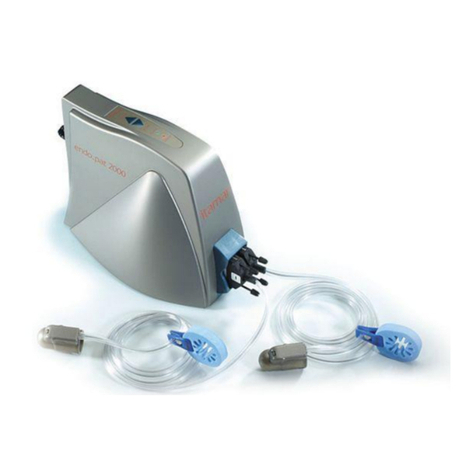
2Endo PAT™x Device Operation Manual
Itamar Medical Ltd.
The Gold Standard for Endothelial Dysfunction evaluation, the Intra-coronary Acetylcholine
(Ach) Challenge method, is routinely performed at the Mayo Clinic.
According to the Intra-coronary Acetylcholine (Ach) Challenge method, a catheter is positioned
in the origin of the left main coronary artery and Ach is infused with incremental concentration
followed by coronary angiogram. The coronary artery diameter is measured in the segment
5mm distal to the tip of a Doppler wire using a computer-based image analysis system. Average
peak velocity (APV) is derived from the Doppler ow velocity spectra and coronary blood ow
(CBF) is determined as: π*(coronary artery diameter/2)
2
*(APV/2). Endothelium-dependent
coronary ow reserve is calculated as percent change in CBF in response to the Ach challenge.
Normal coronary endothelial function is dened as an increase in CBF of >50% and an
increase or less than 20% decrease in the coronary artery diameter in response to the
maximum dose of intra-coronary Ach (ΔCBF > 50% and ΔCAD > -20%)
[Al Suwaidi J, Hamasaki S, Higano ST, Nishimura RA, Holmes DR Jr, Lerman A. Long-term
follow-up of patients with mild coronary artery disease and endothelial dysfunction.
Circulation
101:948-954, 2000]
Synopsis of Clinical Study Protocol:
Objectives:
To evaluate the EndoPATTM2000 device relative to a gold standard procedure as a diagnostic aid for detecting
coronary endothelial dysfunction.
Methodology:
Patients, who had been referred to diagnostic angiography cardiac catheterization laboratory for
diagnostic angiography secondary to signs or symptoms of ischemic heart disease and suspected coronary
endothelial dysfunction and were found to have normal or near to normal angiogram, underwent Intra-
coronary Acetylcholine (Ach) challenge test to assess attenuation in required increases to coronary
blood ow (CBF) and coronary artery diameter (CAD), where each of these parameters served as an
indicator for coronary endothelial dysfunction. Coronary endothelial dysfunction is diagnosed if one
of the following changes is observed in response to the Ach challenge test: ΔCBF ≤ 50% OR ΔCAD ≤
-20%. Patients were then evaluated using the EndoPATTM 2000, which measures Peripheral Arterial Tone
(PATTM) signal changes at the ngertip, to a reactive hyperemia challenge. The PATTM signal is a measure
of the digital pulsatile volume changes and is measured with a non-invasive disposable PATTM probe.
The reactive hyperemia procedure consists of a 3-10 minute baseline recording, 3-5 minutes of blood
ow occlusion to one arm using an lower arm blood pressure cuff, and 3-5 minutes of recording after
cuff release. The expected response is of a post occlusion increase of the PATTM signal amplitude and
the PATTM score is provided automatically by the system’s software and is basically the ratio between
the post- to pre- occlusion average signal size, corrected for systemic changes and baseline level.
Planned Enrollment: 100 patients
Actual Enrollment: 111
Safety Analysis Cohort: 110 (One patient withdrew consent)
Efcacy Analysis Cohort: 94