Norgren FD67 User manual

PROFIBUS-DP MANUAL FOR
FD67 MODULES
ISSUE 1

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
Table of contents
1REGARDING THIS MANUAL ...................................................................................1
1.1 Chapter overview........................................................................................................................ 1
2SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS ........................................................................................2
2.1 Designated use........................................................................................................................... 2
2.2 Qualified personnel .................................................................................................................... 3
2.3 Explanation of symbols.............................................................................................................. 4
2.3.1 Use of attention signs............................................................................................................... 4
2.3.2 Use of danger signs ................................................................................................................. 4
2.3.3 Use of numbering in illustrations...............................................................................................4
2.3.4 Use of handling instructions...................................................................................................... 4
2.3.5 Use of foot notes...................................................................................................................... 4
3CONFIGURATION INFORMATION ..........................................................................5
3.1 FD67 in a Profibus-DP network.................................................................................................. 5
3.1.1 System components................................................................................................................. 5
3.1.1.1 Profibus cables............................................................................................................... 5
3.1.2 General information for successful planning in a Profibus network ............................................ 6
3.1.3 Topology .................................................................................................................................. 6
3.1.4 Termination of bus segments.................................................................................................... 6
3.1.5 Baud rate ................................................................................................................................. 7
3.1.6 Address.................................................................................................................................... 7
3.1.7 Spur lines................................................................................................................................. 7
3.1.8 Design guidelines..................................................................................................................... 7
4MOUNTING AND WIRING........................................................................................ 8
4.1Bus node......................................................................................................................................8
4.2 Assembling the hood of the bus node....................................................................................... 9
4.3Functionalground....................................................................................................................10
4.4 Power supply............................................................................................................................ 11
4.5 Profibus connection ................................................................................................................. 12
4.6 Terminal resistors..................................................................................................................... 13
5SETUP ....................................................................................................................14
5.1 GSD file ..................................................................................................................................... 14
5.2 Allocating and setting the Profibus address........................................................................... 15

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
5.3 Configuration.............................................................................................................................16
5.3.1 Placeholder.............................................................................................................................16
5.3.2 Structure of a configuration string............................................................................................17
5.3.3 Replacing DI modules by DIO modules ...................................................................................18
5.3.4 Configuration examples...........................................................................................................19
5.3.4.1 Configuration of compact modules.................................................................................19
5.3.4.2 Configuration with placeholders .....................................................................................20
5.3.4.3 Configuration with expander modules ............................................................................22
5.3.4.4 Configuration with preconfigured modules .....................................................................23
5.3.4.5 Manual assembling of a configuration string ..................................................................24
5.4 Parameterisation .......................................................................................................................25
5.4.1 Parameter message................................................................................................................26
5.4.1.1 Structure of the standard specific parameters (bytes 0 to 6) ...........................................26
5.4.1.2 User parameters............................................................................................................27
5.4.2 Preconfigured modules ...........................................................................................................28
6SETUP EXAMPLE : STEP BY STEP ..................................................................... 29
6.1.1 Mechanical structure ...............................................................................................................29
6.1.1.1 Mounting the hood of the bus node................................................................................29
6.1.1.2 Interconnecting system components..............................................................................30
6.1.2 Configuration with S7 Hardware Manager ...............................................................................31
7DIAGNOSIS ............................................................................................................ 34
7.1.1 Behaviour in case of interrupted communication......................................................................34
7.2 LED displays..............................................................................................................................35
7.2.1 General information.................................................................................................................35
7.2.2 Bus node ................................................................................................................................35
7.2.2.1 Bus node response to faulty supply voltage ...................................................................37
7.2.3 Displays of digital I/O modules ................................................................................................38
7.2.3.1 LED displays of digital I/O modules................................................................................38
7.2.3.2 Relationship between signal-logical representation and LED response .........................40
7.2.4 Displays of analogue I/O modules ...........................................................................................41
7.2.4.1 Bus IN – LED displays...................................................................................................41
7.2.4.2 M12 sockets – LED Diagnosis displays..........................................................................41
7.2.5 Power distributor displays .......................................................................................................42
7.3 Profibus .....................................................................................................................................43
7.3.1 Diagnosis Overflow .................................................................................................................44
7.3.2 Structure of a diagnosis message............................................................................................45
7.3.2.1 Bytes 0 to 5 : standard diagnostic information ................................................................45
7.3.2.2 Station-related diagnosis bytes 6 to 25 ..........................................................................47
7.3.2.3 ID-related diagnosis bytes 26 to 28................................................................................55
7.3.2.4 Channel-related diagnosis bytes 29 to 31 and following .................................................56
7.4 Evaluation ofthe diagnosismessage in the PLC.....................................................................58
7.5 Troubleshooting.........................................................................................................................58
7.5.1Troubleshooting ina Profibus network.....................................................................................59
7.5.2 Troubleshooting in the internal system connection...................................................................60
8MODULES .............................................................................................................. 61
8.1 FD67NDPM127804 .....................................................................................................................61
8.2 Digital I/O modules....................................................................................................................63
8.2.1 FD67DIOM121216..................................................................................................................64
8.2.1.1 Identification..................................................................................................................64

