ST STDES-50W2CWBC Specification sheet
Other ST Computer Hardware manuals

ST
ST X-NUCLEO-OUT16A1 User manual
ST
ST X-NUCLEO-GFX02Z1 User manual
ST
ST ST7LITEUS2 User manual
ST
ST X-NUCLEO-IHM01A1 User manual

ST
ST X-NUCLEO-IKS4A1 User manual

ST
ST STEVAL-C34KAT1 User manual

ST
ST STM32F411 User manual
ST
ST X-NUCLEO-53L4A2 User manual

ST
ST X-NUCLEO-SAFEA1B Operating instructions
ST
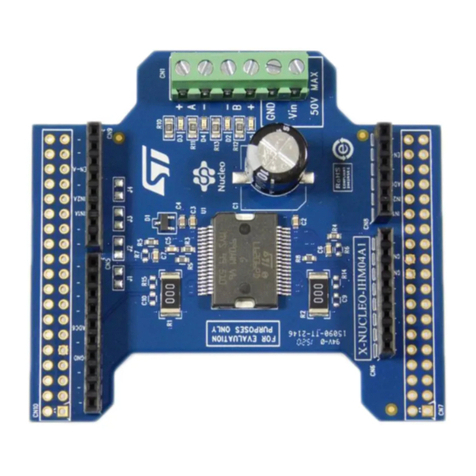
ST X-NUCLEO-IHM04A1 User manual

ST
ST X-NUCLEO-OUT01A2 User manual

ST
ST X-NUCLEO-53L7A1 User manual

ST
ST STNRG328S User manual

ST
ST STEVAL-IFP045V1 User manual
ST
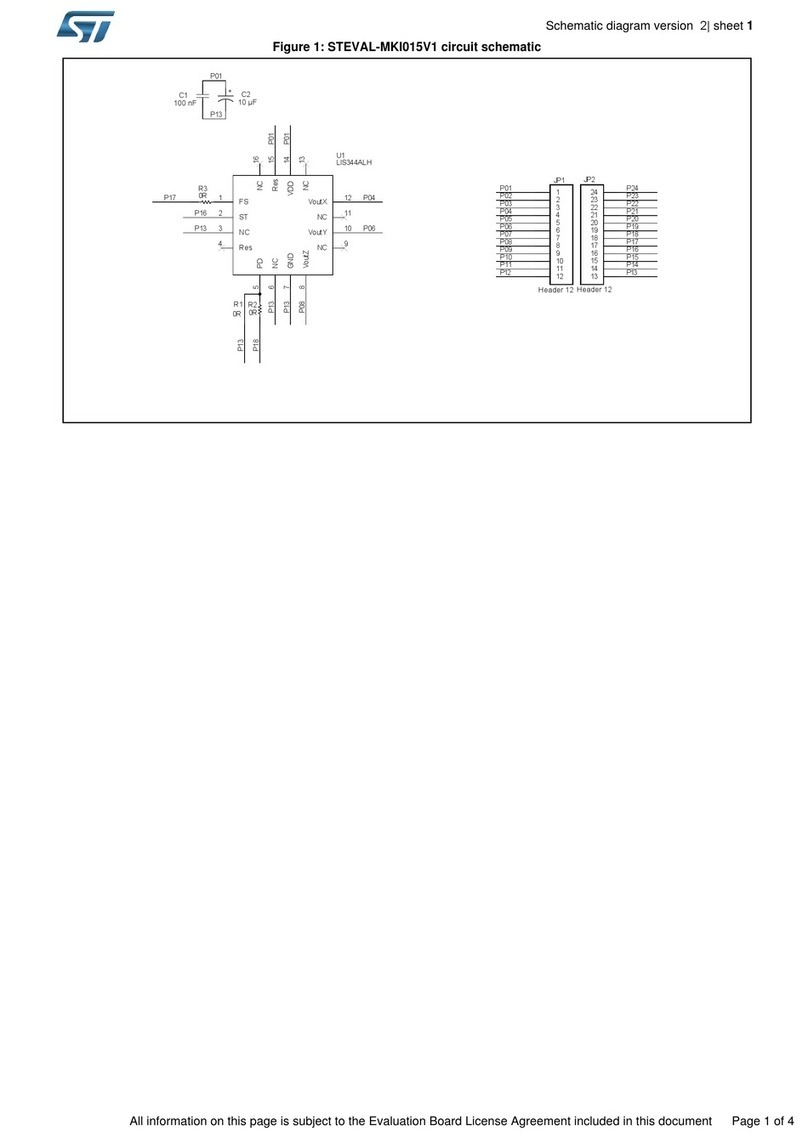
ST STEVAL-MKI015V1 Quick start guide

ST
ST X-NUCLEO-IHM11M1 User manual

ST
ST STR9 User manual

ST
ST STEVAL-IHM017V1 User manual

ST
ST X-NUCLEO-LED61A1 User manual

ST
ST X-NUCLEO-53L1A1 User manual
Popular Computer Hardware manuals by other brands

EMC2
EMC2 VNX Series Hardware Information Guide

Panasonic
Panasonic DV0PM20105 Operation manual

Mitsubishi Electric
Mitsubishi Electric Q81BD-J61BT11 user manual

Gigabyte
Gigabyte B660M DS3H AX DDR4 user manual

Raidon
Raidon iT2300 Quick installation guide

National Instruments
National Instruments PXI-8186 user manual

Intel
Intel AXXRMFBU4 Quick installation user's guide

Kontron
Kontron DIMM-PC/MD product manual

STEINWAY LYNGDORF
STEINWAY LYNGDORF SP-1 installation manual

Advantech
Advantech ASMB-935 Series user manual

Jupiter
Jupiter RAM PACK instructions
Measurement Computing
Measurement Computing CIO-EXP-RTD16 user manual



















