.8-750-5 User manual

GE
GE Power-Break TSUV1 User manual
GE
GE Rapid TripFix User manual
GE
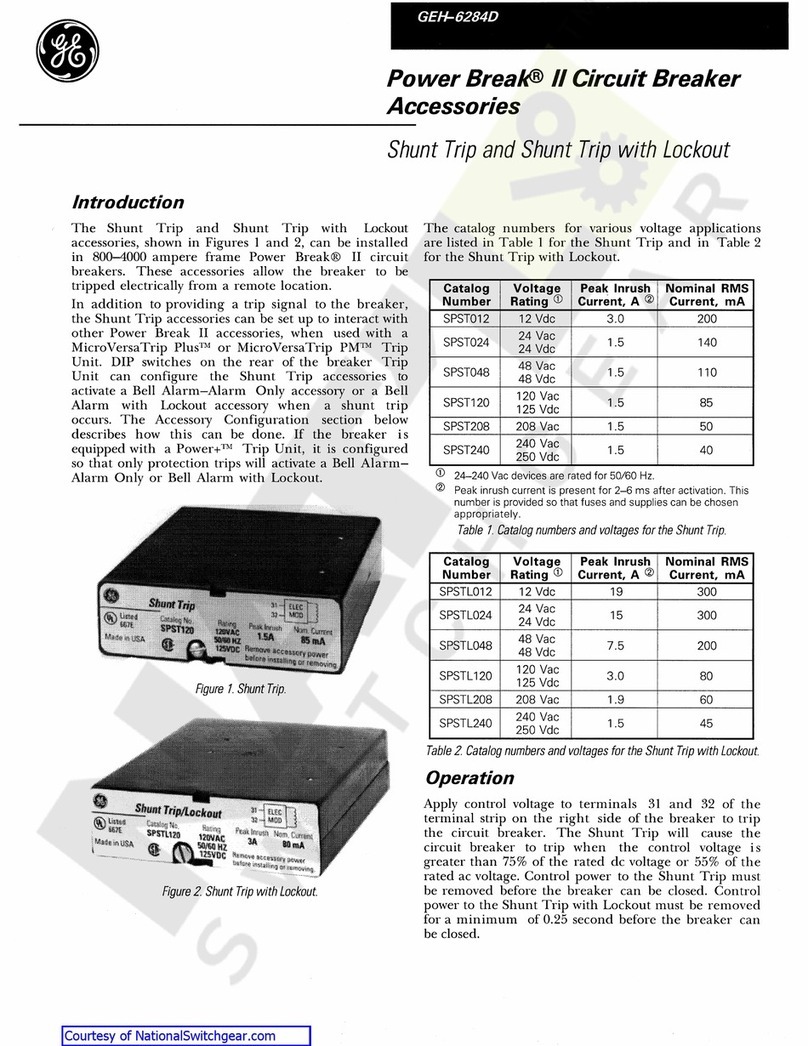
GE SPST012 User manual

GE
GE FK800 User manual

GE
GE GL 310 F1/4031 P/VR User manual

GE
GE AK-1-15 Series User manual
GE
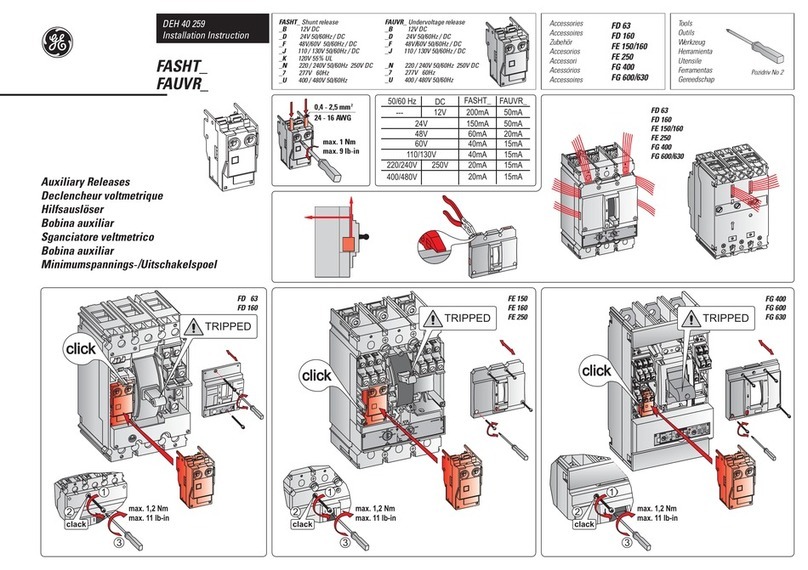
GE FASHT Series User manual

