Version 11/04
BEDIENUNGSANLEITUNG www.conrad.com
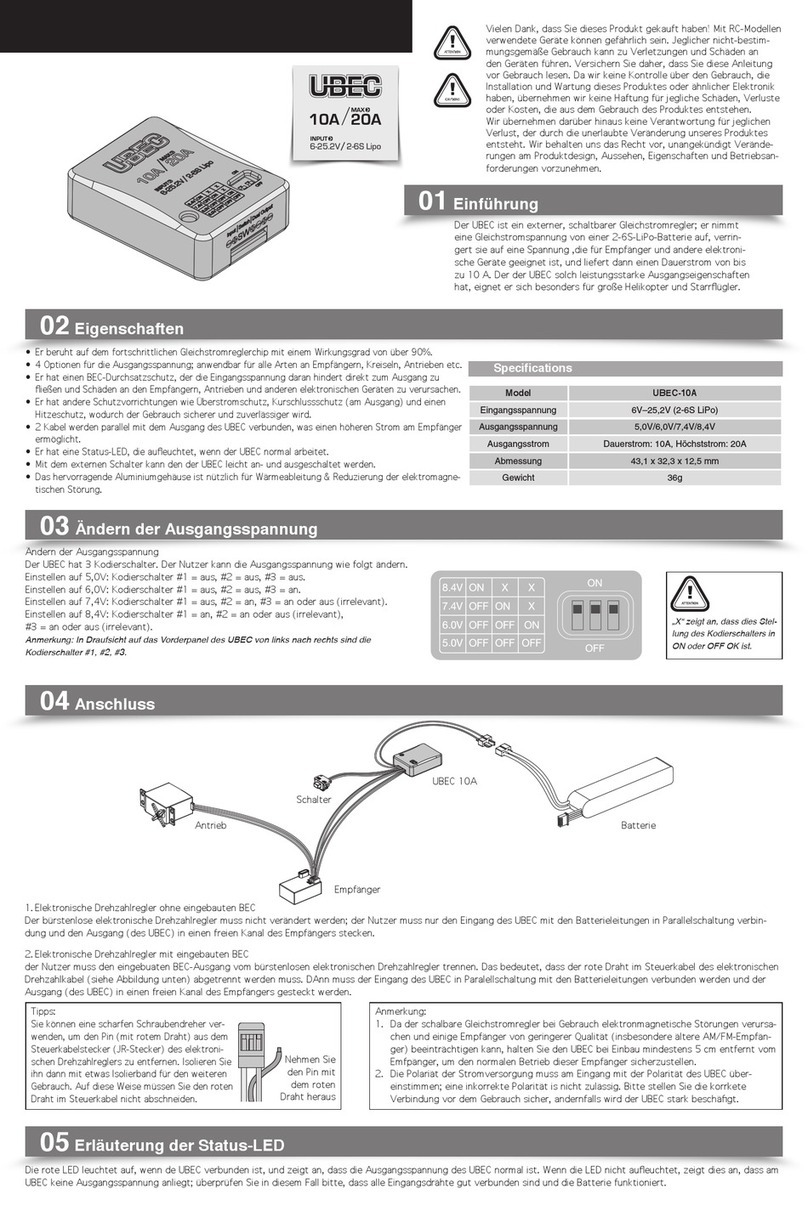
D
Diese Bedienungsanleitung ist eine Publikation der Conrad Electronic
GmbH, Klaus-Conrad-Straße 1, D-92240 Hirschau.
Diese Bedienungsanleitung entspricht dem technischen Stand bei
Drucklegung. Änderung in Technik und Ausstattung vorbehalten.
©Copyright 2004 by Conrad Electronic GmbH. Printed in Germany.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS www.conrad.com
GB
Version 11/04
These operating instructions are published by Conrad Electronic GmbH,
Klaus-Conrad-Straße 1, D-92240 Hirschau/Germany.
The operating instructions reflect the current technical specifications at
time of print. We reserve the right to change the technical or physical
©Copyright 2004 by Conrad Electronic GmbH. Printed in Germany.
SATA-RAID Controller
Item No. 97 45 16
Prescribed Use
The product is designed for installation into a PC compatible computer and
provides serial ATA interfaces (RAID or NON-RAID mode).