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
8.2.1.2 Bit assignments of I/O data........................................................................................... 64
8.2.1.3 Coding of functions....................................................................................................... 64
8.2.1.4 Parameter bytes ........................................................................................................... 65
8.2.1.5 Bit assignments of parameter bytes .............................................................................. 65
8.2.2 FD67DIOM120016 ................................................................................................................. 66
8.2.2.1 Identification ................................................................................................................. 66
8.2.2.2 Bit assignments of I/O data........................................................................................... 66
8.2.2.3 Coding of functions....................................................................................................... 66
8.2.2.4 Parameter bytes ........................................................................................................... 67
8.2.2.5 Bit assignments of parameter bytes .............................................................................. 67
8.2.3 FD67DIM120016.................................................................................................................... 68
8.2.3.1 Identification ................................................................................................................. 68
8.2.3.2 Bit assignments of I/O data........................................................................................... 68
8.2.3.3 Coding of functions....................................................................................................... 68
8.2.3.4 Parameter bytes ........................................................................................................... 69
8.2.3.5 Bit assignments of parameter bytes .............................................................................. 69
8.2.4 FD67DIOM120008 ................................................................................................................. 70
8.2.4.1 Identification ................................................................................................................. 70
8.2.4.2 Bit assignments of I/O data........................................................................................... 70
8.2.4.3 Coding of functions....................................................................................................... 70
8.2.4.4 Parameter bytes ........................................................................................................... 71
8.2.4.5 Bit assignments of parameter bytes .............................................................................. 71
8.2.5 FD67DIM120008.................................................................................................................... 72
8.2.5.1 Identification ................................................................................................................. 72
8.2.5.2 Bit assignments of I/O data........................................................................................... 72
8.2.5.3 Coding of functions....................................................................................................... 72
8.2.5.4 Parameter bytes ........................................................................................................... 73
8.2.5.5 Bit assignments of parameter bytes .............................................................................. 73
8.2.6 FD67DIOM080008 ................................................................................................................. 74
8.2.6.1 Identification ................................................................................................................. 74
8.2.6.2 Bit assignments of I/O data........................................................................................... 74
8.2.6.3 Coding of functions....................................................................................................... 74
8.2.6.4 Parameter bytes ........................................................................................................... 75
8.2.6.5 Bit assignments of parameter bytes .............................................................................. 75
8.2.7 FD67DIM080008.................................................................................................................... 76
8.2.7.1 Identification ................................................................................................................. 76
8.2.7.2 Bit assignments of I/O data........................................................................................... 76
8.2.7.3 Coding of functions....................................................................................................... 76
8.2.7.4 Parameter bytes ........................................................................................................... 77
8.2.7.5 Bit assignments of parameter bytes .............................................................................. 77
8.3 Analogue I/O modules.............................................................................................................. 78
8.3.1 Specific characteristics........................................................................................................... 78
8.3.1.1 Smoothing (AI modules only) ........................................................................................ 78
8.3.1.2 Delta (AI modules only)................................................................................................. 78
8.3.2 FD67AIVM120004.................................................................................................................. 79
8.3.2.1 Identification ................................................................................................................. 79
8.3.2.2 I/O data ........................................................................................................................79
8.3.2.3 Parameter bytes ........................................................................................................... 80
8.3.2.4 Bit assignments of parameter bytes .............................................................................. 81

