Nortel IW SPM IP User manual
Other Nortel PBX manuals

Nortel
Nortel Compact ICS Telephone Feature Card User manual

Nortel
Nortel Meridian 1 Succession 1000 Operating and installation instructions

Nortel
Nortel Meridian 1 Succession 1000 Operating and installation instructions

Nortel
Nortel Meridian 1 PC Console Interface Unit Operating manual

Nortel
Nortel Meridian ITG Line 2.0 Operating and installation instructions

Nortel
Nortel Meridian Meridian 1 User manual

Nortel
Nortel Meridian Meridian 1 User manual

Nortel
Nortel Meridian Companion Product manual

Nortel
Nortel Meridian Meridian 1 User manual

Nortel
Nortel Meridian 1 Succession 1000M Operating and maintenance instructions

Nortel
Nortel Meridian Companion User manual

Nortel
Nortel Meridian Meridian 1 User manual

Nortel
Nortel Meridian 1 PC Console Interface Unit User manual

Nortel
Nortel 1000 Con?guration guide User manual
Nortel
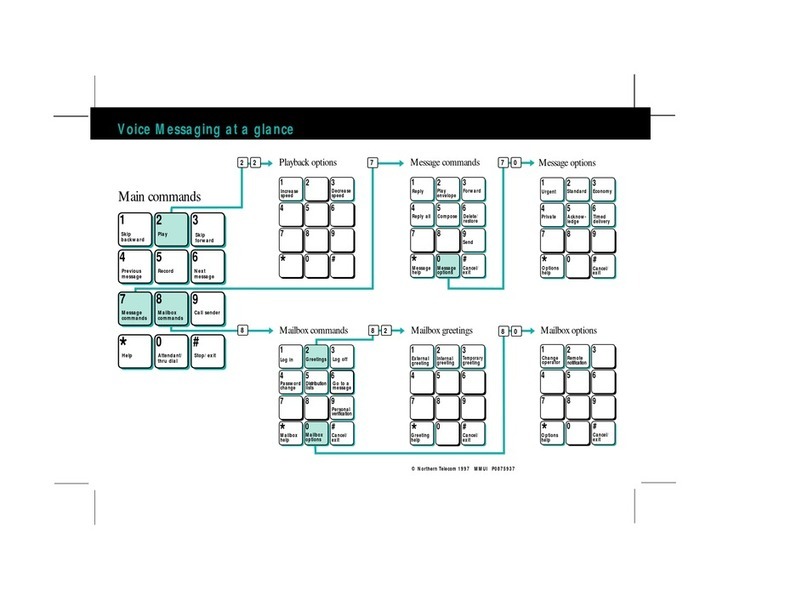
Nortel Meridian Mail User manual

Nortel
Nortel Meridian 1 Succession 1000 User manual

Nortel
Nortel Meridian SL-100 SE Use and care manual

Nortel
Nortel Meridian 1 PC Console Interface Unit User manual
Nortel
Nortel Meridian Mail Instruction Manual

Nortel
Nortel Meridian Companion Dimensions
Popular PBX manuals by other brands

Rauland-Borg
Rauland-Borg Telecenter IV Installation

Grandstream Networks
Grandstream Networks UCM6208 Quick installation guide

ATCOM
ATCOM IPPBX IP02 user manual

Panasonic
Panasonic KX-TVS50 - 2 Port Voicemail System installation manual

bintec elmeg
bintec elmeg elmeg hybird 600 installation guide

Panasonic
Panasonic KX-NS300 Getting started

