GE
GE A Series Pro-Stock TQD User manual

GE
GE EntelliGuard G User guide

GE
GE PowerVac GEK-86132F User manual

GE
GE AKR-3-50 User manual
GE
GE AM-13.8-750-4C User manual

GE
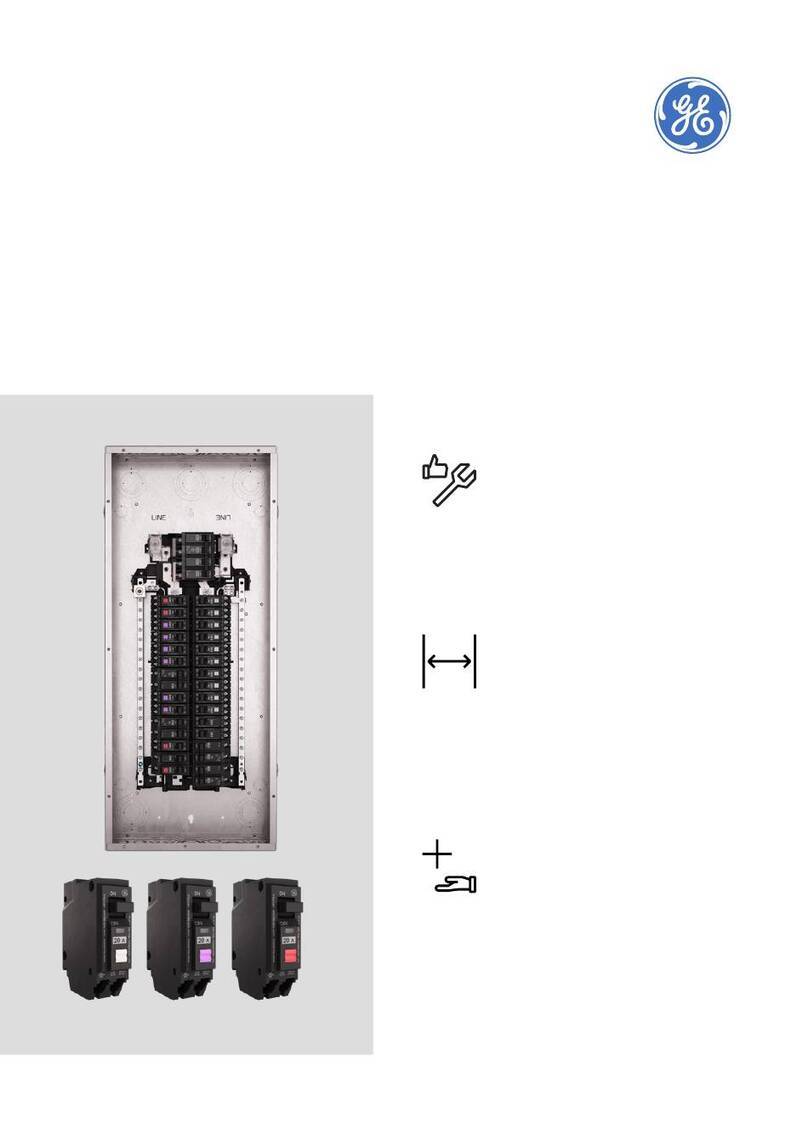
GE GCCC024DR User manual
GE
GE AM-13.8-500-7 User manual
GE
GE AM-13.8-500-5A User manual

GE
GE AK-2-15 User manual

GE
GE ML-14-0 User manual

GE
GE MicroVersaTrip AKR-75 User manual

GE
GE POWER/VAC GEK 86132A User manual
Popular Circuit Breaker manuals by other brands