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
8.3.3 FD67AOVM120004.................................................................................................................82
8.3.3.1 Identification..................................................................................................................82
8.3.3.2 I/O data .........................................................................................................................82
8.3.3.3 Parameter bytes............................................................................................................83
8.3.3.4 Bit assignments of parameter bytes...............................................................................84
8.3.4 FD67AOCM120004.................................................................................................................85
8.3.4.1 Identification..................................................................................................................85
8.3.4.2 I/O data .........................................................................................................................85
8.3.4.3 Parameter bytes............................................................................................................86
8.3.4.4 Bit assignments of parameter bytes...............................................................................86
8.3.5 FD67AICM120004 ..................................................................................................................87
8.3.5.1 Identification..................................................................................................................87
8.3.5.2 I/O data .........................................................................................................................87
8.3.5.3 Parameter bytes............................................................................................................88
8.3.5.4 Bit assignments of parameter bytes...............................................................................88
8.3.6 FD67DODSC0016.......................................................................................................................89
8.3.6.1 Identification……………………………………………………………………………………….89
8.3.6.2 Bit assignments of I/O data…………………………………………………………………… 89
8.3.6.2.1 Output data ODM…………………………………………………………………………………89
8.3.6.3 Parameter bytes.................................................................................................................89
9GLOSSARY ............................................................................................................ 90
9.1 General information about the Profibus...................................................................................90
9.2 FD67 specific.............................................................................................................................91
10 INDEX OF FIGURES ........................................................................................... 92
11 INDEX OF TABLES............................................................................................. 93

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
1
1 Regarding this manual
This manual is intended for Profibus system planners. It contains Profibus specific properties of the FD67
system. Please refer to the System manual for general field bus information. The Technical Data Manual
contains detailed information relevant to technical data, installation and setup of the different Input/Output
modules.
User's manuals for modules of the FD67 series :
" FD67 System handbook,
" FD67 Bus system handbook Profibus
DeviceNet
" FD67 Technical manual
Take care to read the relevant instruction manuals prior to starting up the equipment. The instruction
manuals should be kept in a safe place accessible to all users at all times.
The text, illustrations, diagrams and examples presented in this manual serve solely for the purpose of
explanation, operation and use of Input/Output modules of the FD67 series.
If you should have any further reaching questions regarding the installation and set-up of the equipment
described in this manual, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We would be glad to assist you any time.
Internet : http://www.norgren.com
Norgren reserves the right to change technical specifications or contents of this manual at any time
without notice.
1.1 Chapter overview
The “Safety information” section must be read without fail prior to working with the products and the
system. This section contains information required for safe installation and handling.
The “Configuration Information“ section directs itself to system planners. It offers important information
and details relevant to successful configuration.
The chapter "Mounting and wiring" provides detailed information on mechanical and electrical installation
of the FD67 Profibus-DP node.
The chapter "Setup" is directed towards specialist personnel responsible for startup. It gives important
information for quick and easy startup in a Profibus-DP network.
The chapter "Setup example : step by step shows the setup of a simple FD67 system in a Simatic
environment.
The chapter "Diagnosis" describes visual diagnosis displays and the structure of Profibus diagnostic data.
The "Module" section refers to the structure of parameters and I/O data of the different I/O modules. y of
technical terms can be found at the end of the manual.

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
2
2 Safety instructions
2.1 Designated use
The devices described in this manual serve as decentralized input/output units for connection to a
Profibus-DP network.
The products described in this manual
• were developed, manufactured, inspected and documented in accordance with the applicable safety
standards. These products do not normally pose a danger to persons or property, provided that the
applicable operating and safety instructions for configuration, assembly and operation in the manner
intended are observed.
• meet the requirements set forth in the
• EMC Directive (89/336/EEC, 93/68/EEC and 93/44/EEC)
• Low Voltage Directive (73/23/EEC)
• are designed for use in industrial applications. A characteristic of the industrial environment is that
consumers are not directly connected to the public low voltage system. Extra precautions are
required for use in residential, business and commercial applications.
Warning !
This equipment has a Class A rating and can cause
radio frequency interference in residential areas. In such cases, the operator can be
asked to take appropriate precautions.
Troublefree and safe function of this equipment is guaranteed only if the conditions for proper transport,
storage, installation and assembly are observed.
The designated operation of the equipment is guaranteed only with the housing fully installed.
All devices connected to this equipment must fulfil EN 61558-2-4 and EN 61558-2-6 requirements.
Only qualified and suitably trained electrical tradesmen knowledgeable in the safety standards of
automation technology may perform configuration, installation, setup, maintenance and testing of the
equipment.
Current safety and accident prevention laws valid for a specific application must be observed in the
configuration, installation, setup, maintenance and testing of the equipment.
Only cables and accessories are allowed which meet the requirements and regulations for safety,
electromagnetic compatibility and, where applicable, telecommunication transmission equipment and
specifications.
Information concerning the type of authorized cables and accessories that can be obtained either from
Norgren or your Norgren distributor are described in this manual.