Scope of delivery
•PCIcard
• Data carrier with driver
• SATA cable
• Operating instructions
Features
• Two SATA ports for a total of two SATA devices
• RAID0 or RAID1 operation
• NON-RAID mode is possible (operation of 1 or 2 SATA devices without
RAID)
Installation
First, perform a backup of your data, if data is already stored on
the SATA hard disk(s) you wish to connect to the RAID controller!
Subsequently, the installation can be started.
When in doubt about how to install the device correctly,
please contact an expert or a specialist workshop and let
them do the installation!
Improper installation damages the plug-in card as well as
your computer and all connected devices.
Danger!
Switch off the computer in which the plug-in card is to be
installed and all connected devices and separate all devices
from the mains voltage, pull the mains plug! To switch the
device off via the ON/OFF switch is not enough!
• Open the housing of your computer and carefully take off the lid of the
housing.
• Locate a free PCI slot, remove the respective slot's cover and insert the
PCI card into the PCI slot. Screw the plug-in card tightly, make sure it is
seated properly in the PCI slot!
• Connect each SATA port with a SATA device.
• Close the computer case.
• Reconnect your computer and monitor with the mains voltage and switch
on all devices.
• If your computer does not start correctly, switch it off straight away and
control all settings and cable connections.
Before you open the PC again, the PC needs to be separated
from the mains voltage, see above!
Driver installation
Windows detects the plug-in card automatically. Insert the supplied driver
data carrier into the respective drive of your PC and follow the instructions
displayed. Now Windows possibly needs to be restarted.
How to operate
If you wish to use the connected SATA hard disks without RAID, their
separate partitioning and formatting is very easily carried out with Windows
XP via the computer administration.
Should the hard disks be used as a RAID set, it should first be created.
All the data on the hard disks will be lost!
Restart the computer. While starting your computer (before starting
Windows!) you will be prompted to press the shortcut „CTRL" + „S" or the
„F4" function key to enable the RAID-BIOS.
Now you can create a RAID set (two hard disks must be connected) in the
so-called „RAID Configuration Utility".
Please note: All the data on the hard disks will be lost!
• RAID0
The data is distributed on both hard disks, the data transfer rate
increases. The total capacity is twice as large as that of the smaller one
of the both hard disks.
• RAID1
The data is mirrored, i.e. the same data is stored on the both hard disks.
The total capacity is as large as that of the smaller hard disk (because the
data is mirrored!).
The ideal case would be two identical hard disks connected (the
same version and capacity). Otherwise, the smaller of the both
hard disks defines the maximum capacity. Examples:
RAID0: HDD0=30GB, HDD1=200GB, total=60GB
HDD0=200GB, HDD1=200GB, total=400GB
RAID1: HDD0=30GB, HDD1=200GB, total=30GB
HDD0=200GB, HDD1=200GB, total=200GB
Confirm the question „Are you sure Y/N” by pressing the "Z" key. After
the RAID set is configured, exit the menu and restart the PC.
The RAID set is now available on Windows as a conventional hard disk
which must be partitioned and formatted.
Tips & Notes
• Only one SATA device can be connected to each SATA port.
• There is an adapter intended for conventional IDE-/ATAPI devices (e.g.
IDE hard disk) that enables their operation using an SATA interface.
• A suitable operating system is required for large hard disks (larger than
approx. 137 GB) (e.g. Windows XP, Service pack 1 are recommended).
• In case of older operating systems, data may be lost when this limit is
exceeded (when more than 130-140 GB of data is written on the hard
disk). A partitioning into smaller subsets does not have any positive
effects in this case. Use a more current operating system!
• The use of RAID1 makes it possible to restore the mirrored set using the
"Rebuild Mirrored Set” function available in the menu in case one of the
both mirrored hard disks is defective.
• The „Low Level Format" option available in the menu is usually not
required. Partitioning and formatting using Windows are enough.
• Due to the fact that the controller has its own BIOS, no software is
necessary for operation. Windows treats the RAID0 or RAID1 set as a
conventional separate hard disk without RAID.
• If no RAID set has been created, the both hard disks work like usual
separate hard disks and the RAID controller like a normal SATA
controller without RAID.
