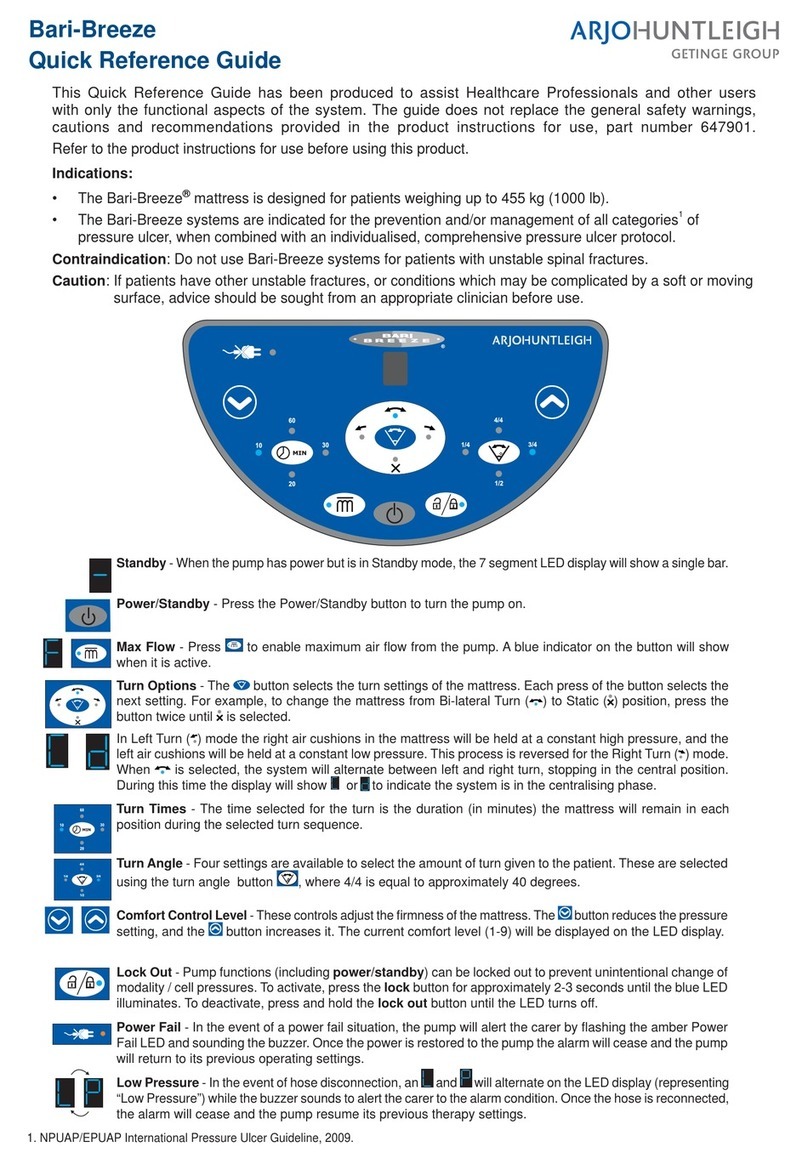
1-2
MAXIMUM PATIENT WEIGHT
•Maximum Patient Weight: 250 lb (114 kg).
SAFETY TIPS
Bed Frame – Always use standard healthcare bed frame with Side Rails and any other safeguards or protocols
that may be appropriate. Frame and Side Rails must be properly sized to eliminate any gaps that might entrap
patient’s head or body.
Brakes – Caster brakes should always be locked once bed is in position. Verify wheels are locked before patient
transfer to or from bed.
Bed Height – To minimize risk of falls or injury, bed should always be in lowest possible position when patient is
unattended.
Side Rails / Patient Restraints – Whether and how to use Side Rails or restraints is a decision that should be
based on each patient’s needs and should be made by the patient and the patient’s family, physician and
caregivers, with facility protocols in mind. Caregivers should assess risks and benefits of Side Rail restraint use
(including entrapment and patient falls from bed) in conjunction with individual patient needs, and should discuss
use or non-use with patient and / or family. Consider not only the clinical and other needs of the patient, but also
risk of fatal or serious injury from falling out of bed and from patient entrapment in or around the Side Rails,
restraints or other accessories. In the US, for a description of entrapment hazards, vulnerable patient profile and
guidance to further reduce entrapment risks, refer to FDA’s Hospital Bed System Dimensional and Assessment
Guidance To Reduce Entrapment. Outside the US, consult the local Competent Authority or Government Agency
for Medical Device Safety for specific local guidance. Consult a caregiver and carefully consider the use of
bolsters, positioning aids or floor pads, especially with confused, restless or agitated patients. It is recommended
that Side Rails (if used) be locked in the full upright position when patient is unattended. Make sure a capable
patient knows how to get out of bed safely (and, if necessary, how to release the Side Rails) in case of fire or other
emergency. Monitor patients frequently to guard against patient entrapment.
When selecting a standard mattress, ensure the distance between top of Side Rails (if used) and top of mattress
(without compression) is at least 8.66 in (220 mm) to help prevent inadvertent bed exit or falls. Consider individual
patient size, position relative to the top of the Side Rail) and patient condition in assessing fall risk.
Skin Care – Monitor skin conditions regularly, especially at bony prominences and areas where moisture or
incontinence may occur or collect, and consider adjunct or alternative therapies for high acuity patients. Early
intervention may be essential to preventing serious skin breakdown.
Fluids –Avoid spilling fluids on Air Supply Unit. If spills do occur, clean fluids from bed and Air Supply Unit wearing
rubber gloves to avoid possibility of shock. Once fluid is removed, check operation of components in area of spill.
NOTE: Fluids remaining on controls can cause corrosion, which may cause components to fail or operate
erratically, possibly producing potential hazards to patient and caregiver.
Lock-Outs –Lock-out feature on Air Supply Unit should be used at caregiver’s discretion to ensure against
unintentional or unauthorized tampering with unit settings.
Avoid Fire Hazards –To minimize risk of fire, connect bed’s Power Cord directly into a wall-mounted outlet. Do
not use extension cords or multiple outlet strips. Review and follow FDA’s Safety Tips for Preventing Hospital Bed
Fires (dated 12/18/03).
No Smoking in Bed –Smoking in bed can be dangerous. To avoid risk of fire, smoking in bed should never be
allowed.
Tobacco Smoke – If routine laundering and cleaning procedures (as described in Preventive Maintenance
section in the Maintenance chapter of the First Step Select Maintenance Manual) are not followed, tobacco
smoke build-up may conceivably reduce amount of air flow through product. Severe air restrictions (whatever the
source) may cause Air Supply Unit to overheat and automatically deactivate.