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
3
2.2 Qualified personnel
Requirements to be met by qualified personnel are based on qualifications profiles described in ZVEI and
VDMA guidelines.
Weiterbildung in der Automatisierungstechnik (Further training in automation technology)
Herausgeber: ZVEI und VDMA (Publisher : ZVEI and VDMA)
Maschinenbau Verlag
Posfach 71 08 64
60498 Frankfurt
Only trained electricians familiar with the contents of this manual may be allowed to install and service the
components described here.
These are understood as being persons who,
• based on their trade qualification, experience and knowledge of relevant standards, are able to
assess the project requirements and to recognize possible hazards.
• based on extensive experience in comparable areas, possess the same level of knowledge as could
be expected of a trained tradesman.
Only Norgren technical personnel are allowed to undertake intervention in the hardware and software of
our equipment, unless the procedure is described in this manual.
Warning !
Unqualified intervention in the hardware and software of our equipment or disregard
of warnings and information provided in this manual can result in injury or serious
damage to man and/or material.

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
4
2.3 Explanation of symbols
2.3.1 Use of attention signs
Notes containing important information are specially marked. These are illustrated as follows :
Attention text ........
2.3.2 Use of danger signs
Danger signs are additionally marked with an enclosing frame.
CAUTION :
Disregard of safety measures may result in damage to equipment and other serious
consequences.
DANGER :
Non-compliance with the relevant safety measures poses a danger to the health
and life of the user.
2.3.3 Use of numbering in illustrations
Illustrations are numbered with white numbers on a black, round field.
Example : #Text 1......
$Text 2......
%Text 3......
The explanatory text follows in tabular form under the same number, in direct context to the preceding
illustration.
2.3.4 Use of handling instructions
Handling instructions describe the sequence of steps during installation, setup, operation and
maintenance that must be strictly observed.
Figures are numbered continuously in ascending order using black numbers in round, white fields.
Example : &Instruction 1........
'Instruction 2........
(Instruction 3........
2.3.5 Use of foot notes
Supplementary information is marked with superscripted numerals (example: Text Text 1) Text Text).
These are explained in the form of footnotes beneath tables or text at the end of the page.

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
5
3 Configuration information
This chapter contains indications and information required for successful installation of your system in a
Profibus-DP network. General field bus information relevant to configuration, installation and operation of
FD67 systems can be found in the following manuals :
FD67 – System manual
FD67 – Technical manual
3.1 FD67 in a Profibus-DP network
FD67 is a modular I/O system designed for decentralized gathering and processing of digital and
analogue process variables. It is made up of a field bus specific bus node and field bus-oriented I/O
modules, which are connected to the bus node via internal system connection.
3.1.1 System components
Min. configuration of a Profibus-DP network :
- one or several bus masters.
- one or several slaves.
- Profibus cables and plugs to interconnect the system units.
- one ore several bus segments linked up by repeaters.
3.1.1.1 Profibus cables
Use only A-type cables, according to EN 50 170 part 8-2. Type B cables are obsolete and should
basically not be used.
Parameter A-type cable
Impedance level / Ω135 to 165 at a frequency of 3 to 20 MHz
Operating capacity (pF/m) ≤30
Loop resistance (Ω/km) ≤110
Wire diameter (mm) > 0,64
Wire cross section (mm2) > 0,34
The wire cross section used must fit the connection possibilities on the bus connector.

