Design
Criteria
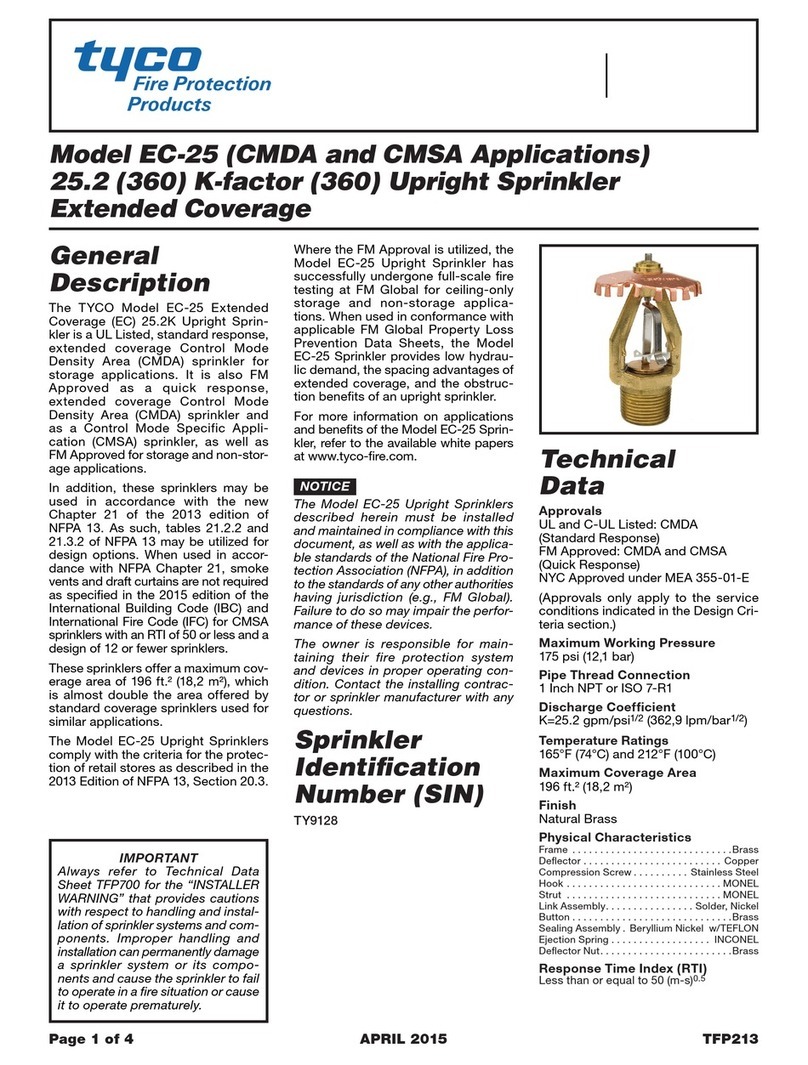
The Model SW-20 and SW-24, 11.2
K-factor, Standard Response, Ex-
tended Coverage Ordinary Hazard
(ECOH) Horizontal Sidewall Sprin-
klers are for use in ordinary hazard
occupancies with non-combustible un-
obstructed construction and with a
ceiling slope not exceeding 2 inches
per foot (9.2°), using the design criteria
provided in Table A, (as well as any
additional requirements specified in
NFPA 13 for Extended Coverage Side-
wall Spray Sprinklers).
A 36 inch (914 mm) clearance must be
maintained between the top of the
sprinkler deflector and any miscellane-
ous storage.
The SW-20 and SW-24 may be in-
stalled on sloped ceilings in loading
docks with a maximum roof slope of 4
inches per foot (18.4°) as shown in
Figure 4 and using the design criteria
provided in Table A.
The SW-20 and SW-24 can be used
only for exposed applications. The SW-
20 and SW-24 cannot be recessed.
Installation
The Model SW-20 and SW-24 Sprin-
klers must be installed in accordance
with the following instructions:
NOTES
Do not install any bulb type sprinkler if
the bulb is cracked or there is a loss of
liquid from the bulb. With the sprinkler
held horizontally, a small air bubble
should be present. The diameter of the
air bubble is approximately 1/16 inch
(1,6 mm).
A leak tight 3/4 inch NPT sprinkler joint
should be obtained with a torque of 10
to 20 ft.lbs. (13,4 to 26,8 Nm). A maxi-
mum of 30 ft.lbs. (40,7 Nm) of torque
is to be used to install sprinklers with
3/4 NPT connections. Higher levels of
torque may distort the sprinkler inlet
and cause leakage or impairment of
the sprinkler.
Do not attempt to make-up for insuffi-
cient adjustment in the escutcheon
plate by under- or over-tightening the
sprinkler. Readjust the position of the
sprinkler fitting to suit.
Step 1. Horizontal sidewall sprinklers
are to be installed with their centerline
perpendicular to the back wall and par-
allel to the ceiling. The word “TOP” on
the deflector is to face towards the
ceiling.
Step 2. With pipe thread sealant ap-
plied to the pipe threads, hand tighten
the sprinkler into the sprinkler fitting.
Step 3. Tighten the sprinkler into the
sprinkler fitting using only the W-Type
3 (End B) Sprinkler Wrench (Ref. Fig-
ure 3). With reference to Figures 1 and
2, the W-Type 3 Sprinkler Wrench is to
be applied to the sprinkler wrench
flats.
Care and
Maintenance
The Model SW-20 and SW-24 Sprin-
klers must be maintained and serviced
in accordance with the following in-
structions:
NOTES
Before closing a fire protection system
main control valve for maintenance
work on the fire protection system that
it controls, permission to shut down the
affected fire protection system must be
obtained from the proper authorities
and all personnel who may be affected
by this action must be notified.
Absence of an escutcheon, which is
used to cover a clearance hole, may
delay the time to sprinkler operation in
a fire situation.
Sprinklers that are found to be leaking
or exhibiting visible signs of corrosion
must be replaced.
Automatic sprinklers must never be
painted, plated, coated or otherwise
altered after leaving the factory. Modi-
fied sprinklers must be replaced.
Sprinklers that have been exposed to
corrosive products of combustion, but
have not operated, should be replaced
if they cannot be completely cleaned
by wiping the sprinkler with a cloth or
by brushing it with a soft bristle brush.
Care must be exercised to avoid dam-
age to the sprinklers - before, during,
and after installation. Sprinklers dam-
aged by dropping, striking, wrench
twist/slippage, or the like, must be re-
placed. Also, replace any sprinkler that
has a cracked bulb or that has lost
liquid from its bulb. (Ref. Installation
Section).
Frequent visual inspections are rec-
ommended to be initially performed for
corrosion resistant coated sprinklers,
after the installation has been com-
pleted, to verify the integrity of the cor-
rosion resistant coating. Thereafter,
annual inspections per NFPA 25
should suffice; however, instead of in-
specting from the floor level, a random
sampling of close-up visual inspec-
tions should be made, so as to better
determine the exact sprinkler condi-
tion and the long term integrity of the
corrosion resistant coating as it may
be affected by the corrosive conditions
present.
The owner is responsible for the in-
spection, testing, and maintenance of
their fire protection system and de-
vices in compliance with this docu-
ment, as well as with the applicable
standards of the National Fire Protec-
tion Association (e.g., NFPA 25), in
addition to the standards of any other
authorities having jurisdiction. The in-
stalling contractor or sprinkler manu-
facturer should be contacted relative
to any questions.
It is recommended that automatic
sprinkler systems be inspected,
tested, and maintained by a qualified
Inspection Service in accordance with
local requirements and/or national
codes.
Page4of6 TFP230