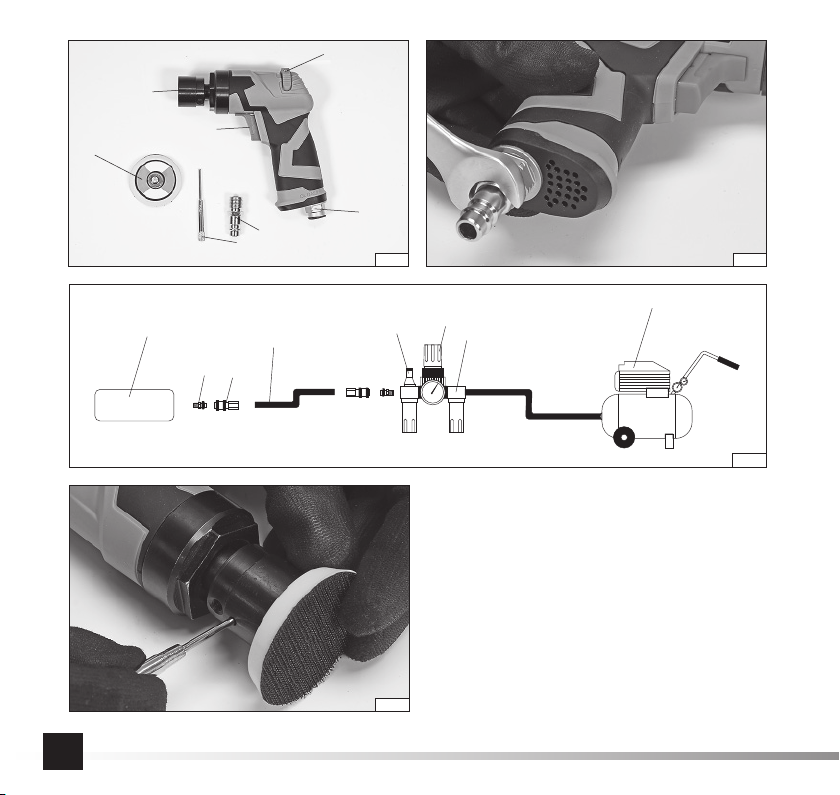
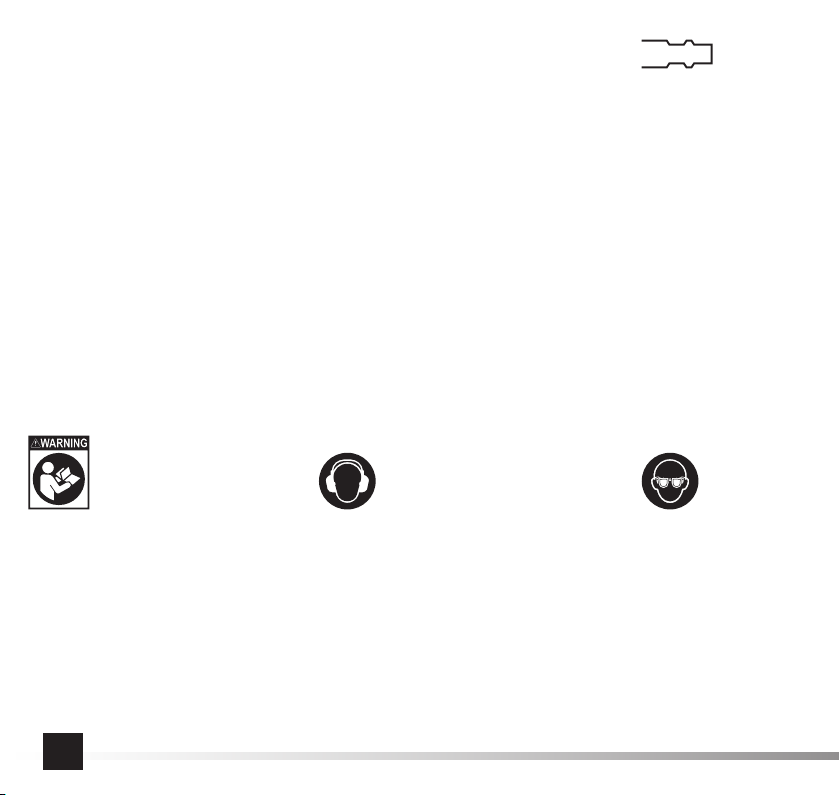
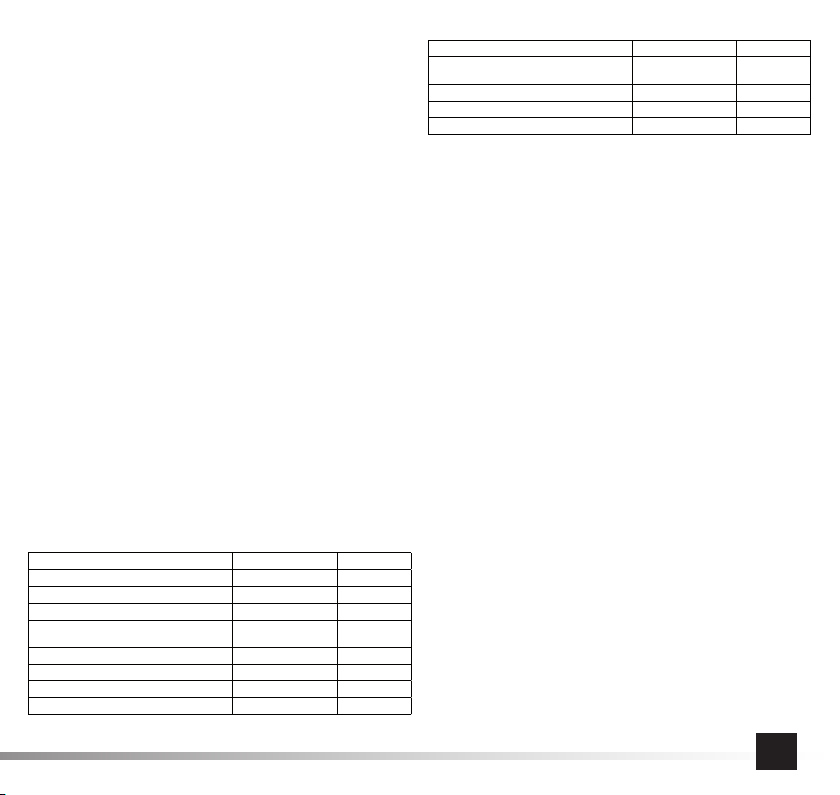
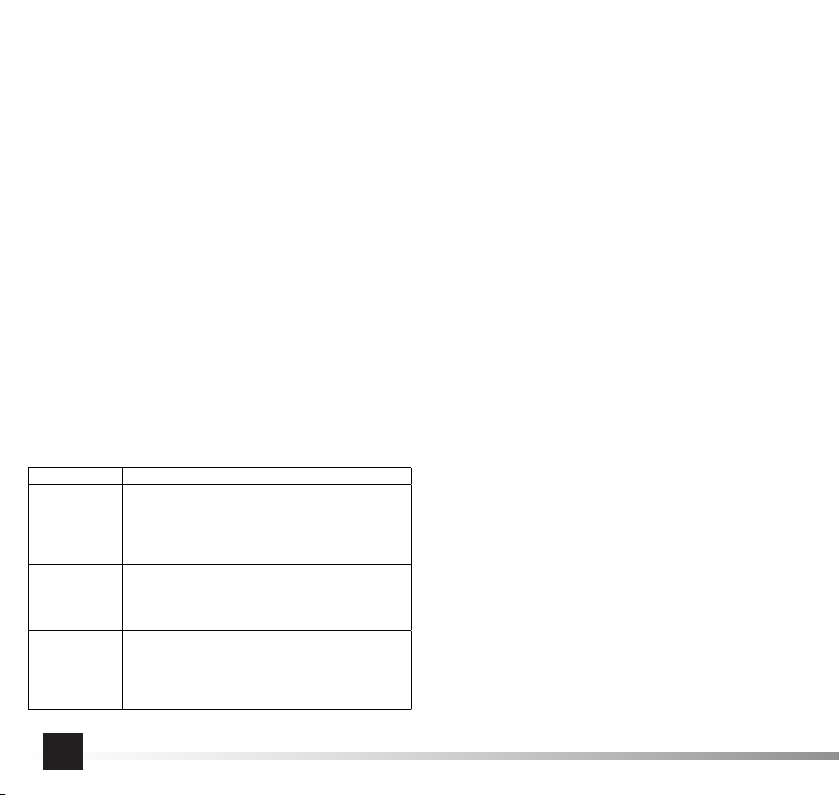
INSTRUKCJA ORYGINALNA 7
PL
ne przewody elektryczne, rury gazowe, itp., które mogą powodować
zagrożenie w przypadku uszkodzenia przy użyciu narzędzia.
Zagrożenia związane z oparami i pyłami
Pył i opary powstałe przy użyciu narzędzia pneumatycznego mogą
spowodować zły stan zdrowia (na przykład raka, wady wrodzone,
astma i/ lub zapalenie skóry), niezbędne są: ocena ryzyka i wdro-
żenie odpowiednich środków kontroli w odniesieniu do tych zagro-
żeń. Ocena ryzyka powinna zawierać wpływ pyłu utworzonego przy
użyciu narzędzia i możliwość wzburzenia istniejącego pyłu. Obsługę
i konserwację narzędzia pneumatycznego należy przeprowadzać
według zaleceń instrukcji obsługi, pozwoli zminimalizować emisję
oparów i pyłu. Wylot powietrza należy tak kierować, aby zminima-
lizować wzbudzanie pyłu w zakurzonym środowisku. Tam gdzie po-
wstają pył lub opary, priorytetem powinna być kontrola ich w źródle
emisji. Wszystkie zintegrowane funkcje i wyposażenie do zbierania,
ekstrakcji lub zmniejszenia pyłu lub dymu powinny być prawidło-
wo użytkowane i utrzymywane zgodnie z zaleceniami producenta.
