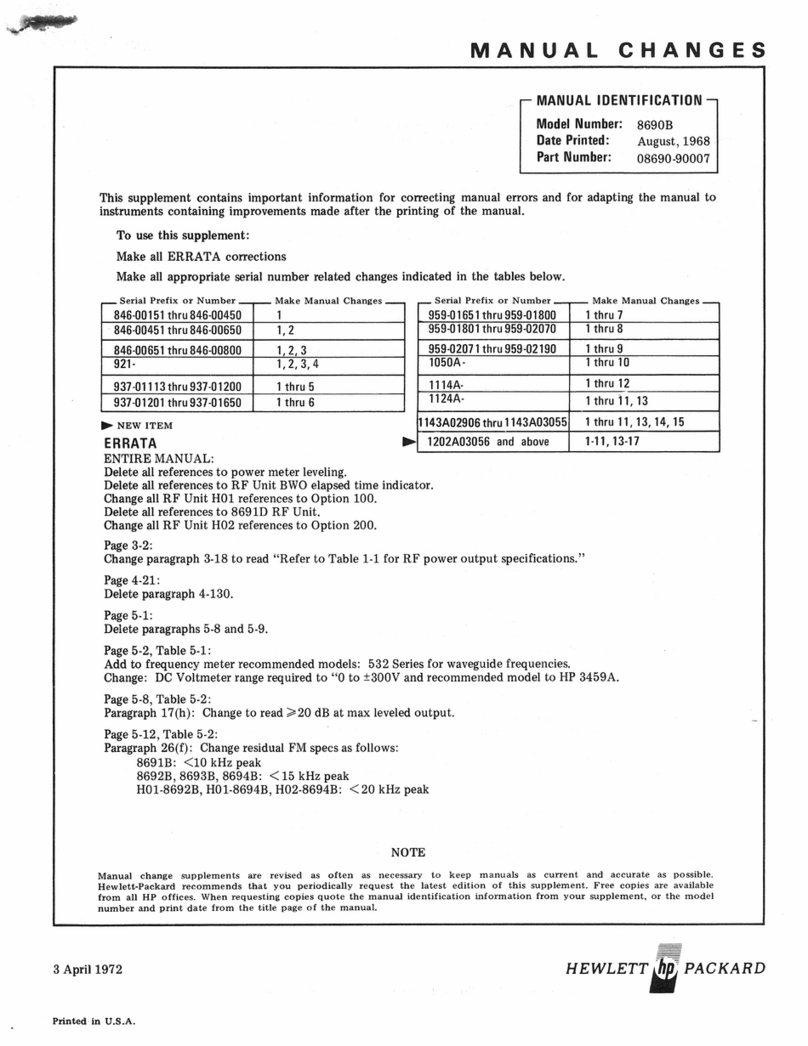
In
This Book
This book shows you how to
coIIDect,
use,
and
troubleshoot your HP logic
analyzervia a Local Area Network (LAN)
connection. This book contains the
following chapters:
• Chapter 1 provides information about
connecting the logic analyzer to
the
network. To effectively use this
chapter, you should be familiar with
your network setup
and
operation.
• Chapter 2 shows you howto access
the
logic analyzer's file system. This is
a prerequisite for some ofthe other
things you can
do
with a logic analyzer
on
the
network.
• Chapter 3 shows you how to display
the
analyzer interface on an XWindow
server,
and
describes
the
basics of
using
the
interface.
• Chapter 4 shows you how to retrieve
measurement data, screen images,
and
status information from your logic
analyzer
on
the
LAN,
and
how to copy
and
restore
configurations.
• Chapter 5 shows you methods for
programming the logic analyzer via
the
network connection.
• Chapter 6 contains additional
infonnation on the logic analyzer's
directory structure
and
dynamic files.
• Chapter 7 describes what to
do
if
you
have a problem using
the
logic
analyzer
on
your network.
Connecting
and
Configuring
I
l":l
Accessing
the
Logic
Analyzer
File
I
LJ
System
Using
the
X
Window
Interface
I
Retrieving
and
Restoring
Data
I
Programming
the
Logic
Analyzer
I
Concepts
I
Troubleshooting
I
Glossary
I
Index
I
iii