IWILL DGL200 User manual
Other IWILL Motherboard manuals

IWILL
IWILL P4GB Series User manual

IWILL
IWILL K7S3 Series User manual

IWILL
IWILL DK8S User manual

IWILL
IWILL DP400 User manual

IWILL
IWILL DNS-SATA User manual
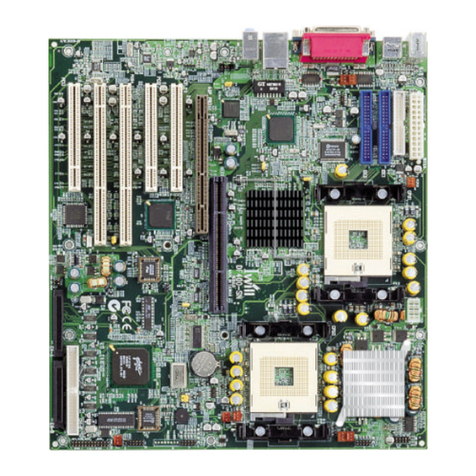
IWILL
IWILL DX400-SN User manual

IWILL
IWILL KK266Plus User manual

IWILL
IWILL Motherboard DJ800 User manual

IWILL
IWILL DH800 User manual

IWILL
IWILL DP533 Series User manual

IWILL
IWILL DPX2-S320 User manual

IWILL
IWILL P4SE2 User manual

IWILL
IWILL DPIILS2 User manual

IWILL
IWILL BS100 User manual

IWILL
IWILL P55TU User manual

IWILL
IWILL mP4G2 Series User manual

IWILL
IWILL P4DA User manual
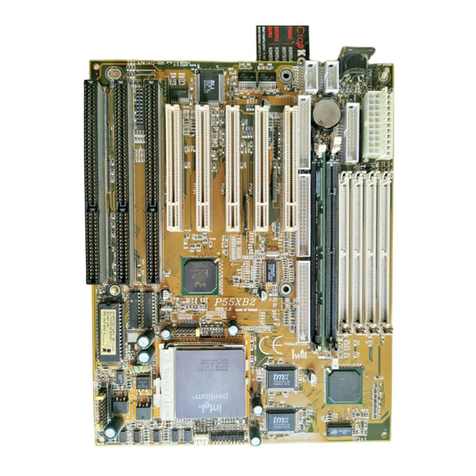
IWILL
IWILL P55XB2 User manual

IWILL
IWILL P4G Series User manual

IWILL
IWILL FB24624100 User manual