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
6
3.1.2 General information for successful planning in a Profibus network
Up to 32 units (including repeaters) are allowed in a bus segment.
According to the selected baud rate, the extension of a Profibus segments must not exceed the max.
recommended values ; see Table 3-1.
Repeaters can be used to divide a network into several segments. So it is possible to operate more than
32 units in an extended Profibus network. However signal delays resulting from the installation of
repeaters must be considered during configuration of the system. Up to 9 repeaters can be installed
between two units.
3.1.3 Topology
♦ Fig. 3-1 : Example of a Profibus network
3.1.4 Termination of bus segments
Both sides of a segment must be fitted with a terminal resistor. The terminal resistors must be supplied to
guarantee a correct physical signal level.
The terminal resistor is either located in the connector or directly integrated into the device. In both cases
it must be observed that in case of failure or application-related voltage cut-off of the unit at the end of a
segment, the terminal resistor may also be switched off to the detriment of the operatability of the whole
segment.
So it might be preferable to install be bus master at the beginning or the end of the bus segment. In case
of breakdown of the bus master, the switching off of the terminal resistor is of no importance. Additional
repeaters or externally supplied terminal resistors may be installed for reliable termination of the other
end of the segment.
The need of additional measures must be determined for every specific case.
Fig. 3-1 shows an example of correct termination in a typical Profibus network.
MASTER
Slave Slave Slave Slave
Repeater
Repeater Slave
Slave SlaveSlave
Terminal resistor

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
7
3.1.5 Baud rate
All the devices in a Profibus network use the same baud rate set by the bus master. It is automatically
recognized by the FD67 bus node.
According to the selected baud rate, the max. admissible cable lengths must be observed (see Table 3-1
below). These values relate to a single bus segment. By using repeaters, it is possible to achieve greater
network extensions over several segments.
Baud rate in kBit/s 9,6 19,2 45,45 93,75 187,5 500 1500 3000 6000 12000
Cable length in m 1200 1200 1200 1200 1000 400 200 100 100 100
♦ Table 3-1 : Max. admissible cable lengths in a Profibus segment
3.1.6 Address
Profibus user addresses range from from 0 to 125. The two address switches of the FD67 bus node allow
to set addresses from 0 to 99.
It is important to ensure that an explicit and unique address is assigned to each Profibus user. The
Profibus address is set directly at the FD67 bus node via two BCD switches that are integrated into to the
base module.
The set address is read in once after a voltage reset. A change of address in operation is not supported.
Detailed information can be found in the FD67 System manual.
3.1.7 Spur lines
As a rule, passive spur lines should be avoided.
If spur lines are required, e.g. for temporary connection to programming or diagnostic devices, use active
spur lines or repeaters. Correct termination must always be assured.
3.1.8 Design guidelines
Design guidelines have been issued by the Profibus User Organization (PNO). They must be strictly
observed, as well as the information contained in the FD67 manuals. See the PNO homepage :
www.profibus.com

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
8
4 Mounting and wiring
Installation and wiring information relevant to I/O modules and internal system connection can be found in
the manual FD67 – Technical manual.
CAUTION :
Mounting, wiring and setting of the Profibus address must be performed while the
equipment is not under power.
4.1 Bus node
Initial contitions
♦ Smooth and flat mounting surface.
♦ The system is dead (cut off).
Mounting material
♦ 2 fastening screws 4 mm in diameter.
♦ 2 DIN 433 T1/T2lock washers.
Tools
♦ Screwdriver, middle-sized
a) Mounting the base module of the bus node
Attach the module to the mounting holes by means of the 2 fastening screws 4 mm in diameter.
The tightening torque is : 2 Nm.
b) Setting the Profibus address
Two address switches are provided to set the bus node address in the Profibus network. Values
between 1 and 99 are allowable.
Two units in a Profibus network must be clearly identifiable ; therefore they must not
be allocated to the same address.
The set address is read in once after the supply voltage is applied. Therefore, a
change of address only takes effect after a module voltage reset.