• At the time these operating instructions were created, a software was
available on the driver CD in the „Silicon_Image \ SIL3112RAID \
Medley” directory. The installation of this software enables configuration
and monitoring of the RAID set. In case of the newer CD versions, the
path could be different.
• As a matter of course, conventional IDE hard disks or other IDE drives
can also be connected to the controller combined with an SATA-IDE
adapter.
• The boot capability of the hard disks connected to the RAID controller
depends on the BIOS/mainboard and its settings.
SATA-RAID-Controller
Best.-Nr. 97 45 16
Bestimmungsgemäße Verwendung
Das Produkt ist zum Einbau in einen PC-kompatiblen Computer
vorgesehen und stellt dort Serial-ATA-Schnittstellen zur Verfügung (RAID-
oder NON-RAID-Modus).
Lieferumfang
•PCI-Karte
• Datenträger mit Treiber
• SATA-Kabel
• Bedienungsanleitung
Merkmale
• Zwei SATA-Ports, für insgesamt zwei SATA-Geräte
• RAID0- oder RAID1-Betrieb
• NON-RAID-Modus möglich (Betrieb von 1 oder 2 SATA-Geräten ohne
RAID)
Einbau
Falls auf der/den SATA-Festplatte(n), die Sie an den RAID-
Controller anstecken wollen, bereits Daten vorhanden sind, so
führen Sie zuerst ein Backup der Daten durch!
Anschließend können Sie mit dem Einbau beginnen.
Falls Sie keine Fachkenntnisse für den Einbau besitzen, so
lassen Sie den Einbau von einer FACHKRAFT oder einer
entsprechenden Fachwerkstatt durchführen!
Durch unsachgemäßen Einbau wird sowohl die Steckkarte
als auch Ihr Computer und alle angeschlossenen Geräte
beschädigt.
Vorsicht, Lebensgefahr!
Schalten Sie den Computer, in den die Steckkarte eingebaut
werden soll und alle angeschlossenen Geräte aus und
trennen Sie alle Geräte von der Netzspannung, ziehen Sie
den Netzstecker! Das Ausschalten über den Ein-/
Ausschalter genügt nicht!
• Öffnen Sie das Gehäuse Ihres Computers und nehmen Sie den Gehäu-
sedeckel vorsichtig ab.
• Suchen Sie einen freien PCI-Steckplatz, entfernen Sie das zugehörige
Slotblech und stecken Sie die PCI-Karte in den PCI-Slot ein. Schrauben
Sie die Steckkarte fest, kontrollieren Sie den korrekten Sitz im PCI-Slot!
• Verbinden Sie je einen SATA-Port mit einem SATA-Gerät.
• Verschließen Sie das Gehäuse Ihres Computers.
• Verbinden Sie Computer und Monitor wieder mit der Netzspannung und
schalten Sie alle Geräte ein.
• Startet Ihr Computer nicht korrekt, so schalten Sie ihn sofort aus und
kontrollieren Sie sämtliche Einstellungen und Kabelverbindungen.
Vor dem erneuten Öffnen des PCs ist der PC von der
Netzspannung zu trennen, siehe oben!
Treiber-Installation
Windows erkennt die Steckkarte automatisch. Legen Sie den mitgelieferten
Treiber-Datenträger in das entsprechende Laufwerk Ihres PCs ein und
folgen Sie allen Anweisungen. Anschließend ist möglicherweise ein
Neustart von Windows nötig.
Betrieb
Wollen Sie die angeschlossenen SATA-Festplatten ohne RAID einsetzen,
können Sie sie nun einzeln partitionieren und formatieren; bei Windows XP
ist dies über die Computerverwaltung sehr einfach möglich.
Sollen die Festplatten jedoch als RAID-Set eingesetzt werden, muss dieses
zuerst angelegt werden.
Dabei gehen alle Daten auf den Festplatten verloren!
Starten Sie den Rechner neu. Beim Starten (noch vor dem Starten von
Windows!) erscheint eine Meldung, dass Sie zum Aktivieren des RAID-
BIOS die Tastenkombination „CTRL” + „S” oder die Funkitionstaste „F4”
drücken sollen („CTRL” entspricht auf der deutschen Tastatur der
Steuertaste „Strg”).
