Contents UM1079
2/38 DocID018789 Rev 4
Contents
1 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.1 Quick start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.2 Getting started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.3 System requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.4 Development toolchain supporting the 32L152CDISCOVERY . . . . . . . . . 7
2.5 Demonstration software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
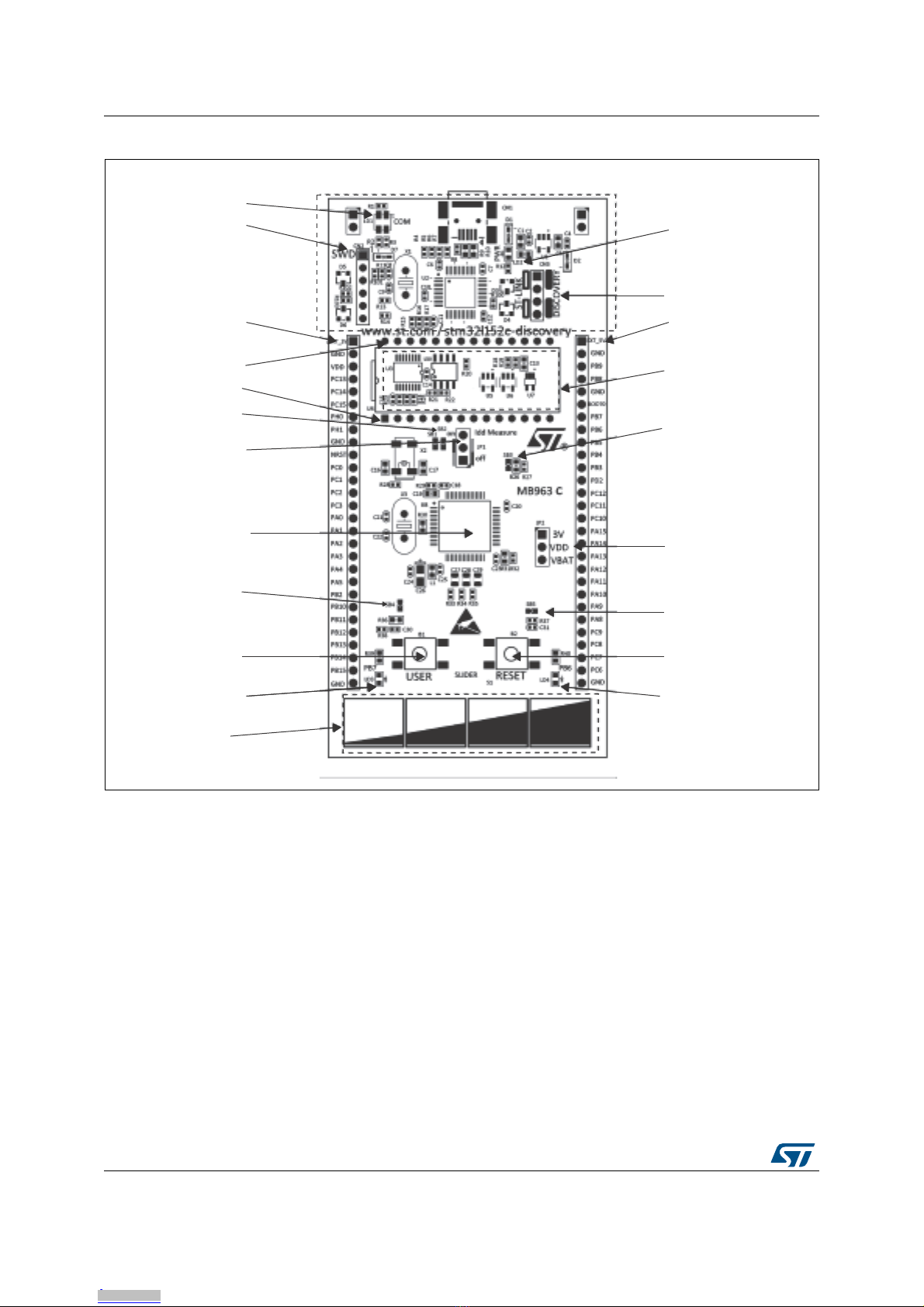
4 Hardware and layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.1 STM32L152RCT6 microcontroller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
4.2 Embedded ST-LINK/V2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4.2.1 Using the ST-LINK/V2 to program/debug the microcontroller on board 14
4.2.2 Using the ST-LINK/V2 to program/debug an external application . . . . . 15
4.3 Power supply and power selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4.4 LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4.5 Pushbuttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4.6 Linear touch sensor / touchkeys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4.7 Built-in IDD measurement circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
4.7.1 High IDD range mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
4.7.2 Low IDD range mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
4.7.3 IBIAS current measurement procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4.8 Solder bridges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
4.9 LCD (24 segments, 4 commons) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5 Extension connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
6 Mechanical drawing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
7 Electrical schematics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Downloaded from Arrow.com.Downloaded from Arrow.com.