“KOMPRESS”OWNER’SMANUAL REL .2.0
_________________________________________________________________________
© Copyright by FLY Products s.r.l. Page
1.1 Safety first, WWW!(Who, Where and When can fly it)
Powered Para Gliding (PPG) is the most exciting, least expensive, safest, and most accessible form of
aviation available! However, it is still aviation, and it brings with it all the inherent potential dangers
of aviation. People can, and do, get hurt, and even killed, in any form of aviation, including PPG.
For that reason it is imperative that before fly with this PPG you must receive proper training from
qualified instructors and obtain a valid PPG license, an then offer PPG the respect all aviation
deserves, respect weather and conditions, and realize that in the end, it is the pilot himself that is fully
responsible for his own safety and the safety of fellow pilots and bystanders.
Depending on every national regulations, the PPG may only be operated in authorized areas and
flights within controlled airspace usually needs a permission given by radio.
Additional requirements like a valid insurance must be fulfilled.
Powered Paragliding is an extremely demanding sport that requires exceptional levels of attention,
judgment, maturity, self-discipline, and attention to detail. It is unlikely that you will be able to
participate in it safely unless you make a conscious and continual commitment to your own safety.
Due to the inherent risks in flying this or any PPG, no warranty of any kind can be made against
accidents, bodily injury, equipment failure, and/or death.
This PPG is not covered by product liability insurance. Do not start it or fly it unless you are
willing to assume all risks inherent in the sport of Powered Paragliding and all responsibility for
any property damage, injury, or death which may result from the use of this product.
Please read and be sure you thoroughly understand this Operator’s Manual before starting or flying
your KOMPRESS. It contains information critical to the safe operation of the Powered Para Glider.
1.2 Notation used
Certain special terms (NOTE, CAUTION, WARNING) will be used throughout this manual. Their
usage is defined below.
A NOTE provides supplemental information to help clarify a point being made in the text. Generally,
a “note” is provided to help assembly, use, or maintenance of the product. Disregarding a “note”
could cause inconvenience, but would not cause damage or personal injury.
A CAUTION provides supplemental information to help clarify an area where equipment damage
could occur. Disregarding a “caution” could result in permanent and significant mechanical damage,
however personal injury is unlikely.
A WARNING provides supplemental information to help clarify an area where personal injury or
death could occur from negligence. Disregarding a warning” could result in serious injury or death.
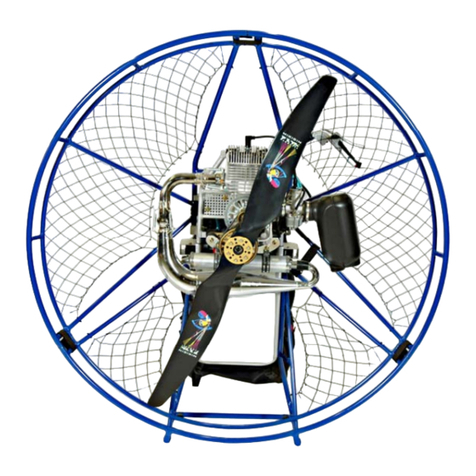
1.3 Congratulations on your new KOMPRESS
Kompress is Fly Products latest design built for easy and compact transportation using a new fully
detachable frame. With a new cage construction, incorporating a simple to use attachment method,
the Kompress is truly compact. The Black Devil M25 engine has proven to have an excellent weight-
to-thrust ratio matched with low noise level and efficient fuel consumption.
1.4 KOMPRESS features
?Easy assembly and disassembly
?Electric Starter
?Power Ignition
?Reduction drive
?Air cooling