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
9
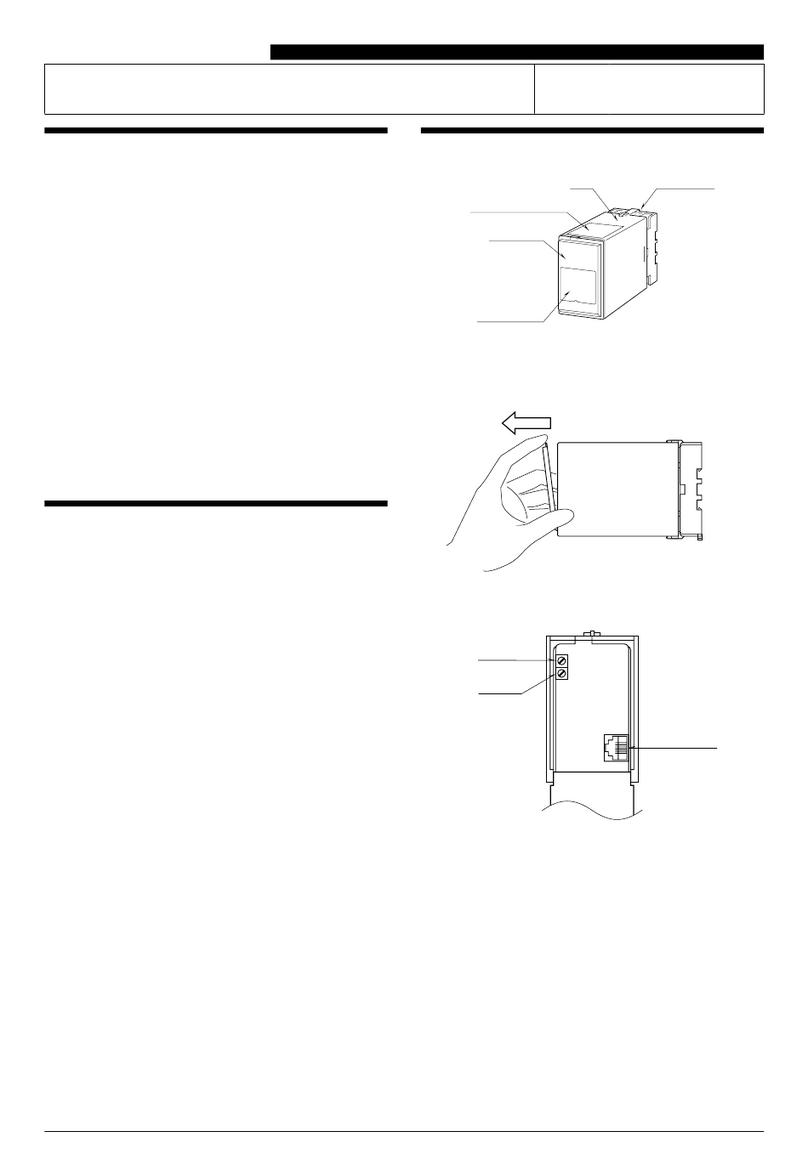
4.2 Assembling the hood of the bus node
Before assembling the hood, it is advisable to set the Profibus address, because the
switches are no more accessible when the hood is attached. It is also recommended
to note the set Profibus address on a label plate.
)
*
%
$
+
♦ Fig. 4-1 : Assembling the hood of the bus node
$ Fastening screws ) Profibus address switches
% Hood * Base module
+ Functional ground connection
&Wire the functional ground connection of the hood.
'Mount the hood on the base module.
(Screw the hood %onto the base module *. The screws are integrated into the hood $. Make sure
that the screws are equally tightened.
The hood must be screwed onto the base module and all the connectors must be
fitted with cables or blind caps in compliance with type IP 67 specifications.

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
10
4.3 Functional ground
Initial conditions
♦ Wiring must be performed while the equipment is not under power.
Tools
♦ Screwdriver
♦ Stripper
♦ Cable terminal pliers
Accessories
♦ Fastening screw
♦ Cable terminal and locking ring
♦ Ground cable (wire)
The FE connection is located on the bottom side of the bus node hood.
$
♦ Fig. 4-2 : FE connection
$ FE connection
The connection cable of the functional ground must be kept as short as possible, in
accordance with EMC specifications.