Wybierać, konserwować i wymieniać narzędzia wstawiane według
zaleceń instrukcji, aby zapobiec wzrostowi oparów i pyłu. Używać
ochrony dróg oddechowych, zgodnie z instrukcjami pracodawcy
oraz zgodnie z wymogami higieny i bezpieczeństwa.
Zagrożenie hałasem
Narażenie, bez zabezpieczeń, na wysoki poziom hałasu może spo-
wodować trwałą i nieodwracalną utratę słuchu oraz inne problemy,
takie jak szum w uszach (dzwonienie, brzęczenie, gwizdanie lub
buczenie w uszach). Niezbędna jest ocena ryzyka oraz wdrożenie
odpowiednich środków kontroli w odniesieniu do tych zagrożeń. Od-
powiednie kontrole w celu zmniejszenia ryzyka mogą obejmować
działania takie jak: materiały tłumiące zapobiegające „dzwonieniu” ob-
rabianego przedmiotu. Używać ochrony słuchu zgodnie z instrukcjami
pracodawcy oraz zgodnie z wymogami higieny i bezpieczeństwa. Ob-
sługę i konserwację narzędzia pneumatycznego należy przeprowa-
dzać według zaleceń instrukcji obsługi, pozwoli uniknąć niepotrzebne-
go wzrostu poziomu hałasu. Jeżeli narzędzie pneumatyczne posiada
tłumik, zawsze należy upewnić się, że jest prawidłowo zamontowany
podczas użytkowania narzędzia. Wybrać, konserwować i wymienić
zużyte narzędzia wstawiane według zaleceń instrukcji obsługi. Po-
zwoli to uniknąć niepotrzebnego wzrostu hałasu.
Zagrożenie drganiami
Pomimo zaprojektowania narzędzi w taki sposób, aby zminimalizo-
wać ryzyko związane z emisją drgań, nie było możliwe całkowite
wyeliminowanie drgań, które mogą powodować ryzyko resztkowe.
Niewłaściwe posługiwanie się narzędziem może spowodować ry-
zyko związane z ekspozycją na drgania. Wartość drgań podana
w instrukcji może niewłaściwie reprezentować poziom drgań w za-
mierzonym użyciu. Narażenie na drgania może spowodować trwałe
uszkodzenia nerwów i ukrwienia rąk oraz ramion. Należy się ciepło
ubrać podczas pracy w niskich temperaturach oraz utrzymywać ręce
ciepłe i suche. Jeśli wystąpi drętwienie, mrowienie, ból lub wybiela-
nie skóry w palcach i dłoni, zaprzestać używania narzędzia pneuma-
tycznego, następnie poinformować pracodawcę oraz skonsultować
się z lekarzem. Obsługa i konserwacja narzędzia pneumatycznego
według zaleceń instrukcji obsługi, pozwoli uniknąć niepotrzebnego
wzrostu poziomu drgań. Wybrać, konserwować i wymienić mate-
riały eksploatacyjne/ narzędzia wstawiane zgodnie z zaleceniami
instrukcji, aby zapobiec niepotrzebnemu wzrostowi poziomu drgań.
Podpierać ciężar narzędzia za pomocą podstawy, napinacza lub sta-
bilizatora, jeżeli jest to możliwe. Trzymać narzędzie lekkim, ale pew-
nym chwytem, z uwzględnieniem wymaganych sił reakcji, ponieważ
zagrożenie pochodzące od drgań jest zazwyczaj większe, gdy siła
chwytu jest wyższa. Nieprawidłowa instalacja tnącego narzędzia
wstawianego może skutkować wzrostem poziomu drgań.
Dodatkowe instrukcje bezpieczeństwa dotyczące narzędzi pneuma-
tycznych
Powietrze pod ciśnieniem może spowodować poważne obrażenia:
- zawsze odciąć dopływ powietrza, opróżnić wąż z ciśnienia powietrza i
odłączyć narzędzie od dopływu powietrza, gdy: nie jest używane, przed
wymianą akcesoriów lub przy wykonywaniem napraw;
- nigdy nie kierować powietrza na siebie lub kogokolwiek innego.
Uderzenie wężem może spowodować poważne obrażenia. Zawsze
należy przeprowadzić kontrolę pod kątem uszkodzonych lub luźnych
węży i złączek. Zimne powietrze należy kierować z dala od rąk
Za każdym razem gdy są stosowane uniwersalne połączenia zakręca-
ne (połączenia kłowe), należy zastosować trzpienie zabezpieczające i
łączniki zabezpieczające przeciwko możliwości uszkodzenia połączeń
pomiędzy wężami oraz pomiędzy wężem i narzędziem. Nie przekra-
czać maksymalnego ciśnienia powietrza podanego dla narzędzia.