Release 1.0
Technical Documentation 01/2006
TD_Repair_L3_SXG75_R1.0.pdf Page 2 of 73
Table of contents:
1Instruction..................................................................................................................................4
2List of available spare parts.....................................................................................................5
3Required equipment for level 3................................................................................................7
4Required software for level 3 ...................................................................................................7
5Radio part...................................................................................................................................8
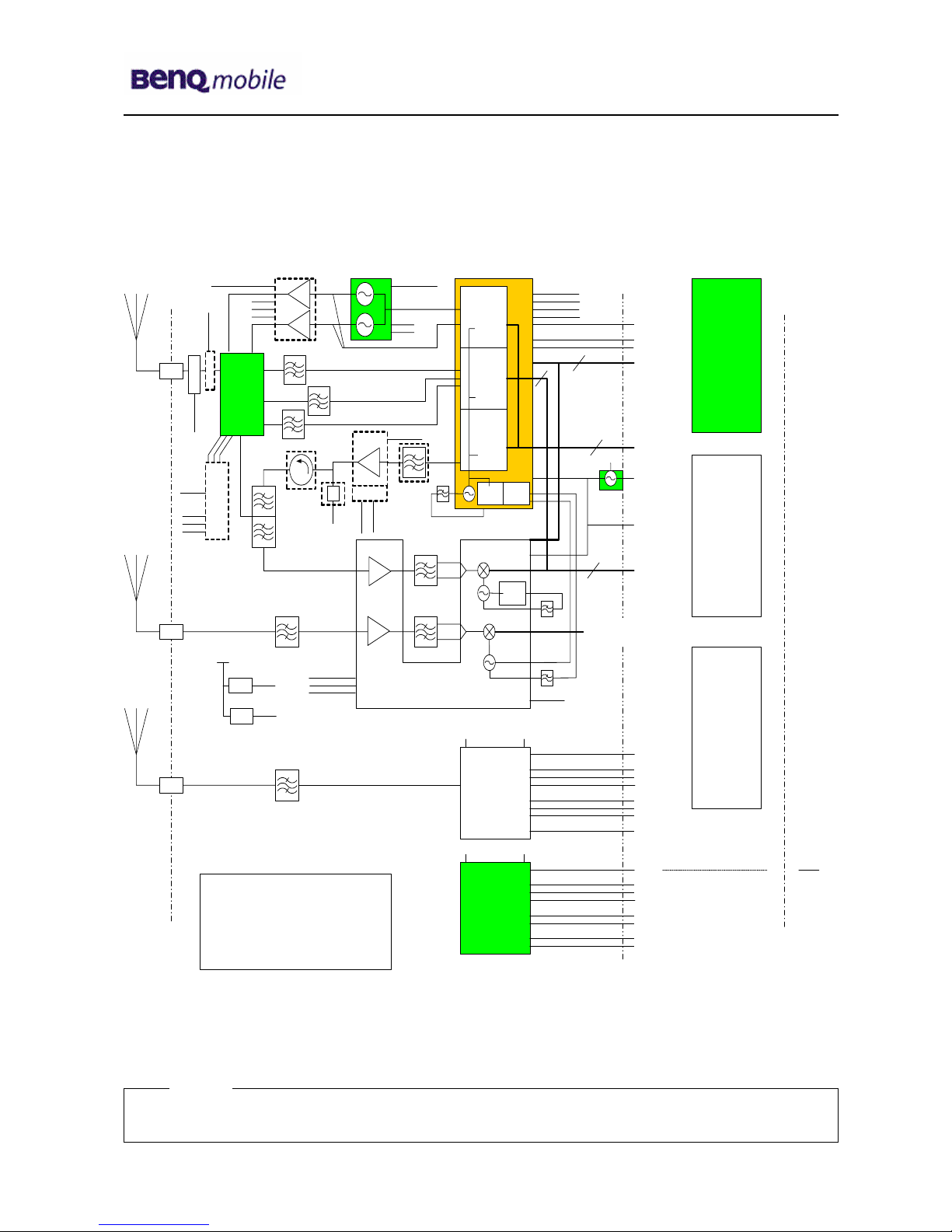
5.1 BLOCK DIAGRAM RF PART.......................................................................................................9
5.2 RECEIVER (RTR6250 AND RFR6250)...................................................................................10
5.3 TRANSMITTER.......................................................................................................................12
5.4 ANTENNA SWITCH .................................................................................................................15
6Baseband .................................................................................................................................17
6.1 BLOCK DIAGRAM ...................................................................................................................17
6.2 MSM6250 PROCESSOR ........................................................................................................18
6.3 MSM6250 INTERFACES ........................................................................................................23
7FM Radio ..................................................................................................................................32
7.1 FM RADIO INTERFACE ...........................................................................................................32
8Power management ................................................................................................................34
8.1 PM6650 FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW ..........................................................................................34
8.2 VOLTAGE REGULATORS AND VOLTAGE CONVERTERS .............................................................36
8.3 ADDITIONAL POWER SUPPLIES...............................................................................................38
8.4 PM6650 SIGNAL INTERFACES ...............................................................................................38
8.5 POWER ON/OFF SEQUENCING...............................................................................................40
9Battery/Charging .....................................................................................................................43
9.1 BATTERY ..............................................................................................................................43
9.2 PHONE SHUTDOWN DUE TO LOW BATTERY .............................................................................43
9.3 CHARGING............................................................................................................................44
10 Audio interference and suspension of pulse charging .......................................................50
11 MMI ...........................................................................................................................................50
11.1 DISPLAY ...............................................................................................................................50
11.2 KEYPAD................................................................................................................................54
12 Acoustics .................................................................................................................................58
12.1 MICROPHONE,SPEAKER AND HANDS-FREE SPEAKER..............................................................59
12.2 AUDIO ACCESSORIES ............................................................................................................59
Company Confidential
2006©BenQ