ABB 5HK Series Installation and operating instructions
Other ABB Circuit Breaker manuals

ABB
ABB AKD-5 User manual

ABB
ABB 15VHK500 User manual

ABB
ABB S800U User manual

ABB
ABB Tmax T8 L5757 Guide
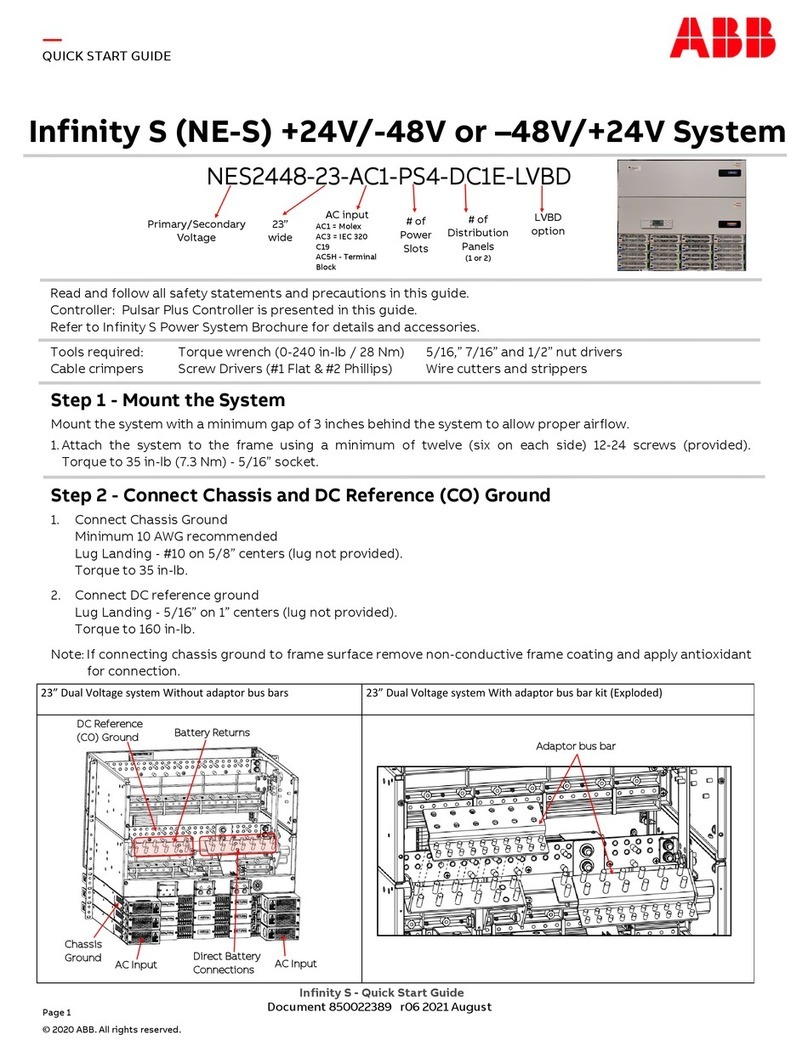
ABB
ABB Infinity S User manual

ABB
ABB VD4 Series User manual

ABB
ABB SF6 LTB 245E1 BLG 1002A User manual

ABB
ABB SACE Emax E2.2 User guide

ABB
ABB SACE Emax 2 E2.2 User manual

ABB
ABB SACE Emax 2 Product manual

ABB
ABB SACE Tmax XT User manual

ABB
ABB SACE Tmax XT User manual

ABB
ABB GE Power Break II User manual

ABB
ABB SACE Emax 2 E6.2 Manual

ABB
ABB VD4 Series User manual
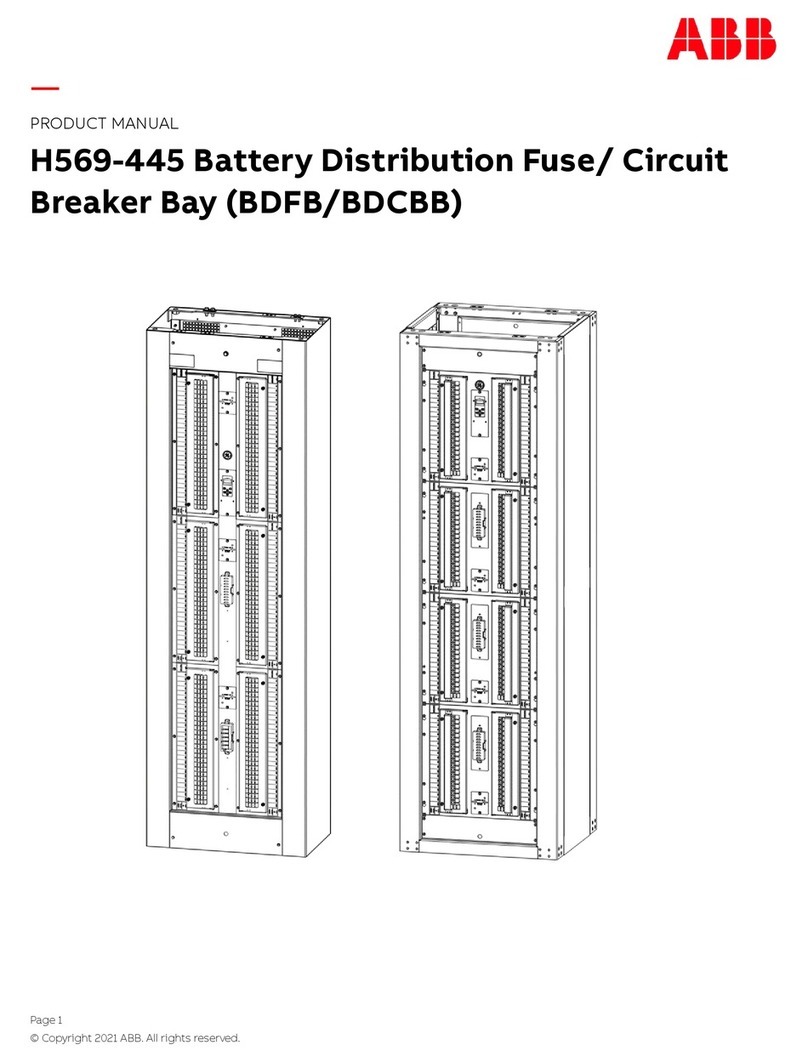
ABB
ABB H569-445 User manual

ABB
ABB SACE Emax 2 User manual

ABB
ABB SACE Emax 2 Manual

ABB
ABB VD4 Series Installation and operating instructions

ABB
ABB SACE Emax 2 User manual
Popular Circuit Breaker manuals by other brands

Eaton
Eaton Power Defense PDG2 Instruction leaflet
Bticino
Bticino L4412CM2 quick start guide

Eaton
Eaton S-T0 Instruction leaflet

OEZ
OEZ 3VA9-RS-4VBH1 Installation, service and maintenance instructions

Siemens
Siemens PSR Instructions, Installation, Operation, Maintenance
Rockwell Automation
Rockwell Automation Allen-Bradley 140G-G manual