Siemens
Siemens Sentron 3VA9157-0PK1 Series operating instructions
hager
hager TS 303 User instruction
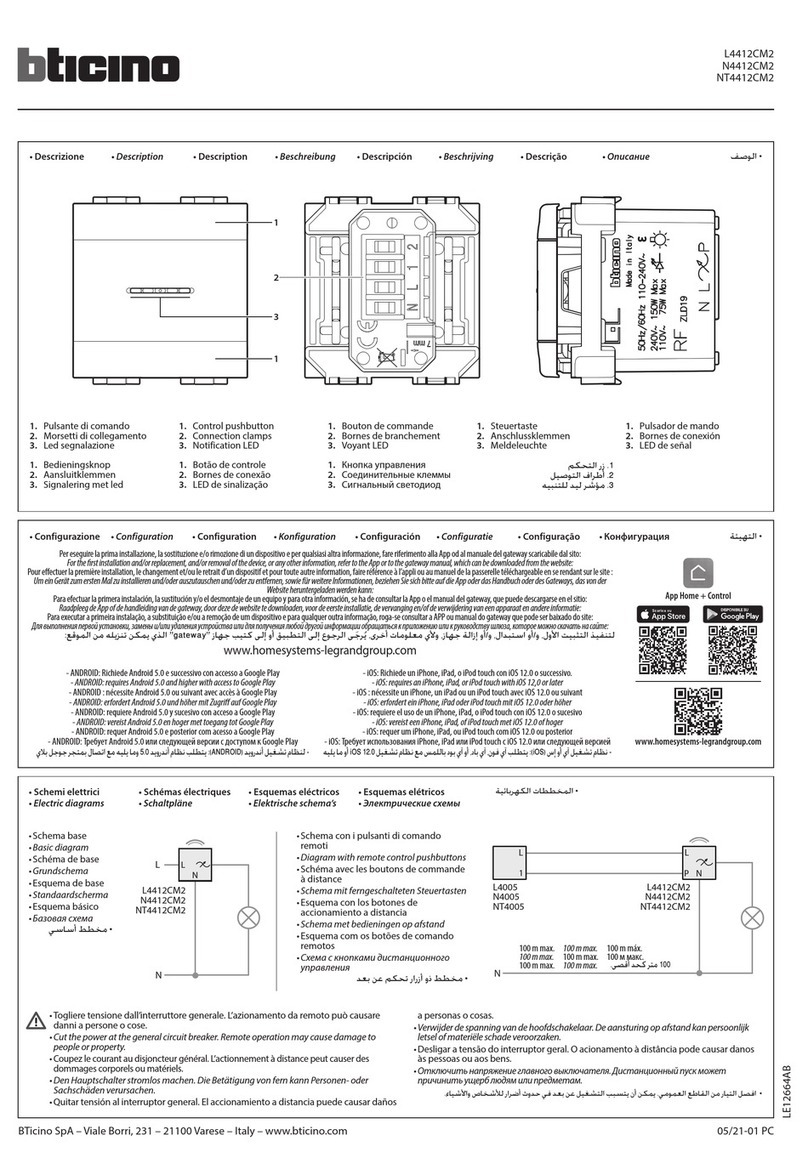
ETI
ETI EFI-4B Instructions for mounting

nader
nader NDM3EU-225 operating instructions
TERASAKI
TERASAKI NHP TemBreak PRO P160 Series installation instructions

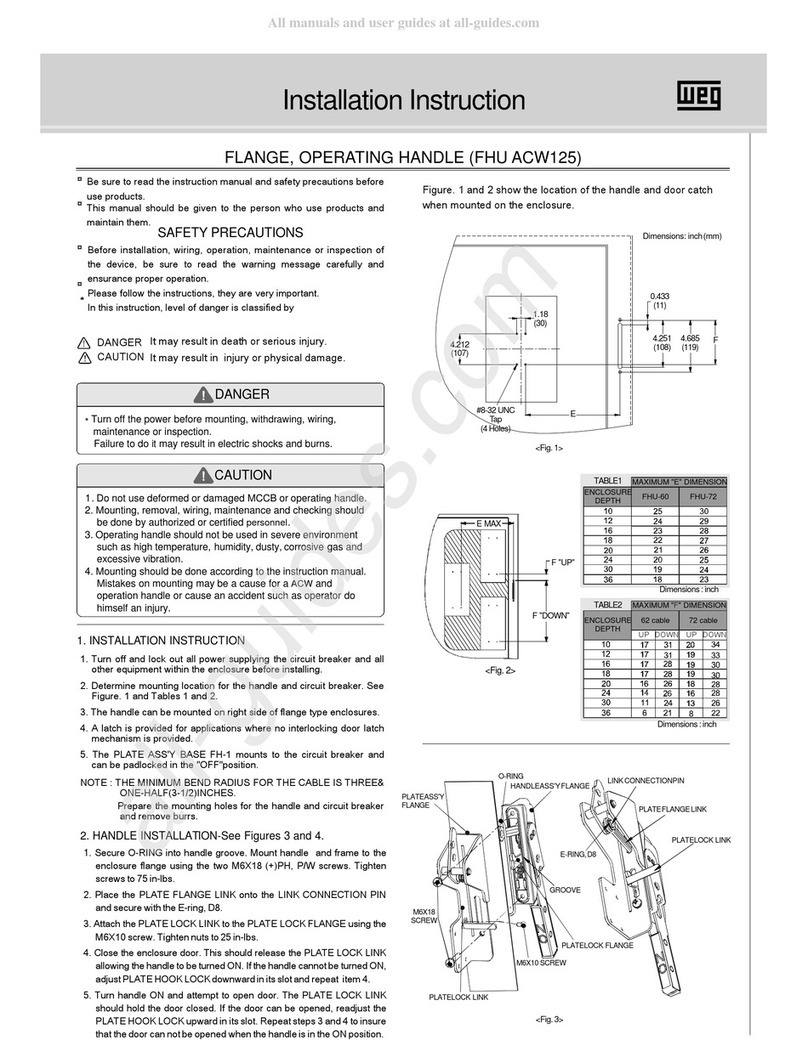
Gladiator
Gladiator GCB150 Installation instruction