SATEL GSM-4/GSM-5 1
CONTENTS
1.
G
ENERAL
............................................................................................................................3
2.
M
ODULE FEATURES
..............................................................................................................3
3.
T
YPICAL MODULE APPLICATIONS
............................................................................................4
3.1 B
ACKUP COMMUNICATION PATH
.................................................................................................. 4
3.2 S
UPERVISION
/
CONTROL OF DEVICES
.......................................................................................... 5
3.3 S
IMULATION OF MONITORING STATION
......................................................................................... 5
3.4 I
NTEGRATION WITH
INTEGRA
CONTROL PANELS
......................................................................... 6
3.5 W
ORKING IN CONJUNCTION WITH
STAM-1
/
STAM-2
MONITORING STATION
................................. 6
3.6 W
ORKING IN CONJUNCTION WITH
PBX
STATIONS
......................................................................... 7
4.
D
ESCRIPTION OF THE MODULE
..............................................................................................7
4.1 D
ESCRIPTION OF THE ELECTRONICS BOARD
................................................................................. 7
4.2 LCD
DISPLAY
.............................................................................................................................. 9
4.3 LED
INDICATORS
[
ONLY
GSM-5] ............................................................................................... 11
4.4 B
UTTONS
................................................................................................................................. 12
4.4.1 Module restart ...................................................................................................................................12
4.5 A
UDIBLE SIGNALING IN THE MODULE
.......................................................................................... 13
4.5.1 When controlling inputs.....................................................................................................................13
4.5.2 When controlling outputs...................................................................................................................13
4.5.3 In service mode.................................................................................................................................13
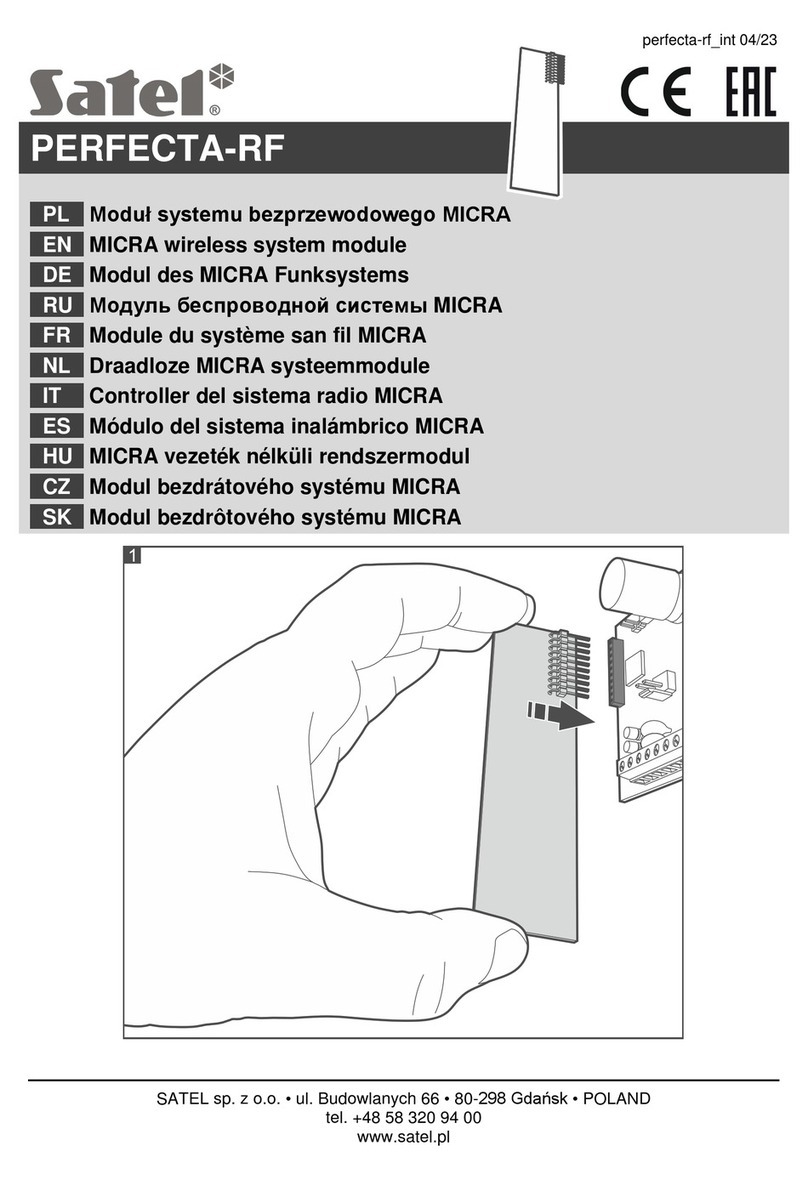
5.
I
NSTALLATION
....................................................................................................................13
6.
P
ROGRAMMING
..................................................................................................................14
6.1 S
ERVICE MODE
......................................................................................................................... 14
6.1.1 Service mode menu ..........................................................................................................................15
6.1.2 Description of functions available only in service mode ...................................................................21
6.1.3 Entering data by means of buttons ...................................................................................................21
6.2 D
LOAD
10
PROGRAM
................................................................................................................. 22
6.2.1 Local programming ...........................................................................................................................22
6.2.2 Remote programming .......................................................................................................................24
6.2.3 Main menu of D
LOAD
10 program ......................................................................................................25
6.2.4 Status bar..........................................................................................................................................26
6.2.5 Changing the program access code .................................................................................................26
6.2.6 "GSM-4 / GSM-5" tab........................................................................................................................27
6.2.7 "SIM 1/2" tab .....................................................................................................................................30
6.2.8 "Control/Inputs/Outputs" tab..............................................................................................................32
6.2.9 "Tel. messaging" tab .........................................................................................................................37
6.2.10 "Reporting" tab ..................................................................................................................................40
6.2.11 "Reporting – inputs" tab ....................................................................................................................44
6.2.12 "TCP/IP downloading" tab.................................................................................................................45
6.2.13 "Firmware update" tab.......................................................................................................................46
6.2.14 "Events buffer" tab ............................................................................................................................47
7.
C
ONTROL
..........................................................................................................................48
7.1 R
EMOTE
................................................................................................................................... 48
7.1.1 Tone control from telephone keypad ................................................................................................48
7.1.2 Using SMS ........................................................................................................................................49
7.1.3 Using CLIP ........................................................................................................................................50
7.2 L
OCAL
...................................................................................................................................... 50
7.2.1 Using the module buttons .................................................................................................................50
7.2.2 From the keypad of telephone connected to telephone line output..................................................51
7.3 C
ONTROL FROM
D
LOAD
10
PROGRAM
........................................................................................ 51
8.
S
TARTING THE REPORTING
.................................................................................................52
8.1 S
TARTING THE
GPRS
REPORTING
............................................................................................. 52
8.1.1 Reporting the module status (GPRS) ...............................................................................................53
8.1.2 Reporting events from the control panel (GPRS) .............................................................................53
8.2 S
TARTING THE
CSD
REPORTING
............................................................................................... 53
8.2.1 Reporting the module status (CSD) ..................................................................................................53
8.2.2 Reporting events from the control panel (CSD)................................................................................53
8.3 S
TARTING THE
SMS
REPORTING
............................................................................................... 54
8.3.1 Reporting the module status (SMS)..................................................................................................54