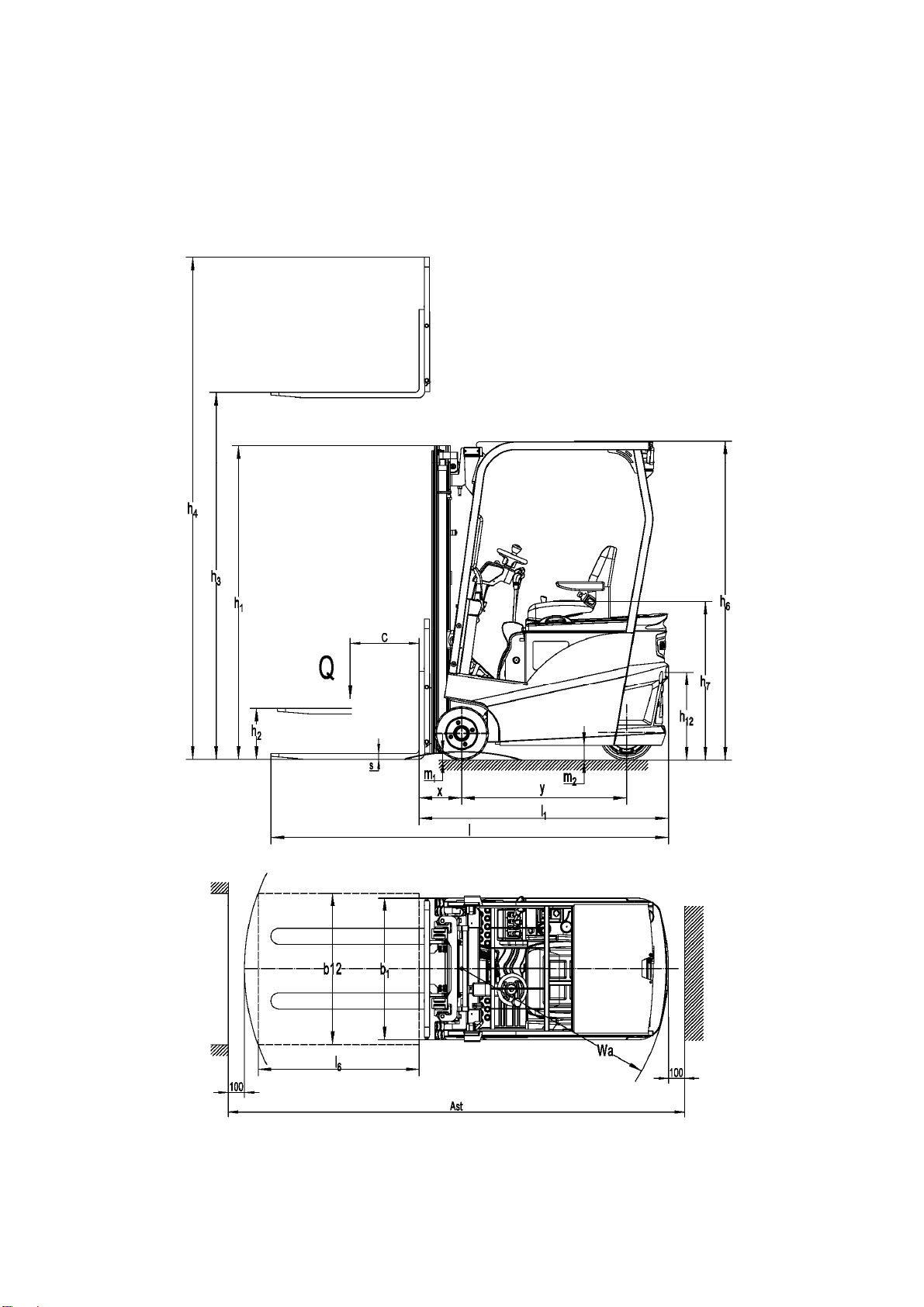
5
Chapter 1 Precautions of using forklift
Forklift drivers and managers must remember the principle of "safety first", and carefully read
this maintenance manual. Operators shall be in strict accordance with this manual to ensure safe
and normal operation.
. Forklift transportationⅠ
The following shall be noted when transporting forklift by container or trucks:
(1) Apply the parking brake;
(2) Fix the main frame and counterweight with steel wires, and use pads to wedge the
corresponding positions at the front and rear tires;
(3) Start lifting from the positions indicated by the "Craning Label" on the forklift.
ⅡForklift storage
(1) Reduce the main frame to the lowest position;
(2) Turn off the electric lock, place the lever rod to the "Nertral" position and unplug the power
cord;
(3) Tighten the hand brake;
(4) Use pads to wedge the front and rear tires ;
(5) If the forklift is to be left unused for a long time, its wheels should be elevated. The
accumulator should be recharged once a month.
PreⅢ-use preparation
(1) Check if all instruments are normal;
(2) Check the tire pressure;
(3) Check the condition of the levers and pedals;
(4) Check if the accumulator voltage is within the working scope, and if the specific gracity of
the electrolyte and the height level of the liquid are appropriate;
(5) Check if the connectors and plug contacts of the electrical system are reliable;
(6) Check for leakage of the hydraulic fluid, electrolyte and brake fluid;
(7) Check the tightness of major fasteners;
(8) Check if the lighting and signal lamps are normal;
(9) Release the parking brake;
(10) Conduct test actions such as lifting and lowering the main frame, tilting forwards and
backwards, steering and braking;
(11) Contamination level of hydraulic oil shall not be greater than 12.
Ⅳ. Operation of the forklift
(1) Only trained and licensed drivers can drive the forklift;
(2) Operators shall wear security shoes, hats, clothing and gloves for protection purpose;
(3) Operators should note the performance and working conditions of mechanical, hydraulic,
electrical and MOSFET governor;
(4) Power on by switching on the key switch, choose the right position of direction switch, and
then rotate the steering wheel to see if the forklift can steer.
If ok, slowly depress the speed pedal and maintain an appropriate speed;
(5) Observe the voltage meter, if the voltage indicated by the voltage meter is below 41V
during working, immediately stop operation, and recharge the accumulator or replace with another
fully charged accumulator;
(6) Weight of loads handled should not exceed the specified value and fork spacing and
location should be appropriate. The fork should be fully inserted below all the goods, which shall
be uniformly distributed on the fork. Uneven loading shall be avoided;
(7) If the distance between loads‘ center of gravity and the fork arm is no more than 500mm, the
maximum load shall be the rated capacity. If the distance between loads‘ center of gravity and the fork
arm is more than 500mm, the maximum load shall be less than the rated capacity;
(8) When carrying loads, the main frame should tit backwards to the maximum extent and the
fork arm should be in contact with the goods. Raise the fork to about 200mm away from the
ground before driving;
(9) Standing under the fork and on the lifting fork are forbidden;