4
INDEX PART I
Chapter 1 Overview ...................................................................................................................................... 7
1.1 Product Name......................................................................................................................... 7
1.2 Applications and Scope.......................................................................................................... 7
1.3 Operating Environment........................................................................................................... 7
1.4 Impact on Environment and Resources.................................................................................. 7
1.5 Safety...................................................................................................................................... 7
Chapter 2 Working Theories........................................................................................................................ 8
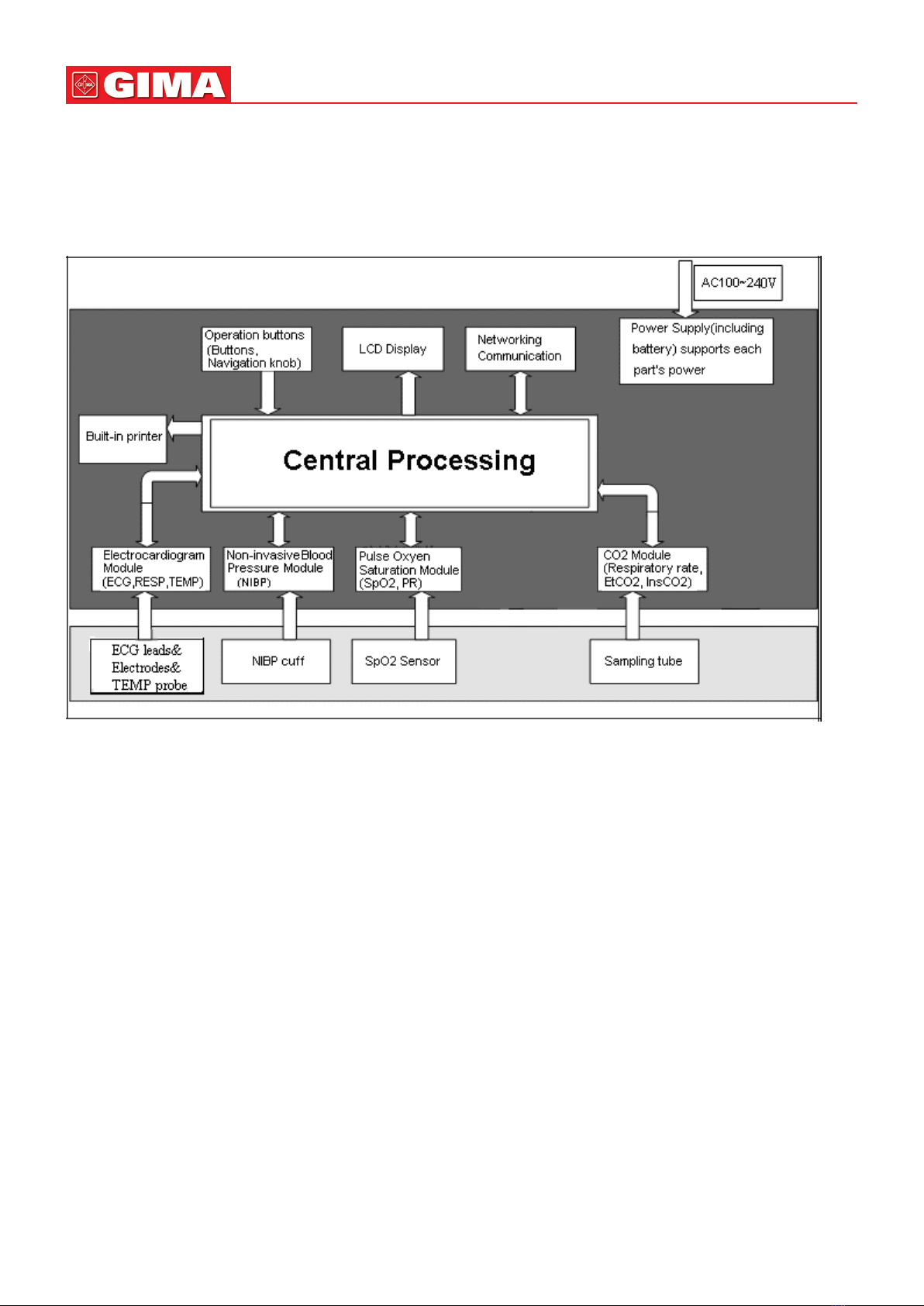
2.1 Overall Structure..................................................................................................................... 8
2.2 Composition ........................................................................................................................... 8
2.3 Working Theories .................................................................................................................... 8
Chapter 3 Installation and Connection....................................................................................................... 9
3.1 Installation............................................................................................................................... 9
3.1.1 Opening the Box and Check.......................................................................................... 9
3.1.2 Connecting the AC Power Cable ................................................................................... 9
3.1.3 Starting the Monitor ..................................................................................................... 10
3.2 Connection ........................................................................................................................... 10
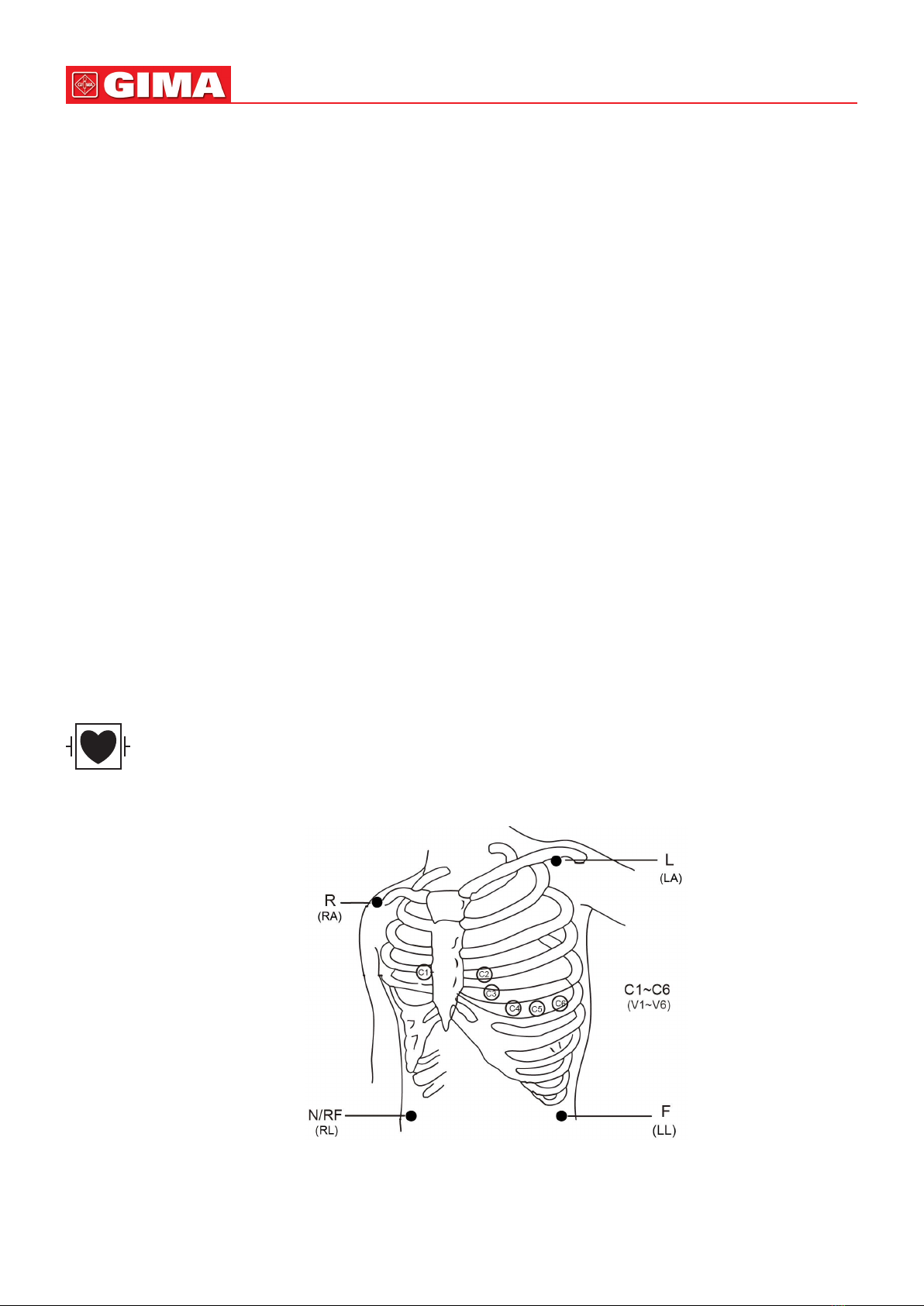
3.2.1 ECG Cable/Lead Wires Connection............................................................................. 10
3.2.2 Cuff Connection for Blood Pressure Measurement ..................................................... 12
3.2.3 SpO2Probe Connection.............................................................................................. 14