In dem sog. „RAID Configuration Utility” können Sie nun ein RAID-Set
anlegen (es müssen zwei Festplatten angeschlossen sein).
Bitte beachten Sie: Dabei gehen alle Daten auf den Festplatten
verloren!
• RAID0
Die Daten werden auf die beiden Festplatten aufgeteilt, die
Datenübertragungsgeschwindigkeit erhöht sich. Die Gesamtkapazität
beträgt das Doppelte der kleineren der beiden Festplatten.
• RAID1
Die Daten werden gespiegelt, d.h. auf den beiden Festplatten sind die
gleichen Daten enthalten. Die Gesamtkapazität beträgt die der kleineren
Festplatte (Daten werden ja gespiegelt!).
Idealerweise sind zwei gleiche Festplatten (gleiche Version,
gleiche Kapazität) angeschlossen. Andernfalls gibt die kleinere
der beiden Festplatten die Maximalkapazität vor. Beispiele:
RAID0: HDD0=30GB, HDD1=200GB, Gesamt=60GB
HDD0=200GB, HDD1=200GB, Gesamt=400GB
RAID1: HDD0=30GB, HDD1=200GB, Gesamt=30GB
HDD0=200GB, HDD1=200GB, Gesamt=200GB
Die Frage nach der Bestätigung („Are you sure Y/N”) ist mit der Taste
„Z” zu bestätigen. In diesem Moment ist noch kein deutscher
Tastaturtreiber aktiv. Deshalb sind die Tasten „Y” und „Z” vertauscht.
Nach dem Einrichten des RAID-Sets können Sie das Menü verlassen, der
PC wird neu gestartet.
Unter Windows steht nun das RAID-Set wie eine herkömmliche Festplatte
zur Verfügung, die Sie partitionieren und formatieren müssen.
Tipps & Hinweise
• An jedem SATA-Port kann nur ein einziges SATA-Gerät angesteckt wer-
den.
• Für herkömmliche IDE-/ATAPI-Geräte (z.B. IDE-Festplatte) gibt es
Adapter, um sie an einer SATA-Schnittstelle zu betreiben.
• Für große Festplatten (ab ca. 137 GByte) ist ein dazu geeignetes
Betriebssystem erforderlich (z.B. Windows XP, Service-Pack 1 empfoh-
len).
• Bei älteren Betriebssystemen kommt es beim Überschreiten dieser
Grenze (wenn also mehr als ca. 130-140 GByte Daten auf die Festplatte
geschrieben werden) zu Datenverlust. Eine Partitionierung in kleinere
Teile hat in diesem Fall keine positiven Auswirkungen. Verwenden Sie
ein aktuelleres Betriebssystem!
• Bei Verwendung von RAID1 kann im Menü über die Funktion „Rebuild
Mirrored Set” das gespiegelte Set wieder hergestellt werden, wenn eine
der beiden gespiegelten Festplatten defekt war.
• Die im Menü verfügbare Option „Low Level Format” ist in der Regel nicht
erforderlich. Es genügt die Partitionierung und Formatierung unter Win-
dows.
• Da der Controller über ein eigenes BIOS verfügt, ist zum Betrieb keine
Software erforderlich. Für Windows sieht das RAID0- bzw. RAID1-Set so
aus wie eine herkömmliche einzelne Festplatte ohne RAID.
• Wird kein RAID-Set angelegt, arbeiten die beiden Festplatten wie her-
kömmliche einzelne Festplatten, der RAID-Controller wie ein herkömmli-
cher SATA-Controller ohne RAID.
• Zum Zeitpunkt der Erstellung dieser Bedienungsanleitung war auf der
Treiber-CD im Verzeichnis „Silicon_Image \ SIL3112RAID \ Medley” eine
Software zu finden, nach deren Installation das RAID-Set konfiguriert
bzw. überwacht werden kann. Der Pfad könnte sich bei neueren Versio-
nen der CD evtl. ändern.
• Selbstverständlich können auch herkömmliche IDE-Festplatten oder
andere IDE-Laufwerke in Verbindung mit einem SATA-IDE-Adapter am
Controller angeschlossen werden.
• Ob die am RAID-Controller angeschlossenen Festplatten bootfähig sind,
ist vom BIOS/Mainboard und dessen Einstellung abhängig.