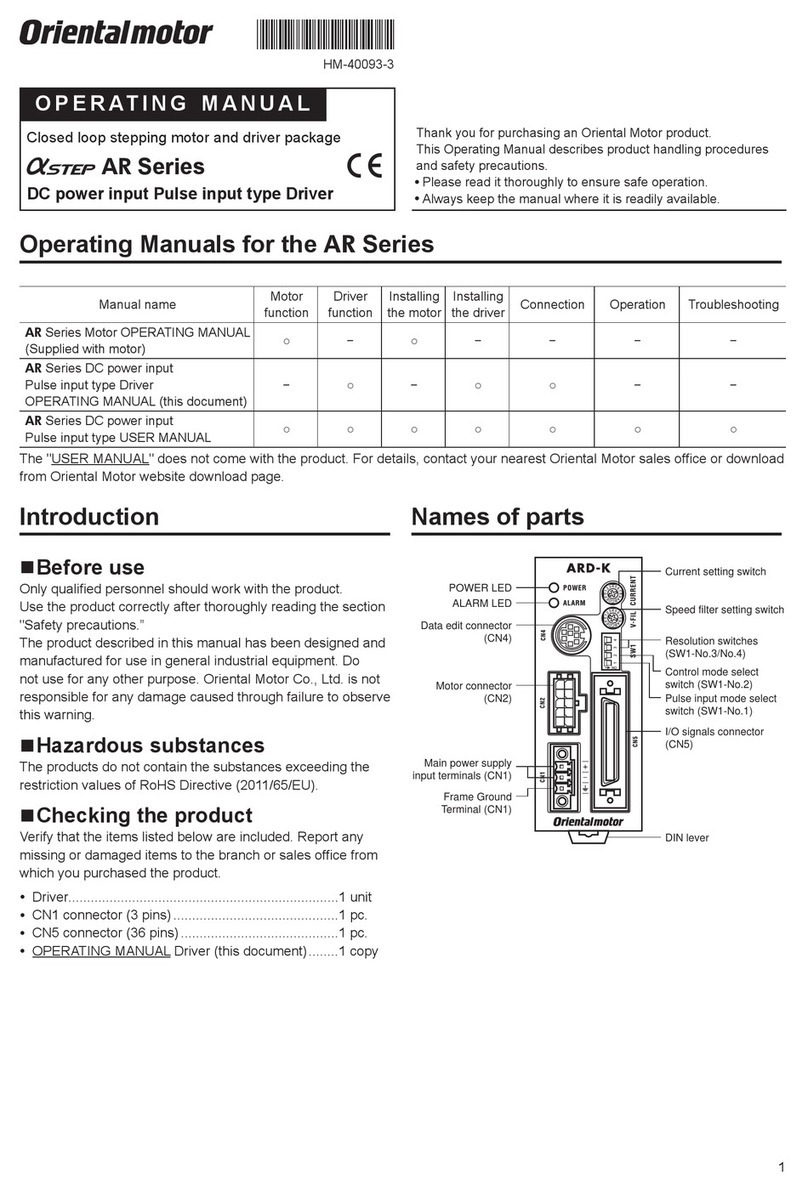
10
9. Locked rotor burnout protection
The motor is equipped with a protective function to prevent the motor from burning when the output shaft is locked.
Thermal protection
"TP" is stamped on the motor nameplate. The motor has an "auto reset" type thermal protector built into its motor coil. When the motor reaches a
predetermined temperature, the internal thermal protector is activated and the motor is stopped.
Always turn the power o before performing inspections.
Thermal protector activation range:
Power is turned o at 130±5 °C (266±9 °F)
Power is turned back on at 85±20 °C (185±36 °F)
10. Troubleshooting
When the motor cannot be operated properly, refer to the contents described in this section and take an appropriate remedial action. If the problem
persists, contact your nearest oce.
Condition Check item Remedial action
A motor does not rotate.
A motor may not rotate.
Check if the correct voltage is applied. Verify the voltage specications with the nameplate of the motor,
and apply the suitable voltage.
Check if the power supply and the motor are connected
properly. Refer to the connection diagram, and connect properly.
Check if there is disconnection or improper connection. Check the connection for the wiring, terminal block, and crimp
terminals, and connect properly.
Check if an overload is occurred. Reduce a load.
(For electromagnetic brake motors)
Check if the electromagnetic brake is released.
Refer to the connection diagram. Connect the lead wires
(orange) for electromagnetic brake properly and release the
electromagnetic brake.
The motor rotates in
the reverse direction.
Check if the power supply and the motor are connected
properly. Refer to the connection diagram, and connect properly.
(When a gearhead is used)
Check if the gear ratio that causes the gearhead output
shaft to rotate in the opposite direction to the motor
output shaft is used.
Check the rotation direction of the motor output shaft and that of
the gearhead output shaft, and perform connection properly.
Check if the direction viewed is correct.
The rotation direction represents that when viewed from the
motor output shaft side. Check the direction from which the
product is viewed.
The motor becomes
unusually hot.
[The motor case
temperature exceeds
90°C (194 °F).]
Check if the correct voltage is applied. Verify the voltage specications with the nameplate of the motor,
and apply the suitable voltage.
Check if an overload is occurred. Reduce a load.
Check if the ambient temperature exceeds the operating
range. Reconsider the ventilation condition.
Check if operating and stopping the motor are repeated
in a short cycle. Check if operated exceeding the rating of
specications.
Reconsider the operating cycle such as extending the stop time.
Perform forced cooling using a fan or reconsider the ventilation
conditions.
Noise is generated.
Check if the type o pinion for the motor and gearhead
is the same.
Refer to“Assembling the motor and gearhead” on p.6, and
assemble a gearhead having the same type of pinion as the
motor pinion shaft.“Combination of motors and gearheads”on
the p.3
(When a gearhead is used)
Check if the sound becomes smaller when a load is
increased.
If the sound becomes smaller when a load is increased, it may be
due to backlash of the gearhead. The noise can be suppressed if a
friction load is applied.