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
11
4.4 Power supply
Initial conditions
Wiring must be performed while the equipment is not under power.
Tools
Stripper, screwdriver and a special tool if you do not use pre-wired conductors. Possibly a tool to screw
down the knurled ring.
Connecting the power connector 7/8“
&Insert the plug of the power connector into the corresponding socket of the bus node. See to it that
the ends meet exactly and make sure that the plug is completely stuck into the socket.
' Screw down the plug with the knurled ring.
Pin 1 0 V1
Pin 2 0 V
Pin 3 PE
Pin 4 Sensor & Bus supply
Pin 5 Actuator supply
♦ Fig. 4-3 : Pin assignments of the 7/8“ power connector 7/8“ (Mini-Style)
♦ Fig. 4-4 : Assembly of the 7/8“ power connector (Mini-Style)
The max. admissible cable cross-section 1.5 mm². It is limited by the 7/8" connector.
CAUTION :
Reverse polarity of the power supply can damage the module.
1The 0V reference at Pin 1 and Pin 2 is connected in the device.
POWER
12
3
45

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
12
4.5 Profibus connection
Initial conditions
Wiring must be performed while the equipment is not under power.
Tools
Stripper, screwdriver and a special tool if you do not use pre-wired conductors. Possibly a tool to screw
down the knurled ring.
Connecting the Profibus cable
&Insert the plug of the Profibus cable into the corresponding socket of the bus node. See to it that
the ends meet exactly and make sure that the plug is completely stuck into the socket.
' Screw down the plug with the knurled ring.
Bus In Bus Out
Contact Signal Signification
1 VP Power supply-Plus (P 5 V)
2 RxD/TxD-N RxD/TxD–N, A-line (green)
3 DGND Data transfer potential (reference potential to VP)
4 RxD/TxD-P RxD/TxD–P, B-line (red)
5 Screen Screen or ground
Thread Screen Screen or ground
♦ Fig. 4-5 : Contact assignments of Profibus M12 sockets (B-encoded)
40 mm
7 mm
%
$
+
)
♦ Fig. 4-6 : Assembling of the Profibus cable
The shield should preferably be applied over the surface of the thread. If this is not
possible, the shield can be connected via Pin 5. Both possibilities for applying the
shield can also be used together.
$Bus cable
%Screen
+Green line (A)
)Red line (B)
BUS IN
52
3
4
1
BUS OUT
1
2
3
4
5

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
13
4.6 Terminal resistors
Both sides of a Profibus segment must be fitted with a terminal resistor. In case of a FD67 bus node, the
terminal resistor must be installed on the connector of the extension Profibus interface of the hood.
Part No. Description
FD67K Profibus-DP terminal resistor
FD67BLKM120000 M12 x 1 FD67 blanking cap (4 pcs)
Initial conditions
- The terminal resistor must be screwed down while the system is not under power.
- The bus node is located at the beginning or at the end of a Profibus segment.
Tools
Possibly a tool to screw down the knurled ring.
Connecting the terminal resistor
&Insert the terminal resistor into the corresponding socket of the extension Profibus interface of the
hood. See to it that the ends meet exactly and make sure that the plug is completely stuck into the
socket.
' Screw down the terminal resistor with the knurled ring.

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
14
5 Setup
5.1 GSD file
For operation of the devices described in this manual, you require the GSD file
FD67 GSD file
The GSD file can be ordered through Norgren’s Internet homepage :
http://www.Norgren.com/
or through your branch of Norgren.

FD67 Profibus-DP Manual
15
5.2 Allocating and setting the Profibus address
The Profibus address is set directly at the FD67 bus node via two BCD switches. Values between 1 and
99 are allowable.
The set address is read in once after the supply voltage is applied. Therefore, a
change of address only takes effect after a module voltage reset.
It is important to ensure that an explicit and unique address is assigned to each
Profibus user.
Table of contents
Other Norgren Control Unit manuals

Norgren
Norgren VP23 Series User manual

Norgren
Norgren Prospector A00 5A Series User manual

Norgren
Norgren VR10 Instruction Manual

Norgren
Norgren VS18 Manual

Norgren
Norgren VP60 Series User manual

Norgren
Norgren VR10 Installation and operating instructions

Norgren
Norgren HERION G1/4 User manual

Norgren
Norgren VP51 User manual

Norgren
Norgren 82 Series User manual
Popular Control Unit manuals by other brands
Emerson
Emerson Numatics DeviceLogix G2-2 Series Quick start manual
Turbonetics
Turbonetics Evolution Wastegate 10780 Installation instructions manual

Simplex
Simplex 2004 Series installation guide

SMA
SMA 1C4-313-001-001 Replacement manual

H3C
H3C MSR Router Comware 5 Series Guide

Festo
Festo CPX-E-1CI manual