3.2.4 CO2 Sensor Connection .............................................................................................. 17
3.2.5 TEMP Probe Connection ............................................................................................. 20
3.2.6 Loading Printing Paper ................................................................................................ 21
Chapter 4 Alarm.......................................................................................................................................... 22
4.1 Alarm Description ................................................................................................................. 22
4.1.1 Alarm Condition ........................................................................................................... 22
4.1.2 Alarm Priority................................................................................................................ 22
4.1.3 Alarm Modes................................................................................................................ 23
4.1.4 Alarm Setting ............................................................................................................... 23
4.2 Alarm Technical Specications ............................................................................................. 23
Chapter 5 Technical Specications .......................................................................................................... 24
5.1 ECG Monitoring .................................................................................................................... 24
5.2 RESP Monitoring .................................................................................................................. 25
5.3 TEMP Monitoring .................................................................................................................. 25
5.4 NIBP Monitoring ................................................................................................................... 25
5.5 SpO2 Monitoring................................................................................................................... 26
5.6 Pulse Rate Monitoring .......................................................................................................... 26
5.7 CO2 Monitoring .................................................................................................................... 26
5.8 Data Recording..................................................................................................................... 26
5.9 Other Technical Specications ............................................................................................. 26
5.10 Classication....................................................................................................................... 26
5.11 Guidance and manufacturer’s declaration - Electromagnetic compatibility....................... 27
Chapter 6 Packaging and Accessories .................................................................................................... 29
6.1 Packaging ............................................................................................................................. 29
6.2 Accessori .............................................................................................................................. 29
Chapter 7 Working Principles.................................................................................................................... 30
7.1 Introduction to ECG Measurement ....................................................................................... 30
7.1.1 How to Obtain High Quality ECG and Accurate Heart Rate Value .............................. 30
7.1.2 Factors affecting ECG signal ....................................................................................... 30
7.2 Introduction to Blood Pressure Measurement...................................................................... 31
7.2.1 Blood Pressure Measuring Principle............................................................................ 31
7.2.2 Factors affecting NIBP measuring ............................................................................... 32
7.2.3 Clinical Limitations ....................................................................................................... 32
7.3 Introduction to Oxygen Saturation Measurement................................................................. 33
7.3.1 SpO2Measuring Principle ........................................................................................... 33
7.3.2 SpO2Measurement Restrictions (interference reason) ............................................... 33
7.4 Introduction to Respiration Measurement ............................................................................ 34
7.4.1 Respiration Measuring Principle .................................................................................. 34
7.4.2 Factors affecting respiration monitoring ...................................................................... 34
7.5 Introduction to Temperature Measurement .......................................................................... 34